
eBook - ePub
Boron-Based Fuel-Rich Propellant
Properties, Combustion, and Technology Aspects
- 323 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
About this book
Boron-Based Fuel-Rich Solid Rocket Propellant Technology is a professional book that systematically introduces the latest research progress for boron-based fuel-rich solid propellants. It covers surface modifications, coating and agglomerating techniques, granulation, and characterization of amorphous boron powders, and its application to fuel-rich solid rocket propellants. Technologies for controlling the processing methods and combustion performance of fuel-rich propellants are examined, and the book concludes with a summary of the research progress in boron-based fuel-rich solid propellants and a look forward to the foreseeable development trends of military applications.
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription.
No, books cannot be downloaded as external files, such as PDFs, for use outside of Perlego. However, you can download books within the Perlego app for offline reading on mobile or tablet. Learn more here.
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 1000+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn more here.
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more here.
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS or Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Yes, you can access Boron-Based Fuel-Rich Propellant by WeiQiang Pang in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Technology & Engineering & Civil Engineering. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.
Information
1
Basic Formulations and Components of Ramjet Propellants
1.1 Fuel-Rich Propellants
The solid rocket ramjet propulsion system features fast velocity, lightweight, small volume, high specific impulse, long range, simple structure, and reliability. It has a strong defense penetration power and strike force, and will be one of the best propulsion schemes for modern air-to-air missiles and anti-ship missiles.1, 2 and 3 Compared with traditional solid rocket motors, solid rocket ramjets use fuel-rich propellants, taking oxygen from air as the main oxidizer for the secondary combustor, which obviously increases the range of the weapon. The solid ramjet mainly includes Solid Rocket Ramjet and Solid Fuel Ramjet, where fuel-rich propellants are mostly used in the solid ramjet. Besides, in recent years, fuel-rich solid propellants are also used in solid fuel ramjets and air-turbo rockets with better theoretical performance. Fuel-rich propellants mainly include boron-based fuel-rich propellants, aluminum-based fuel-rich propellants, and magnesium-based fuel-rich propellants.4,5 Among them, the calorific value released by the full combustion of “medium energy” Mg-based and Al-based fuel-rich propellants is around 19–22 MJ·kg−1, the specific impulse can reach 5,000–8,000 N·S·kg−1, while the calorific value released by the full combustion of high-energy boron-based fuel-rich propellants is 30–34 MJ·kg−1, with a specific impulse of about 1.6–1.8 times of that of Al-based fuel-rich propellants and about 3 times that of solid propellants.6, 7, 8 and 9 The earlier data indicate that high-energy boron-based fuel-rich propellants have aroused widespread attention from researchers as one of the most ideal propulsion energy sources for solid motors. More than 40% mass fraction of boron powder in the fuel-rich propellants has been successfully developed,10,11 with 40–42 MJ·kg−1 of calorific value and 13,994 N·s·kg−1 of specific impulse. Compared with the researches on boron-based fuel-rich propellants conducted abroad,12 the researchers in China mainly concentrated on the fuel-rich propellants with around 35% of boron, whose performance was far from meeting the requirements of high-energy fuel-rich propellants. How to increase boron quantity in fuel-rich propellants poses a challenge to the preparation techniques of fuel-rich propellants, becoming a key technology that must be tackled in the development of such propellants. According to theoretical analysis, applying high-energy boron-based fuel-rich propellants to the solid ramjets of the new generation for medium- and long-range air-to-air missiles and cruise missiles can meet the performance requirement of high speed and long range.13
1.2 Main Components of Boron-Based Fuel-Rich Solid Rocket Propellant
Boron-based fuel-rich solid rocket propellants are a kind of composite solid propellants with binders as the matrix and solid fillers. Its main components are macromolecule binders (e.g., hydroxyl-terminated polybutadiene [HTPB]), oxidizers (e.g., ammonium perchlorate [AP]), metal fuels (e.g., boron powder B, Mg powder or aluminum powder), ballistic modifiers, plasticizers, and curing agents, which are used to render certain performance to the fuel-rich propellants. In the propellant formulation, additives with different functions and performance modifiers are also added, such as combustion catalysts, bonding agents, and antioxidants.
