
Electric Machines
Modeling, Condition Monitoring, and Fault Diagnosis
- 272 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Electric Machines
Modeling, Condition Monitoring, and Fault Diagnosis
About this book
With countless electric motors being used in daily life, in everything from transportation and medical treatment to military operation and communication, unexpected failures can lead to the loss of valuable human life or a costly standstill in industry. To prevent this, it is important to precisely detect or continuously monitor the working condition of a motor. Electric Machines: Modeling, Condition Monitoring, and Fault Diagnosis reviews diagnosis technologies and provides an application guide for readers who want to research, develop, and implement a more effective fault diagnosis and condition monitoring scheme—thus improving safety and reliability in electric motor operation. It also supplies a solid foundation in the fundamentals of fault cause and effect.
Combines Theoretical Analysis and Practical Application
Written by experts in electrical engineering, the book approaches the fault diagnosis of electrical motors through the process of theoretical analysis and practical application. It begins by explaining how to analyze the fundamentals of machine failure using the winding functions method, the magnetic equivalent circuit method, and finite element analysis. It then examines how to implement fault diagnosis using techniques such as the motor current signature analysis (MCSA) method, frequency domain method, model-based techniques, and a pattern recognition scheme. Emphasizing the MCSA implementation method, the authors discuss robust signal processing techniques and the implementation of reference-frame-theory-based fault diagnosis for hybrid vehicles.
Fault Modeling, Diagnosis, and Implementation in One Volume
Based on years of research and development at the Electrical Machines & Power Electronics (EMPE) Laboratory at Texas A&M University, this book describes practical analysis and implementation strategies that readers can use in their work. It brings together, in one volume, the fundamentals of motor fault conditions, advanced fault modeling theory, fault diagnosis techniques, and low-cost DSP-based fault diagnosis implementation strategies.
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
1
Introduction
- Post the standard lifetime
- Wrong-rated power, voltage, and currentTABLE 1.1
Number of Motors by ApplicationApplicationPopulationFans and pumps3,847,161Air compressor632,731Others7,954,438TOTAL12,434,330Source: US Department of Energy (2002). http://www1.eere.energy.gov/manufacturing/tech_deployment/pdfs/mtrmkt.pdf - Unstable supply voltage or current source
- Overload or unbalanced load
- Electrical stress from fast switching inverters or unstable ground
- Residual stress from manufacturing
- Mistakes during repairs
- Harsh application environment (dust, water leaks, environmental vibration, chemical contamination, high temperature)
- Electrical faults
- Open or short circuit in motor windings (mainly due to winding insulation failure)
- Wrong connection of windings
- High resistance contact to conductor
- Wrong or unstable ground
TABLE 1.2
Motor System Energy Usage by ApplicationApplication GWh / Yr Fans and pumps 221,417Air compressor91,050Others262,961TOTAL575,428Source: US Department of Energy (2002). http://www1.eere.energy.gov/manufacturing/tech_deployment/pdfs/mtrmkt.pdf FIGURE 1.1
FIGURE 1.1
2009 Honda FCX Clarity Fuel Cell Vehicle test drive photo gallery. From Christine and Scott Gable, http://alternativefuels.about.com/od/fuelcellvehiclereviews/ig/09-Honda-FCX-Clarity-Fuel-Cell/ - Mechanical faults
- Broken rotor bars
- Broken magnet (or partial demagnetization)
- Cracked end-rings
- Bent shaft
- Bolt loosening
- Bearing failure
- Gearbox failure
- Air-gap irregularity
- Outer motor drive system failures
- Inverter system failure
- Unstable voltage/current source
- Shorted or opened supply line
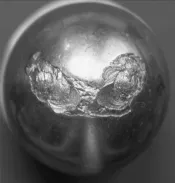
Bearing ball fault and subsequent fatigue damage. Vibration consultant. http://www.vibrationconsultants.co.nz/Fault%20Diagnosis.html
Table of contents
- Cover Page
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Contents
- Preface
- 1 Introduction
- 2 Faults in Induction and Synchronous Motors
- 3 Modeling of Electric Machines Using Winding and Modified Winding Function Approaches
- 4 Modeling of Electric Machines Using Magnetic Equivalent Circuit Method
- 5 Analysis of Faulty Induction Motors Using Finite Element Method
- 6 Fault Diagnosis of Electric Machines Using Techniques Based on Frequency Domain
- 7 Fault Diagnosis of Electric Machines Using Model-Based Techniques
- 8 Application of Pattern Recognition to Fault Diagnosis
- 9 Implementation of Motor Current Signature Analysis Fault Diagnosis Based on Digital Signal Processors
- 10 Electric Implementation of Fault Diagnosis in Hybrid Vehicles Based on Reference Frame Theory
- 11 Robust Signal Processing Techniques for the Implementation of Motor Current Signature Analysis Diagnosis Based on Digital Signal Processors
- Index