
Point of Care Ultrasound Made Easy
- 154 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Point of Care Ultrasound Made Easy
About this book
Point of Care Ultrasound Made Easy (POCUSME) is an exciting and innovative book that aims to teach all healthcare professionals how to do simple and clinically relevant ultrasound scanning at the point of care. This book will help you solve clinical problems at the bedside across a range of specialty areas, including: trauma, emergency medicine, respiratory medicine, cardiology, general surgery, otolaryngology and vascular surgery. Straightforward and practical, and designed for clinicians who are generally unfamiliar with ultrasound scanning, it will make a positive difference to your clinical practice, and help improve the delivery of optimised patient care. So read the book, grab an ultrasound machine, and please embrace the Point of Care Ultrasound movement!
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
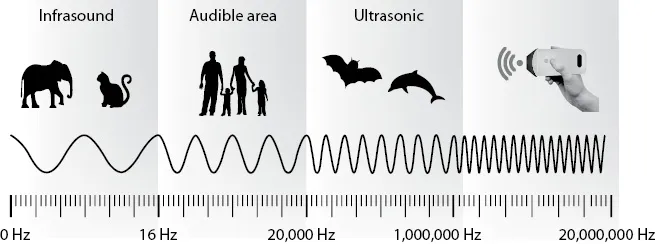
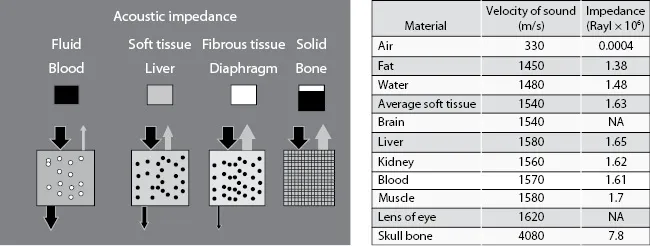
Table of contents
- Cover
- Half Title
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Dedication
- Contents
- Foreword
- Acknowledgements
- Contributors
- Part I: Background to Point-of-Care Ultrasound Made Easy (POCUSME)
- Part II: Ultrasound Assessments by Body System
- Part III: Assessment
- Index