
eBook - ePub
Manual of Neuroanesthesia
The Essentials
- 502 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
Manual of Neuroanesthesia
The Essentials
About this book
This book will provide all the basic details of neuroanaesthesia and how management of different neurosurgical cases may differ. Simple issues such as neurological examination of patient, understanding CT-scan and MRI scans along with anaesthetic management are discussed in simple language, making this book a ready-reckoner. The title provides an insight into all possible aspects of anesthetic management of neurosurgical and commonly encountered neurologic patients. The book also includes chapters related to allied specialities such as critical care, neurology and neuroradiology, making it a complete package.
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription.
No, books cannot be downloaded as external files, such as PDFs, for use outside of Perlego. However, you can download books within the Perlego app for offline reading on mobile or tablet. Learn more here.
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 1000+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn more here.
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more here.
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS or Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Yes, you can access Manual of Neuroanesthesia by Hemanshu Prabhakar, Charu Mahajan, Indu Kapoor, Hemanshu Prabhakar,Charu Mahajan,Indu Kapoor in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Medicine & Anesthesiology & Pain Management. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.
Information
Topic
MedicineSubtopic
Anesthesiology & Pain ManagementPART I
Basic principles of neuroanesthesia
1 Anatomical considerations
Gyaninder P. Singh
2 Intracranial pressure
Vasudha Singhal
3 Cerebral perfusion pressure
Nicole Collins and Alaa Abd-Elsayed
4 Brain protection
Judith Dinsmore and Rebecca Campbell
1
Anatomical considerations
GYANINDER P. SINGH
Introduction
Central nervous system
Brain
Spinal cord
Peripheral nervous system
Cranial nerves
Spinal nerves
Cerebrospinal fluid
References
Introduction
The nervous system in humans can be divided into two main parts, the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. The brain and spinal cord form the main divisions of the central nervous system (CNS). The cranial and spinal nerves along with their ganglia comprise the peripheral nervous system (Table 1.1). The organization of nervous system is shown in the flow chart.
Central nervous system
Brain
The skull houses the brain and is composed of 28 bones that are mostly paired, but those situated in the midline are unpaired. Internally, the skull cavity is divided into the anterior, middle, and posterior cranial fossa. Vessels and nerves pass in and out of the skull through various foramina (Table 1.2).
The CNS develops from a hollow cylindrical tube called the neural tube. During embryogenesis, the developing brain (i.e., anterior part of the neural tube) is seen to be divided into five continuous parts (telencephalon, diencephalon, mesencephalon, metencephalon, and myelencephalon) from anterior to posterior. As the developing brain enlarges, some regions overgrow the other areas. Thus, some areas get submerged (hidden from the surface) as the brain grows and folds over itself.1 The cavity of the neural tube is retained as ventricles in the brain and central canal in the spinal cord, which forms a continuous channel filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) (Figure 1.1).
Gross anatomy of the brain
The brain is enclosed in a bony cranial cavity and is surrounded by three layers of meninges: the outer dura mater, the middle arachnoid mater, and the innermost pia mater. The brain is divided into the forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain2 (Figure 1.2).
