
eBook - ePub
Advanced Manufacturing for Optical Fibers and Integrated Photonic Devices
- 220 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
Advanced Manufacturing for Optical Fibers and Integrated Photonic Devices
About this book
Advanced Manufacturing for Optical Fibers and Integrated Photonic Devices explores the theoretical principles and industrial practices of high-technology manufacturing. Focusing on fiber optic, semiconductor, and laser products, this book:
- Explains the fundamentals of standard, high-tech, rapid, and additive manufacturing workshops
- Examines the production lines, processes, and clean rooms needed for the manufacturing of products
- Discusses the high-technology manufacturing and installation of fiber optic cables, connectors, and active/passive devices
- Describes continuous improvement, waste reduction through 5S application, and management's responsibilities in supporting production
- Covers Lean Manufacturing processes, product improvement, and workplace safety, as well as internal/external and ISO auditing
- Offers a step-by-step approach complete with numerous figures and tables, detailed references, and a glossary of terms
- Employs the international system of units (SI) throughout the text
Advanced Manufacturing for Optical Fibers and Integrated Photonic Devices presents the latest manufacturing achievements and their applications in the high-tech sector. Inspired by the author's extensive industrial experience, the book provides a comprehensive overview of contemporary manufacturing technologies.
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription.
At the moment all of our mobile-responsive ePub books are available to download via the app. Most of our PDFs are also available to download and we're working on making the final remaining ones downloadable now. Learn more here.
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 1000+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn more here.
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more here.
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS or Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Yes, you can access Advanced Manufacturing for Optical Fibers and Integrated Photonic Devices by Abdul Al-Azzawi in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Technology & Engineering & Industrial Engineering. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.
Information
1 | Workshops |

1.1 INTRODUCTION
At the beginning of the Industrial Revolution, workshops were developed for mass production. A workshop can be a small room, a big bungalow, or a building that provides the facilities for a manufacturing floor, tools, machinery, and systems. The facilities may be required for the manufacture or repair of manufactured goods. Workshops can be developed for a big mass production that would lead to a large factory. Workshops were developed in the last century using high manufacturing techniques for high-technology devices and systems productions. Workshops can be used for the production of goods or for social and other required activities in science, technology, planning, and teaching.
1.2 STANDARD WORKSHOPS
Standard workshops are the most used space for manufacturing goods in small and large quantities. The workshops can be for one type of manufacturing product or multiple purposes. Workshops are used for mechanical, wood, and metal work products. Workshops are classified as follows:
• Academic workshop
• Acting workshop
• Agricultural workshop
• Air-space workshop
• Building woodshop
• Chemical workshop
• E- or online workshop
• Educational workshop
• Electrical workshop
• Electronic workshop
• Mechanical workshop
• Multiple production workshop
• Music workshop
• Office workshop
• Photography workshop
• Photonics workshop
• Production workshop
• Series workshop
• Sheltered workshop
• Sociology workshop
• Songwriter workshop
• Telecommunication workshop
• Training workshop
• Etc.
1.3 HIGH-TECH WORKSHOPS
Standard workstations are used by employees during the entire shift. The station is used for the productivity, health, safety, and comfort of employees, as well as for promoting effective interaction among employees, technologies, and the environment in which both must operate. Figure 1.1 shows a standard workstation. The station should be accommodating so that personnel may interface effectively with tools and devices. Tools, jigs, and devices should be sized to fit the station and each individual user. The station should be designed to facilitate task performance and minimize fatigue and injury by fitting tools and devices to the body size, strength, and range of motion of the user. Some stations are equipped with shelves, one or double fluorescent lights, a true earth connection for electrostatic discharge (ESD) devices, electric outlet connections, and an air pressure supply gun. There are many sizes of standard stations. The most preferable size is 75 × 150 cm (2.5 × 5 ft), as shown in Figure 1.1.

FIGURE 1.1 Standard workstations.
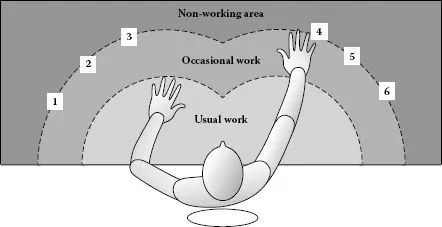
FIGURE 1.2 A standard workstation with six assembly parts.
Figure 1.2 shows an employee working on a single assembly standard workstation. The manual part dispensers for the six different single assembly parts are arranged in semicircular form around the assembly position. The numbering of the manual part dispensers corresponds to the single part numbers as shown in Figure 1.2. The mean distances for reaching and collecting between the work piece position and the individual gripping positions of the six parts should be in a comfortable reaching position to the employee, according to health and safety regulations. Each workstation type has its standard regulations for working distances for reaching, gripping, collection, assembly, and release.
