![]()
Section IV
Nanofluids in Solar Applications
![]()
11
An Insight of Ionanofluids Flow and Heat Transfer Behavior for Solar Energy Applications
Alina Adriana Minea and S.M. Sohel Murshed
CONTENTS
11.1 Introduction
11.2 Preparation and Stability of Ionanofluids
11.3 Ionanofluids Thermal Conductivity
11.3.1 Effect of Temperature on Thermal Conductivity
11.3.2 Effect of Concentration of Dispersed Nanoparticles on Thermal Conductivity
11.4 Ionanofluids Heat Capacity
11.5 Ionanofluids Convective Heat Transfer
11.6 Solar Energy Applications
11.7 Conclusion
Nomenclature
Greek Symbols
Abbreviations
References
11.1 Introduction
Ionanofluids (INFs) are suspensions of nanoparticles in ionic liquids (ILs), and they are a new class of heat transfer fluids. They are also a new type of nanofluids. The interesting and potential applications of these new fluids can be in the area of both nanofluids and ILs. Ionic liquids are entirely made of ions and have the melting point lower than 100°C [1]. Recently, the development of room temperature ionic liquids have attracted tremendous interest from researchers and industrial people due to their low melting temperatures (<30°C) which allow these host fluids for INFs to be used in wide range of applications [2]. Ionic liquids exhibit several unique features that allow to develop and synthesize by tailoring of the cation-anion structure for desired physiochemical properties and thus for the targeted applications. As these liquids are not combustible or volatile at ambient conditions and also are recyclable, they are considered as environmental-friendly fluids [3,4]. Ionic liquids also have extremely low vapor pressure, high thermal stability, as well as high heat capacity, and the combination of these features makes ILs and thus ionanofluids better heat transfer fluids.
Some studies [e.g., 5] also suggested that, due to their very low vapor pressure preventing them to be cooled by evaporations, ILs can be used for thermal energy storage in an open system. Thus, ionic liquids and their suspensions of nanoparticles (INFs) can be good media for thermal storage systems as well as heat transfer fluids in solar power generation applications.
França [6] demonstrated that the combination of nanomaterials with ILs show great potential as heat transfer fluids through the enhancement of the thermal properties and heat transfer.
Since the first work on carbon nanotubes (CNT) mixed in ionic liquids (i.e., INFs) reported by Fukushima and Aida [7] in 2007, numbers of research works [8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28] have been performed in this new area of ionanofluids. However, the research on various properties and heat transfer features of these new heat transfer fluids are still at very early stage and some findings are carefully reviewed in later sections.
In terms of real-life applications, few research groups (e.g., [14,15,16,24]) demonstrated that ionanofluids could be very well suited for solar energy applications, especially for the efficient absorption of the solar radiation and for its transmission to heating/cooling systems. This chapter aims to provide an insight of these new fluids thermal properties and convective heat transfer behavior particularly focusing on their solar energy applications.
11.2 Preparation and Stability of Ionanofluids
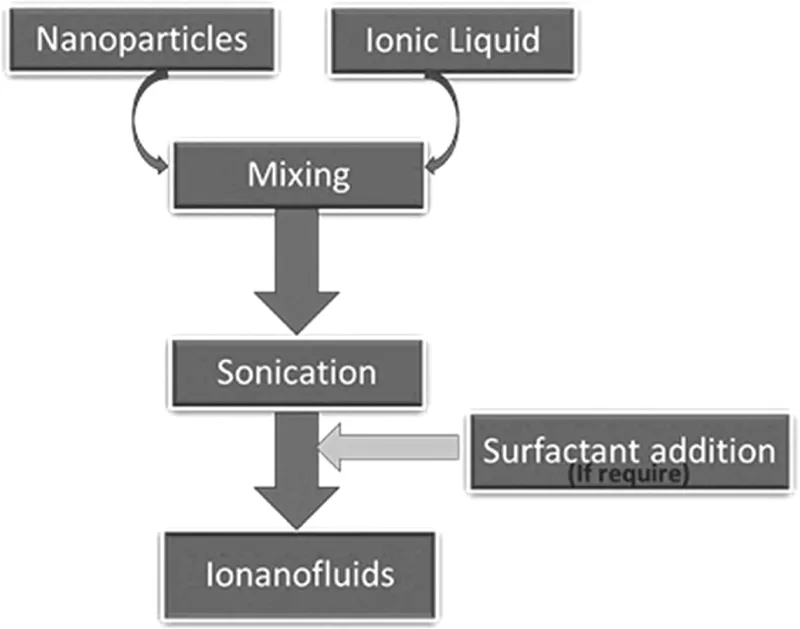
Preparation of ionanofluids and ensuring their stability are the first step for their properties characterization and applications. Although conventional nanofluids are prepared in two methods (i.e., one-step and two-steps) [29], ionanofluids are mostly prepared by two-step methods as demonstrated in Figure 11.1.
It is of great importance to make sure that the added nanoparticles are properly (if possible homogenously) dispersed in base ILs and ionanofluids have long stability. However, it is very challenging to achieve long-term stability of INFs as many factors such as nanoparticles types, size shapes, purity, and degree of agglomerations, as well as properties of host fluids (ILs) are involved in this process. As for nanofluids, various techniques including sonication, surfactant addition, agitation, and surface treatment of nanoparticles are commonly employed for the dispersion and stability of ionanofluids. However, in most cases, researchers used sonication and addition of surfactants for better stability. Both of these means need to be carefully studied and understood before applying them to the preparation of nanofluids for their better stability and properties without changing the chemistry of nanofluids and the original structures of nanoparticles [30]. Although ultrasonication is most widely used in nanofluids as well as ionanofluids studies, there is a lack of adequate knowledge on the effects of its various parameters and duration of use. Also, no standard dispersion procedure or protocol for ultrasonication is available either for nanofluids or for ionanofluids, and therefore proper dispersion of nanoparticles and long-term stability of these new fluids remain very challenging.
FIGURE 11.1 Flow chart of preparation of ionanofluids by two-step method.
11.3 Ionanofluids Thermal Conductivity
In the literature, thermal conductivity of INFs is the most studied property under different temperature and concentrations of nanoparticles [20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,31]. In this section, influences of both of these parameters on this key property of ionanofluids are discussed besides summarizing some representative results.
11.3.1 Effect of Temperature on Thermal Conductivity
In general, temperature has mixed effect on thermal conductivity of these new fluids. For instance, Franca et al. [20] found that the thermal conductivities of their [C4mim][(CF3SO2)2N] and [C2mim][EtSO4]-based multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) ionanofluids remained almost constant with increasing temperature. Ferreira et al. [23] also reported that temperature has almost no influence on the thermal conductivity of several INFs used in their study. Whereas several other studies in the literature [21,25,28,32] reported even a decrease of thermal conductivity of INFs with temperature increase. Some studies also found slight increase in the enhanced thermal conductivity of INFs with increasing temperature [e.g., 25]. Ribeiro et al. [27] measured thermal conductivity of several INFs at a fixed 1 wt.% concentration of MWCNT at various temperatures between 20°C and 80°C and at pressure of 0.1 MPa. Except [C4mim][PF6]/MWCNT iona...