Forebrain
This is divided into the diencephalon (central part) and the telencephalon or cerebrum. Hidden from the surface of the brain, the diencephalon consists of a dorsal thalamus and a ventral hypothalamus, and the subthalamus and epithalamus as its other divisions. The thalamus is an important station for all sensory systems except the olfactory pathway. The subthalamus consists of the cranial part of red nucleus and the substantia nigra. The epithalamus consists of the habenular nuclei and the pineal gland. The habenular nucleus is the center for integration of the olfactory, visceral, and somatic afferent pathways. The pineal gland does not contain nerve cells but adrenergic sympathetic fibers derived from the superior cervical sympathetic ganglia. The hypothalamus controls and integrates the functions of the autonomic nervous system and the endocrine system and plays a vital role in maintaining body homeostasis.2
Organization of nervous system
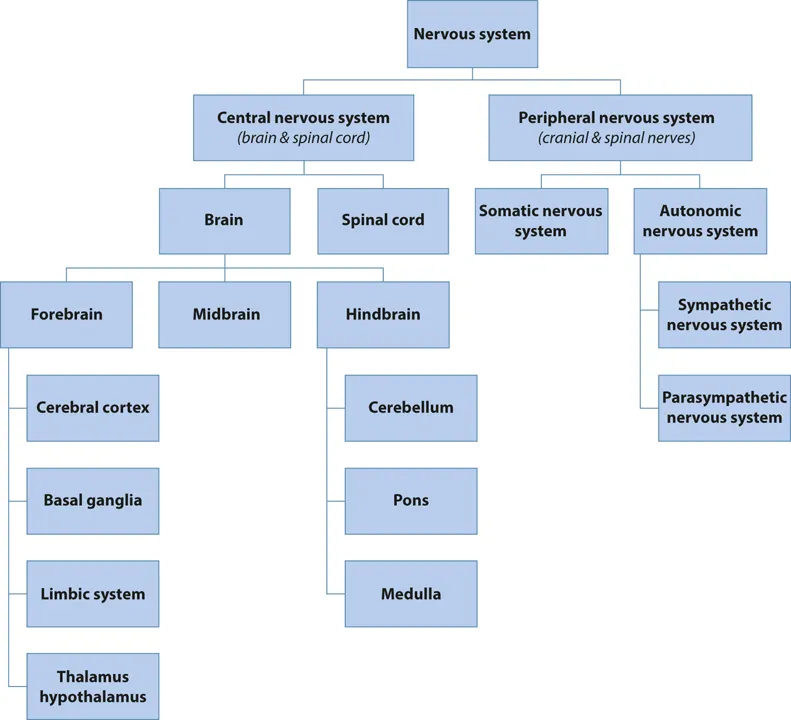
Table 1.1 Division of Nervous System and Cavities of the Brain and Spinal Cord
| Central nervous system | |
|---|---|
| a. Brain | Cavities |
| Forebrain (or prosencephalon) | |
| Telencephalon | Right and left lateral ventricles |
| Cerebral cortex, basal ganglia, limbic system | |
| Diencephalon | Third ventricle |
| Thalamus, hypothalamus | |
| Midbrain (or mesencephalon) | Cerebral aqueduct |
| Hindbrain (or rhombencephalon) | Fourth ventricle |
| Metencephalon | |
| Pons | |
| Cerebellum | |
| Myelencephalon | |
| Medulla oblongata | |
| b. Spinal cord | Central canal |
| Cervical segments | |
| Thoracic segments | |
| Lumbar segments | |
| Coccygeal segments | |
| Peripheral nervous system | |
| a. Cranial nerves and their ganglia (12 pairs) | |
| 12 cranial (I–XII) nerves | |
| b. Spinal nerves and their ganglia (31 pairs) | |
| 08 cervical | |
| 12 thoracic | |
| 05 lumbar | |
| 05 sacral | |
| 01 coccygeal |
Table 1.2 Foramina of Skull and Structure Passing through them
| Cranial fossae (bones forming) | Foramina | Structures passing |
|---|---|---|
| Anterior cranial fossa (frontal, ethmoid, sphenoid: body and lesser wing) Middle cranial fossa (parietal, temporal, sphenoid: body and greater wing) | Cribriform plate of ethmoid Foramen cecum Anterior ethmoidal canal Posterior ethmoidal canal Optic canal Superior orbital fissure | Olfactory nerve filaments Anterior ethmoidal nerves and vessels Emissary vein Anterior ethmoidal nerve and vessels Posterior ethmoidal nerves and vessels Optic nerve surrounded by meninges Ophthalmic artery nerves: oculomotor, trochlear, abducent, lacrimal, frontal, nasociliary nerve, filaments from internal carotid artery, sympathetic plexus Vessels: orbital branch of middle meningeal artery, recurrent branch of ophthalmic artery, superior ophthalmic vein, inferior ophthalmic vein |
| Foramen rotundum | Maxillary nerve | |
| Foramen ovale | Mandi... |
Table of contents
- Cover
- Half Title
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Dedication
- Table of Contents
- Foreword
- Preface
- Editors
- Contributors
- Part I: Basic Principles Of Neuroanesthesia
- Part II: Examining the Neurosurgical Patient
- Part III: Monitoring the Neurosurgical Patient
- Part IV: Anaesthesia for the Neurosurgical Patient
- Part V: Positioning the Neurosurgical Patient
- Part VI: Fluid Management of the Neurosurgical Patient
- Part VII: Case-Specific Management
- Part VIII: Perioperative Complications In Neurosurgical Patients
- Part IX: Basics of Neuroradiology
- Part X: Basics of Neurointensive Care
- Part XI: Special Considerations
- Appendix: Scales and scores
- Index