The station work surface should be adjusted so that it is elbow height. If it cannot be adjusted, the height of the chair can be adjusted. If necessary, a footrest can be used. Furthermore, materials that are used frequently should be located within easy reach. Other materials should be placed just outside this easy-to-reach zone. It is also a good idea to put some materials completely out of reach. This will force the employee to get out of the chair and move around, promoting blood circulation and therefore reducing the stress on the employee’s body.
1.4 RAPID MANUFACTURING WORKSHOPS
The rapid development of workshops is as a result of using new manufacturing techniques, which produce products with low cost and according to a customer’s standards. Current manufacturing techniques are mostly controlled by automation setups. The manufacturing processes are mostly controlled by a computer using a mathematical code. Rapid workshops done in parallel batch production can provide an advantage in speed and lower cost compared to alternative manufacturing techniques, such as plastic injection molding or die casting. Rapid workshops can be used in the production of custom design parts, general consumption parts, standard production lines, large products, and series production.
1.5 ADDITIVE MANUFACTURING WORKSHOPS
Additive manufacturing workshops are the process of making a product by adding layers in a relatively efficient way, such that there is little waste or reduction of materials and the floor area is used efficiently. In this way, the addition of a manufacturing process can be implemented to an automated production line in a rapid workshop. The most popular examples are the production of inkjet printing, aerosol jet printing of electronic circuits, and 3D printing.
1.6 AN EXAMPLE OF WORKSHOP MODIFICATIONS
As described in this book, a workshop that is a room, an area, or a small establishment has many types of tools and machines where manual or light industrial work can be done. Workshops can be used for many types of manufacturing products. Workshops also have a combination of tools and machines for multiproduct design selections. For example, examine the combination of wood and metal work machines shown in Figure 1.3. This figure shows the machines for wood and metal works are distributed randomly around the floor. This example was a project completed by the author.
As shown in Figure 1.3, the workshop uses tools, jigs, and machines for different wood and metal products. Some of them are shown in Figure 1.4. This workshop operates in the traditional way of using tools, jigs, and machines. In this way, the workshop can produce many product designs.
Machines provide high power for small jobs in general design products. The conditions of the machines consume energy and have high operating costs. Consequently, the cost will add on to the price of the products. Figure 1.3 also shows that a combination of wood and metal work machines is a fire hazard due to flying sparks from metal cutting and grinders. The machines are also not arranged in subsequent manufacturing steps (one step followed by the next) to easily complete a product.
Let us audit the workshop setup and performance. The following can be highlighted:
• Machines, service machines, and tools are distributed randomly
• High power consumption machines
• Large size machines
• Missing manufacturing processes and file documentations
• Weak lighting distribution
• Old air-conditioning systems and uniform air distribution in the workshop
• Inappropriate air section fan locations
• Low employee morale
• Bad air quality generated from some of the machines, spray painting, and cleaning materials
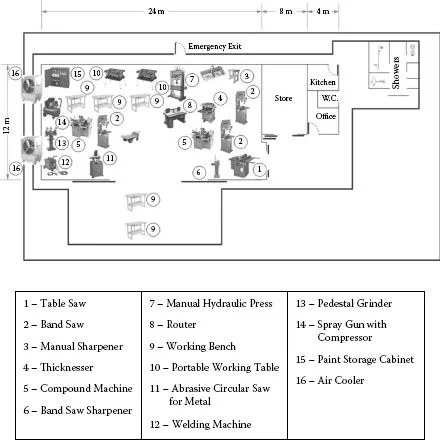
FIGURE 1.3 Wood and metal workshop.
• No inventory lists for the items and products
• Bad production storage locat...
Table of contents
- Cover
- Half Title
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Table of Contents
- Preface
- Acknowledgments
- About the Author
- Chapter 1 Workshops
- Chapter 2 Production Lines
- Chapter 3 Manufacturing Procedures
- Chapter 4 Clean Rooms
- Chapter 5 High Manufacturing Technology
- Chapter 6 Fiber Optic Cable Types and Installations
- Chapter 7 Manufacturing of Passive Fiber Optic Devices
- Chapter 8 Manufacturing of Active Fiber Optic Devices
- Chapter 9 Continuous Improvement in a Production Line
- Chapter 10 Types of Waste
- Chapter 11 Application of the 5Ss in Manufacturing Lines
- Chapter 12 Management and Employee Responsibilities
- Chapter 13 Lean Manufacturing
- Chapter 14 Product Improvement
- Chapter 15 Time Management in a Professional Environment
- Chapter 16 Internal, External, and ISO Auditing
- Chapter 17 High-Tech Manufacturing Safety
- Glossary
- References
- Index