
- 358 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
About this book
Soil and Fertilizers: Managing the Environmental Footprint presents strategies to improve soil health by reducing the rate of fertilizer input while maintaining high agronomic yields.
It is estimated that fertilizer use supported nearly half of global births in 2008. In a context of potential food insecurity exacerbated by population growth and climate change, the importance of fertilizers in sustaining the agronomic production is clear. However, excessive use of chemical fertilizers poses serious risks both to the environment and to human health.
Highlighting a tenfold increase in global fertilizer consumption between 2002 and 2016, the book explains the effects on the quality of soil, water, air and biota from overuse of chemical fertilizers. Written by an interdisciplinary author team, this book presents methods for enhancing the efficiency of fertilizer use and outlines agricultural practices that can reduce the environmental footprint.
Features:
-
- Includes a thorough literature review on the agronomic and environmental impact of fertilizer, from degradation of ecosystems to the eutrophication of drinking water
-
- Devotes specific chapters to enhancing the use efficiency and effectiveness of the fertilizers through improved formulations, time and mode of application, and the use of precision farming technology
-
- Reveals geographic variation in fertilizer consumption volume by presenting case studies for specific countries and regions, including India and Africa
-
- Discusses the pros and cons of organic vs. chemical fertilizers, innovative technologies including nuclear energy, and the U.N.'s Sustainable Development Goals
Part of the Advances in Soil Sciences series, this solutions-focused volume will appeal to soil scientists, environmental scientists and agricultural engineers.
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
1 | Effects of Fertilizers on Soil Quality and FunctionalityRattan Lal |
1.1 INTRODUCTION
1.1.1 GLOBAL FERTILIZER USE
Year | World Population (Billions) | Total Grain Production (Million Tons) | Per Capita Grain Production (Kg) |
|---|---|---|---|
2008/09 | 6.789 | 2241.6 | 330 |
2009/10 | 6.872 | 2241.5 | 332 |
2010/11 | 6.957 | 2200.4 | 316 |
2011/12 | 7.041 | 2314.4 | 328 |
2012/13 | 7.126 | 2266.2 | 318 |
2013/14 | 7.211 | 2474.7 | 367 |
2014/15 | 7.295 | 2532.0 | 347 |
2015/16 | 7.380 | 2058.0 | 278 |
2016/17 | 7.464 | 2186.0 | 292 |
2017/18 | 7.547 | 2142.0 | 283 |
2018/19 | 7.631 | 2120.0 | 277 |
2019/20 | 7.713 | ||
2020/21 | 7.795 |
Fertilizer | Fertilizer Use (106 Mg/yr) | Annual Growth (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1959/60 | 1989/90 | 2018 | 2020 | 1960–1990 | 1990–2020 | |
Nitrogen | 9.5 | 79.2 | 169.0 | 170.8 | 7.1 | 4.4 |
Phosphorus | 9.7 | 37.5 | 51.2 | 53.1 | 4.5 | 1.1 |
Potash | 8.1 | 26.9 | 47.2 | 49.5 | 4.0 | 1.2 |
Total | 27.4 | 143.6 | 267.4 | 273.4 | 5.5 | 2.9 |
1.1.2 THE SOIL-WATER-AIR-QUALITY NEXUS
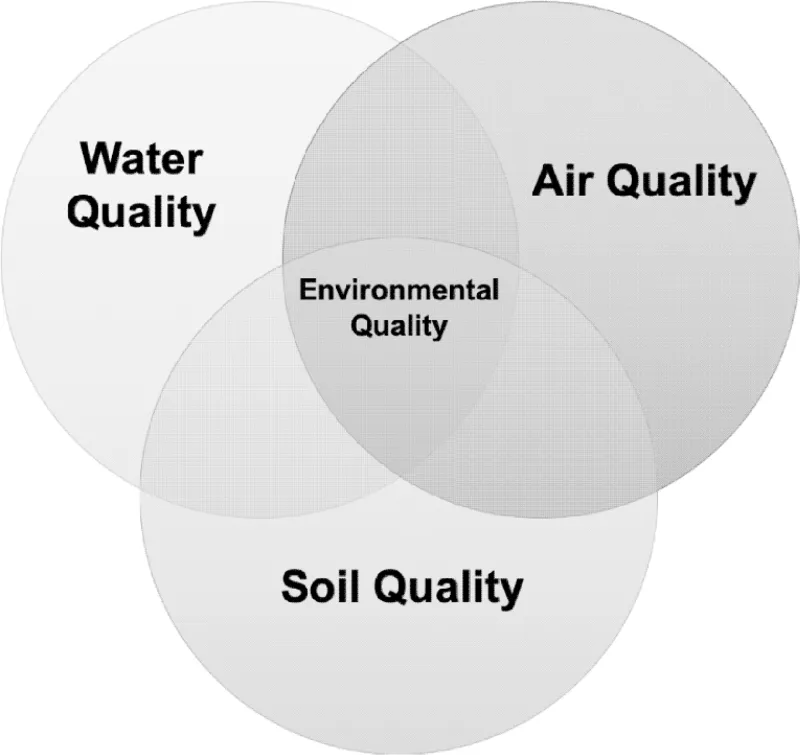

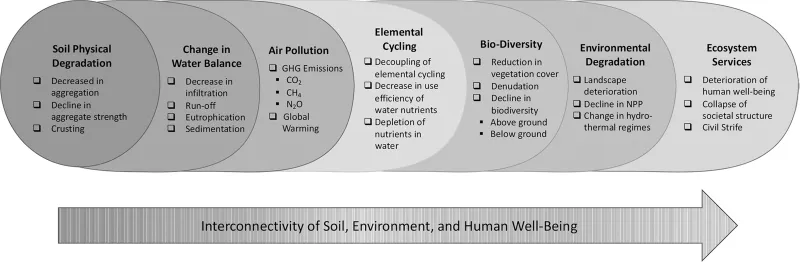
1.1.3 OBJECTIVES AND EXPECTED OUTPUT

1.2 GLOBAL FOOD DEMAND
1.2.1 TRENDS I...
Table of contents
- Cover
- Half Title
- Series Page
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Table of Contents
- Preface
- Editor
- Contributors
- Chapter 1 Effects of Fertilizers on Soil Quality and Functionality
- Chapter 2 Treatment of Wet Organic Waste by Hydrothermal Carbonization
- Chapter 3 Crop Residue Management for Improving Soil Carbon Storage, Nutrient Availability, and Fertilizer Use Efficiency
- Chapter 4 Improving Soil Fertility through Fertilizer Management in Sub-Saharan Africa
- Chapter 5 The Storage of Organic Carbon in Dryland Soils of Africa: Constraints and Opportunities
- Chapter 6 Manures versus Fertilizers in Rainfed Dryland Production Systems of India
- Chapter 7 Reducing Emission of Greenhouse Gases from Fertilizer Use in India
- Chapter 8 Soil Health and Fertilizer Use in India
- Chapter 9 Applications of Isotopes in Fertilizer Research
- Chapter 10 Managing Fertilizers in Soils of Paddy Rice
- Chapter 11 Nuclear Powered Agriculture: Fertilizers and Amendments
- Chapter 12 Nitrogen Dynamics and Management in Rainfed Drylands: Issues and Challenges
- Chapter 13 Tailored Fertilizers: The Need of the Times
- Chapter 14 Managing Soils for Reducing Dependence on Chemicals and Import of Resources into Agroecosystems
- Index