
Introduction to Experimental Biophysics
Biological Methods for Physical Scientists
- 764 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
About this book
Praise for the First Edition
"essential reading for any physical scientist who is interested in performing biological research." ?Contemporary Physics
"an ambitious text…. Each chapter contains protocols and the conceptual reasoning behind them, which is often useful to physicists performing biological experiments for the first time." –Physics Today
This fully updated and expanded text is the best starting point for any student or researcher in the physical sciences to gain firm grounding in the techniques employed in molecular biophysics and quantitative biology. It includes brand new chapters on gene expression techniques, advanced techniques in biological light microscopy (super-resolution, two-photon, and fluorescence lifetime imaging), holography, and gold nanoparticles used in medicine. The author shares invaluable practical tips and insider's knowledge to simplify potentially confusing techniques. The reader is guided through easy-to-follow examples carried out from start to finish with practical tips and insider's knowledge. The emphasis is on building comfort with getting hands "wet" with basic methods and finally understanding when and how to apply or adapt them to address different questions.
Jay L. Nadeau is a scientific researcher and head of the Biomedical Engineering in Advanced Applications of Quantum, Oscillatory, and Nanotechnological Systems (BEAAQONS) lab at Caltech and was previously associate professor of biomedical engineering and physics at McGill University.
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
1Introduction and Background
1.1Basic Biochemistry
Molecules important to molecular biophysics
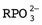
- Amino acids (polymerize to form peptides and proteins). There are twenty naturally occurring amino acids, whose structure consists of a central carbon atom with a carboxylic acid on one end and a primary amine on the other, and a side chain that branches off the first carbon after the amine. The side chain determines the amino acid’s identity and ranges from a hydrogen (glycine) to complex charged or aromatic groups (Figure 1.2). Short chains of amino acids are called peptides and may be synthesized by organisms like fungi in order to kill bacteria. The example shown is bacitracin, which is a cyclic peptide active against many bacteria; it is often found in first-aid creams. Some peptides are available from biological suppliers, and custom peptides are also available, though costly. Full-length proteins are encoded genetically and synthesized as a long polypeptide chain. They then fold to form their final tertiary structure; the example shown is green fluorescent protein, or GFP, which has 238 amino acids. The physics of protein folding still remains largely a mystery. Proteins usually cannot be purchased but must be expressed and...
Table of contents
- Cover
- Half Title Page
- Series Page
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Contents
- Series Preface
- Preface
- Acknowledgments
- Author
- Contributors
- Chapter 1 Introduction and Background
- Chapter 2 Basic Molecular Cloning of DNA and RNA
- Chapter 3 Expression of Genes in Bacteria, Yeast, and Cultured Mammalian Cells
- Chapter 4 Advanced Topics in Molecular Biology
- Chapter 5 Protein Expression Methods
- Chapter 6 Protein Crystallization
- Chapter 7 Introduction to Biological Light Microscopy
- Chapter 8 Advanced Light Microscopy Techniques
- Chapter 9 Advanced Topics in Microscopy II: Holographic Microscopy
- Chapter 10 Quantitative Cell Culture Techniques
- Chapter 11 Semiconductor Nanoparticles (Quantum Dots)
- Chapter 12 Gold Nanoparticles
- Chapter 13 Advanced Topics in Gold Nanoparticles: Biomedical Applications
- Chapter 14 Surface Functionalization Techniques
- Chapter 15 Electrophysiology
- Chapter 16 Spectroscopy Tools and Techniques
- Chapter 17 Introduction to Nanofabrication
- Glossary
- Appendix A Common Solutions
- Appendix B Common Media
- Appendix C Restriction Endonucleases
- Appendix D Common Enzymes
- Appendix E Fluorescent Dyes and Quenchers
- Appendix F Fluorescent Proteins
- Index