
- 351 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
About this book
The idea of complex numbers dates back at least 300 years—to Gauss and Euler, among others. Today complex analysis is a central part of modern analytical thinking. It is used in engineering, physics, mathematics, astrophysics, and many other fields. It provides powerful tools for doing mathematical analysis, and often yields pleasing and unanticipated answers.
This book makes the subject of complex analysis accessible to a broad audience. The complex numbers are a somewhat mysterious number system that seems to come out of the blue. It is important for students to see that this is really a very concrete set of objects that has very concrete and meaningful applications.
Features:
- This new edition is a substantial rewrite, focusing on the accessibility, applied, and visual aspect of complex analysis
- This book has an exceptionally large number of examples and a large number of figures.
- The topic is presented as a natural outgrowth of the calculus. It is not a new language, or a new way of thinking.
- Incisive applications appear throughout the book.
- Partial differential equations are used as a unifying theme.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
Chapter 1
Basic Ideas
1.1 Complex Arithmetic
1.1.1 The Real Numbers
1.1.2 The Complex Numbers
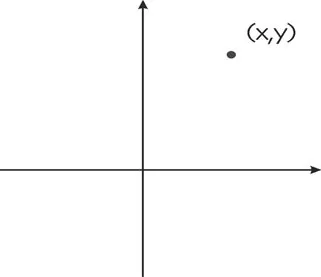
(1.1) |
(1.2) |
Table of contents
- Cover
- Half Title
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Dedication
- Table of Contents
- Preface to the Second Edition for the Instructor
- Preface to the Second Edition for the Student
- Preface to the First Edition.
- 1 Basic Ideas
- 2 The Exponential and Applications
- 3 Holomorphic and Harmonic Functions
- 4 The Cauchy Theory
- 5 Applications of the Cauchy Theory
- 6 Isolated Singularities
- 7 Meromorphic Functions
- 8 The Calculus of Residues
- 9 The Argument Principle
- 10 The Maximum Principle
- 11 The Geometric Theory
- 12 Applications of Conformal Mapping
- 13 Harmonic Functions
- 14 The Fourier Theory
- 15 Other Transforms
- 16 Boundary Value Problems
- Appendices
- List of Notation
- Table of Laplace Transforms
- A Guide to the Literature
- References
- Index
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app