
Supercritical Fluids Technology in Lipase Catalyzed Processes
- 160 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Supercritical Fluids Technology in Lipase Catalyzed Processes
About this book
Enzymes are currently used in various industries, most commonly in food, detergents, and pharmaceuticals production. Lipases are hydrolytic enzymes that demonstrate great potential as an alternative to conventional catalysts in a number of industrial applications. A complete understanding of enzymes, and their proteins structure and environmental behavior, can greatly aid in the further development of industrial applications. Supercritical Fluids Technology in Lipase Catalized Processes provides basic information about enzymes, their sources, reaction kinetics, and main industrial applications. The book focuses in lipases. their main sources, structure, and features, with an emphasis on their specificity and interfacial activity, and presents proven techniques for isolating, extracting, and purifying.
Comprised of six compact chapters, this comprehensive guide introduces:
- Immobilization techniques and immobilized lipases that allow repeated use (which is essential from an economic point of view)
- Different bioreactor configurations using immobilized lipases
- The latest information on the available technologies in lipolytic reactions
- The advantages of nonaqueous media in biochemical synthesis over aqueous and solvent-free systems
- Material on the use of lipases in nonaqueous media to overcome the drawbacks usually encountered with the use of conventional chemical catalysts
- The use of supercritical fluids (SCFs) as a green alternative reaction medium
- Factors affecting the physical properties of lipases in this medium and, hence, their activity and stability
- A case study using supercritical carbon dioxide (SC-CO2) for biodiesel production
- Novel, cutting-edge technology, using immobilized enzymes to reduce the overall production cost
Supercritical Fluids Technology in Lipase Catalized Processes
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
1 | Enzymes Fundamentals |
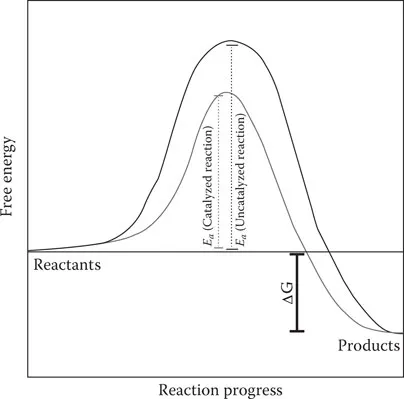
Effect of Enzyme Use on Reaction Activation Energy
Reaction | Catalyst | Activation Energy (cal/mol) | Reference |
Hydrogen peroxide decomposition | Without catalyst Platinum surface | 18,000 11,700 | Campbell and Farrell, 2011; Spencer et al., 2010 |
Potassium iodide | 13,500 | ||
Catalase | 5500 | ||
Ethyl butyrate hydrolysis | Hydrochloric acid | 16,800 | Steward and Bidwell, 1991 |
Lipase | 4500 | ||
Sucrose hydrolysis | Hydrochloric acid | 26,000 | Goss, 1973 |
Invertase | 13,000 | ||
Casein hydrolysis | Hydrochloric acid | 20,600 | Braverman and Berk, 1976 |
Lipase | 12,000 |
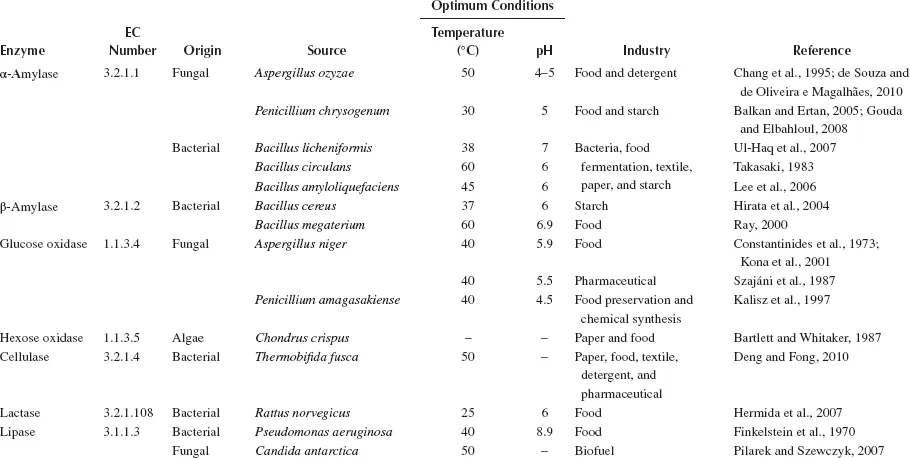
Common Microbial Enzymes and Their Industrial Uses
Six Major Classes of Enzymes
Class | Function | Examples |
Oxidoreductases | Catalyze oxidoreduction reactions by adding/removing hydrogen bonds | Glucose oxidase, lactate, alcohol dehydrogenase, laccase |
Transferases | Transfer of amino, fatty acid, methyl or phosphate functional groups from one molecule to another | Starch phosphorylase, amylosucrase, dextransucrase, levansucrase, aspartate aminotransferase |
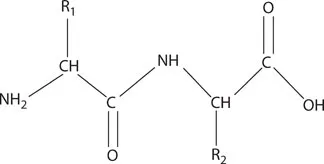
Hydrolases | Catalyze the hydrolysis of carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, or phosphoric acids esters by breaking single bond and add water across bond | Feruloyl esterases, lipase, chlorophyllase, α-amylases, β-amylases, chymosin |
Lyases | Catalyze the breaking/forming of chemical bonds by means other than hydrolysis | Alliinases, cystine lyases, his... |
Table of contents
- Cover
- Half Title
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Dedication
- Table of Contents
- Preface
- Acknowledgments
- Authors
- Chapter 1 Enzymes Fundamentals
- Chapter 2 Lipases
- Chapter 3 Lipase Immobilization
- Chapter 4 Kinetics of Soluble and Immobilized Enzymes
- Chapter 5 Lipase-Catalyzed Reactions in Nonaqueous Media
- Chapter 6 Lipase-Catalyzed Production of Biodiesel Using Supercritical Technology
- Index