![]()
|
1 | Large-Scale Energy Storage An Overview Huamin Zhang |
CONTENTS
1.1General Introduction
1.2Requirements of Large-Scale Energy Storage Techniques
1.3Types and Characteristics of Large Energy Storage Techniques
1.4Development of Different Energy Storage Techniques
1.4.1Hydro-Pumping Energy Storage Technology
1.4.1.1Mechanism of Hydro-Pumping Energy Storage Technology
1.4.1.2Current Situation of Hydro-Pumping
Energy Storage Technology
1.4.1.3Developmental Tendencies of Hydro-Pumping Energy Storage Technology
1.4.2Compressed Air Energy Storage Technology
1.4.2.1Mechanism of Compressed Air Energy Storage Technology
1.4.2.2Development of Compressed Air Energy Storage
1.4.2.3Developmental Tendencies of Compressed Air Energy Storage Technology
1.4.3Lithium-Ion Batteries
1.4.3.1Mechanism of Lithium-Ion Batteries
1.4.3.2Lithium-Ion Battery Technology
1.4.3.3Developmental Tendencies of Lithium-Ion Battery Technology
1.4.4Sodium–Sulfur Batteries
1.4.4.1Mechanism of Sodium–Sulfur Batteries
1.4.4.2Sodium–Sulfur Energy Storage Battery System
1.4.4.3Current Status of Sodium–Sulfur Battery Technology
1.4.5Sodium–Nickel Batteries
1.4.5.1Working Mechanism of Sodium–Nickel Batteries
1.4.5.2Sodium–Nickel Energy Storage Battery Systems
1.4.5.3Current Status of Sodium–Nickel Battery Technology
1.4.5.4Developmental Tendencies of Sodium–Nickel Batteries
1.5Summary and Perspective
References
1.1GENERAL INTRODUCTION
Throughout history, the development of energy technology has changed human life. Every innovation in the area of energy is accompanied by the rapid progress of socially productive forces, the huge improvement of human life quality, and great changes in human environment. In summary, the use of energy for human society has experienced four revolutions. The use of fire was the first human energy revolution; for example, using firewood for cooking, heating, and defense. The use of fossil fuels (e.g., coal and oil) was the second human energy revolution. From the early eighteenth century, the discovery and exploitation of coal, as well as the invention of coal-fired steam engine technology, brought human society into industrial civilization. In the mid-nineteenth century, the large-scale production and use of oil brought about the first industrial revolution. Internal combustion engines, cars, planes, and other new inventions changed the style of life and work. Faraday’s electricity inventions were a revolution in human energy use. In the 1940s, the invention of the controlled nuclear reactor was the prelude to the third energy revolution. Then, in 1973, the first oil crisis indicated that the oil age would end, and the depletion of fossil energy was expected, as well as global climate change. The appeal of clean, renewable energy utilization is growing, and its purpose is to gradually replace fossil energy sources with renewable sources of energy (including hydroelectric energy, biomass energy, solar energy, wind energy, geothermal energy, marine energy, hydrogen energy, etc.), to ensure the sustainable development of humanity. The fourth human energy revolution has begun.
Energy can be divided into primary and secondary energy. Primary energy refers to energy resources that exist in nature, including fossil fuels such as coal, petroleum, natural gas, oil shale, shale gas, and coalbed methane, and nonfossil energy such as water, wind, solar, geothermal, thermal, wave, and tidal energy. Secondary energy is generated from primary energy, including electricity, hydrogen, steam, gas, ethanol, liquefied petroleum gas, gasoline, kerosene, diesel oil, and heavy oil.
On the other hand, energy can be divided into two other categories, nonrenewable energy and renewable energy, based on the self-sustainable and recovery characteristics. Nonrenewable energy sources include fossil fuels (e.g., coal, gas, oil, etc.) and nuclear energy. Nonrenewable energy is difficult to reproduce in the short term. Renewable energy sources, including hydroelectric, wind, solar, geothermal, thermal, wave, and tidal energy, can be reproduced repeatedly.
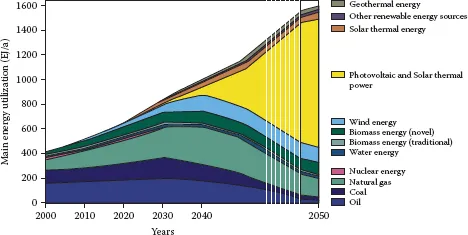
Figure 1.1 forecasts the statistics and trends of global primary energy demand, which is mainly constituted by nonrenewable fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and natural gas [1]. However, limited nonrenewable energy sources cannot guarantee the sustainable development of humanity. According to statistics, in 2009, the global consumption of primary energy was 12,132 Mtoe, while it was only 7,219 Mtoe in 1980 [1]. It is predicted that the proven reserves of global oil and gas will be exhausted in 40 years and 60 years, respectively, at current consumption rates. In addition, the use process of fossil energy emits large amounts of sulfides, nitrides, CO2, and greenhouse gases, leading to the deterioration of the global climate and increasing the frequency of extreme weather events.
FIGURE 1.1Global demand and forecast of primary energy (until 2009). (From Fatih Biro, L., World Energy Outlook 2010 [J/OL], 2010 [1].)
The consensus is that the large-scale application of renewable energy sources, mainly solar and wind power, is necessary to guarantee the sustainable development of human society. Although humans have used wind and solar energy for a long time (e.g., windmills and solar cooking), the large-scale use of wind power only began in the twentieth century. Currently, wind power is growing quickly and might reach 474 GW by 2020, according to a World Energy Council forecast [2]. Besides that, the utilization of solar energy has developed quickly in recent years, including photothermal conversion (solar cookers, solar heating systems, and solar thermal power), photovoltaic (PV) conversion, and photocatalytic conversion (e.g., artificial photosynthesis, PV hydrogen production). Photoelectric conversion has been successfully commercialized, with comprehensive environmental benefits. However, the intermittent nature of wind and solar energy make it difficult to directly transport and dispatch through the power grid. How to ensure power quality, under the premise of the safe and stable operation of the power grid, becomes the bottleneck in the further development of renewable energies.
Another important utilization of large-scale energy technology is the construction of smart power grids. Due to the continuous improvement of people’s living standards, the demand for electricity has increased rapidly. The current global power generation capacity has reached about 15 TW. By the middle of this century, the installed capacity will be doubled. By the end of the century, the installed capacity will be three times that at the beginning of the century. The rapid growth of the power generation capacity needs to synchronize with the expansion of the transmission and distribution networks. However, the traditional power grid is usually designed for the maximum load, resulting in high grid infrastructure investment and low system utilization, and it is difficul...