
Emerging Security Algorithms and Techniques
- 318 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Emerging Security Algorithms and Techniques
About this book
Cyber security is the protection of information systems, hardware, software, and information as well from theft, damages, interruption or misdirection to any of these resources. In other words, cyber security focuses on protecting computers, networks, programs and data (in use, in rest, in motion) from unauthorized or unintended access, change or destruction. Therefore, strengthening the security and resilience of cyberspace has become a vital homeland security mission.
Cyber security attacks are growing exponentially. Security specialists must occupy in the lab, concocting new schemes to preserve the resources and to control any new attacks. Therefore, there are various emerging algorithms and techniques viz. DES, AES, IDEA, WAKE, CAST5, Serpent Algorithm, Chaos-Based Cryptography McEliece, Niederreiter, NTRU, Goldreich–Goldwasser–Halevi, Identity Based Encryption, and Attribute Based Encryption.
There are numerous applications of security algorithms like cyber security, web security, e-commerce, database security, smart card technology, mobile security, cloud security, digital signature, etc.
The book offers comprehensive coverage of the most essential topics, including:
- Modular Arithmetic, Finite Fields
- Prime Number, DLP, Integer Factorization Problem
- Symmetric Cryptography
- Asymmetric Cryptography
- Post-Quantum Cryptography
- Identity Based Encryption
- Attribute Based Encryption
- Key Management
- Entity Authentication, Message Authentication
- Digital Signatures
- Hands-On "SageMath"
This book serves as a textbook/reference book for UG, PG, PhD students, Teachers, Researchers and Engineers in the disciplines of Information Technology, Computer Science and Engineering, and Electronics and Communication Engineering.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
1
Modular Arithmetic
- 1.1 Introduction to Number Theory
- 1.1.1 Integers
- 1.1.2 Integer Arithmetic
- 1.1.3 Arithmetic Operations
- 1.2 Modular Arithmetic
- 1.2.1 Examples
- 1.3 Additive Inverse
- 1.3.1 Examples
- 1.4 Multiplicative Inverse
- 1.4.1 Examples
- 1.5 Matrix
- 1.5.1 Examples
- 1.6 Linear Congruence
- 1.6.1 Solution of Linear Congruence
- 1.7 Prime and Relative Prime Numbers
- 1.7.1 Prime Numbers
- 1.7.2 Relatively Prime Numbers
- 1.7.3 Examples
- 1.8 Greatest Common Divisor (Euclid’s Algorithm, Bézout’s Algorithm, and Extended Euclid’s Algorithm)
- 1.8.1 Greatest Common Divisor
- 1.8.1.1 Examples
- 1.8.2 Euclid’s Algorithm
- 1.8.2.1 Example
- 1.8.3 Bézout’s Theorem
- 1.8.4 Extended Euclid’s Algorithm
- 1.8.4.1 Examples
- 1.9 Conclusion
- References
1.1 Introduction to Number Theory
1.1.1 Integers

1.1.2 Integer Arithmetic
1.1.3 Arithmetic Operations
- Addition
- Subtraction
- Multiplication
- Division.
- Addition: It states that the addition of two integers is always an integer.
- 2 + 5 = 7

- −7 + 4 = −3

- Subtraction: It states that the subtraction of two integers is again an integer.
- 6 − 4 = 2
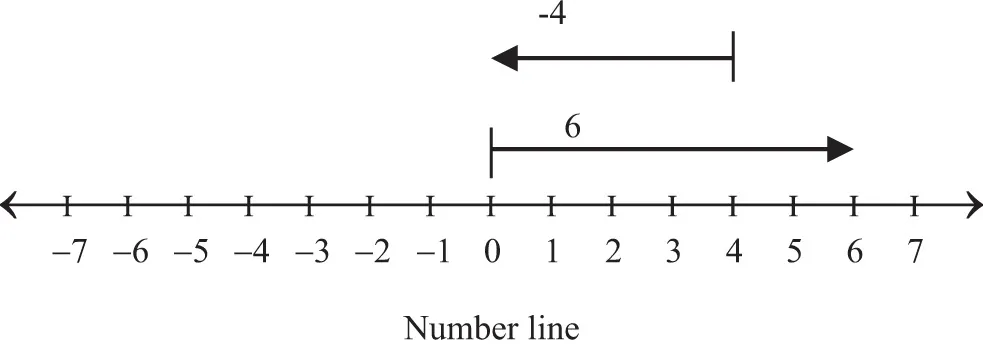
- Multiplication: It states that multiplying two integers always results in an integer.

- Division...
Table of contents
- Cover
- Half Title
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Table of Contents
- Perface
- Editors
- Contributors
- 1. Modular Arithmetic
- 2. Finite Fields
- 3. Prime Number
- 4. Discrete Logarithm Problem
- 5. Integer Factorization Problem
- 6. Symmetric Algorithms I
- 7. Symmetric Algorithms II
- 8. Asymmetric Cryptography
- 9. Post-Quantum Cryptography
- 10. Identity-Based Encryption
- 11. Attribute-Based Encryption
- 12. Key Management
- 13. Entity Authentication
- 14. Message Authentication
- 15. Digital Signatures
- 16. Applications
- 17. Hands-On “SageMath”
- Index
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app