1.2.1 Binders
Binder is a polymeric compound that can bind other components in the propellant into ensemble with ideal performance. Although binders only take 10%–15% of mass fraction in solid propellants, it plays an important role. On the one hand, it can be taken as a high-energy fuel to produce CO2 and H2O by reacting with oxidizers, thus producing thrust; on the other hand, it can enable metal additives, oxidizers, and combustion modifiers to be evenly bound and form solid grains that possess certain strength under both high and low temperatures, form a continuous matrix in boron-based fuel-rich propellants, and provide combustible elements such as C and H during combustion to release energy. Binders widely used in recent years include high polymers such as HTPB and glycidyl azide polymer (GAP), which are cost effective, have the mobility close to Newtonian fluid with low viscosity, and enables more solid components to be added. Besides, modern binders are compatible with highly active chemicals such as Mg powder. HTPB, known as hydroxygum, is one kind of telechelic liquid rubber, including free radical type and anionic type, with polybutadiene as the backbone. Based on the number of terminal hydroxyl, HTPB can be divided into difunctional hydroxygum and polyfunctional hydroxygum. The hydroxygum is an important variety of liquid rubber that has good transparency, low viscosity, oil resistance and antioxidation, good low temperature characteristics, and good processing performances. It can produce in bulk with three-dimensional network structures by reacting with a chain extender under room and high temperatures. This material has excellent mechanical properties; water, wear, acid, and alkali resistance; and electrical insulation properties. It is stable at indoor temperatures and does not produce any tiny crack when used. The structural formula is as follows:
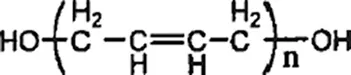
1.2.2 Metal Fuels
In recent years, an important development way is to add metal fuels. Boron powder, magnesium powder, and aluminum powder with high calorific value can be used as metal fuels for propellants. Since boron powder has a series of necessary physical and chemical features such as heavy weight and volumetric calorific value, it becomes the prime metal fuel choice, especially for the weaponry system that is restrained in weight and volume.14 High-energy boron-based fuel-rich propellants meet the requirement of engine performance, and are an ideal choice for solid rocket ramjets15 in terms of their theoretical design or development practice.
Fuel-rich propellants have higher density specific impulse because of the added metal fuels with high calorific value and higher density. As well-known, beryllium (Be) has higher calorific value, but beryllium and its combustion products are highly toxic substances; lithium has very small density and very high activity, and Li is not compatible with many propellant components. Both cannot be put into use. The main properties of three common metals and their oxides are summarized in Tables 1.1 and 1.2. Here after, we consider B as a “metal” fuel.
TABLE 1.1
Basic Properties of Three Types of Metals16, 17 and 18
Basic Properties of Three Types of Metals16, 17 and 18

TABLE 1.2
Basic Characteristics of Three Types of Metal Oxides16, 17 and 18
Basic Characteristics of Three Types of Metal Oxides16, 17 and 18
Metal Oxidizers | Molecular mass | Density (g·cm−3) | Melting Point (°C) | Boiling Point (°C) |
B2O3 | 69.62 | 2.46 | 460 | 1,860 |
Al2O3 | 101.96 | 3.97 | 2,045 | 2,980 |
MgO | 40.30 | 3.58 | 2,800 | 3,580 |
From Tables 1.1 and 1.2, it can be seen that B, Al, and Mg powder fuels have their own advantages and disadvantages. In terms of energy, aluminum has the highest density of 2.70 g·cm−3, boron the second, and magnesium the lowest density of 1.74 g·cm−3. The oxygen consumption of Mg is the lowest, having a value of 0.66 g; yet, boron ranks first with 2.22 g of oxygen consumption, which is three times that of Mg and Al. In terms of combustion, the melting points and boiling points of magnesium, aluminum, and boron increase successively, and combustion difficulties also increase. The melting points of magnesium and aluminum are low, at around 660°C, while the melting point of boron can be as high as 2,074°C. The boiling points of aluminum and boron are similar, and the boiling point of boron can reach 2,550°C, while Mg has a minimum boiling point of 1,117°C. The gasification heat of boron can reach 535.81 kJ·mol−1 and that of aluminum is about half that of boron, and that of magnesium is one-third less than that of boron. In terms of heat, magnesium has the lowest, only half of that of boron, and boron’s heat is 400 kJ·mol−1 less than aluminum. Yet since the atomic mass of aluminum is twice that of boron, the quality calorific value and volume calorific value of boron are both larger than those of aluminum. The quality calorific value of aluminum is 31.02 MJ·kg−1, while that of boron is 58.30 MJ·kg−1. In terms of metal oxide, B2O3 has the lowest melting point of 460°C, MgO has the highest melting point of 2,800°C, and that of Al2O3 reaches 2,045°C; the melting point of MgO is the highest, reaching 3,580°C, and the boiling point of Al2O3 is 2,980°C and that of B2O3 is 1,860°C. After comprehensively considering factors such as energy performance and combustion properties, boron powder is selected as the main metal fuel additive; meanwhile, a small amount of magnesium powder or aluminum powder was added to enable fuel-rich propellants to possess good ignition performance.
1.2.2.1 Boron in Nature
In nature, boron mainly exists in the form of borate, such as boric acid, alkali metal, and alkaline-earth metal, and the element boron does not exist by itself in nature. In China, boron minerals are sparsely distributed, with few high-graded boron minerals with exploitation values. There is natural borax in places such as Qinghai and Tibet, and endogenic boron ore with szaibelyite as the main ore in Northeast China, and a little reserve of boron minerals in other places. Most Chinese manufacturers of boron powder are located in Yingkou City, taking local boron ore as the raw material and producing amorphous boron powder with different specifi...
Table of contents
- Cover
- Half Title
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Table of Contents
- Preface
- Foreword
- Summary
- Authors
- Abbreviations
- 1. Basic Formulations and Components of Ramjet Propellants
- 2. Surface Modification and Characterization of Boron Powder
- 3. The Surface-Interfacial Properties of Boron and Binder System
- 4. Rheological Properties
- 5. Energetic Properties
- 6. Combustion Properties
- 7. Combustion Performance of Model Propellant with Boron and Boron-Containing Compounds
- 8. Application Perspectives and Development Trends of Boron-Based Fuel-Rich Propellants
- Index