
- 230 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Application Service Providers in Business
About this book
Learn how to use Application Service Providers to enhance the future of your business!
Application Service Providers in Business is a comprehensive analysis of the present ASP model and its place in business today. Business success in today's information-intensive marketplace depends on a company's ability to acquire and fully use the latest advancements in business-critical applications. By having these applications delivered as services over the Internet, businesses can lessen the demands on company IT staff, and increase the ability to get complex software into use immediately. Within this context, a new outsourcing business model called ASP (Application Service Provider) has emerged that is transforming how businesses access and leverage software applications. The book explains the specific contingent ASP models, including business, enterprise, functional-focused, and vertical market ASPs, and ASP aggregators. It demonstrates how different ASP models have fulfilled diverse market/customer expectations and explores future scenarios for current ASP business models. Case studies, tables, and figures illustrate important concepts and make complex information easy to access and understand.
Based on a thorough analysis of the ASP market environment, the book provides detailed Best Practices Guidelines that managers of ASPs can use to improve the chances of success of their respective ASPs. It outlines contingency factors such as application offerings, customer selection, operations, and strategic fit. The book also not only assists business managers in deciding on whether to use an ASP, but it presents ways to use ASPs to effectively support their business process. The ability to provide the workforce with access to data whenever and wherever is crucial for positively impacting a company's profitability, and ASPs provide the software to make it possible.
Topics included in Application Service Providers in Business are:
- Best Practices Guidelines
- strategic management
- management decision making and planning
- IT management and outsourcing
- future of the ASP market
- ASP business models
- and much more!
Application Service Providers in Business is a comprehensive resource for executives, managers, professors, and business students in the US and worldwide. Using the information and guidelines provided, executives and managers can learn how to use ASPs to enhance their business, and managers of ASPs can learn how to increase their chance of success in the competitive ASP market. The material is also appropriate as a textbook for management and computer information/software development classes.
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
Chapter 1
Application Service Providers: An Overview
Introduction
ASP Defined
ASP Models’ Main Features
- Application centric: ASPs provide access to, and management of, an application that is commercially available or especially developed for the ASP.
- Renting application access: ASP services offer customers access to a new application environment without making investments in licenses, servers, people, and other resources. The ASP either owns the software or has a contractual agreement with the software vendor to license access to the software.
- Centrally managed: ASP services are managed from a central location rather than at each customer’s site. Customers access applications remotely, such as over the Internet or via leased lines.
- One-to-many offerings: The ASP often partners with other vendors to package standardized offerings that many companies will subscribe to over a specific contract period.
- Delivering on the contract: The ASP is responsible, in the customer’s eyes, for delivering on the customer contract, ensuring that the service is provided as promised.
- owning and operating software applications;
- owning, operating, and maintaining the servers that run the applications;
- employing the workforce needed to maintain the applications;
- making applications available to customers everywhere via the Web (Internet) or other dedicated networks; and
- billing the service on a per-user basis.
- 1969: The U.S. Department of Defense commissions ARPANET, the first variant of the Internet, developed by the Advanced Research Project Agency (ARPA).
- 1979: ARPA establishes the Internet Configuration Control Board, a further significant step toward the Internet.
- 1982: The TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol) model for connectivity in telecommunications networks, developed by the U.S. Department of Defense in 1972, is established as the protocol suite for ARPANET, leading to one of the first definitions of “Internet.”
- 1984: DNS (Domain Name System, a hierarchical system of servers maintaining databases enabling the conversion of domain names [the unique name of a node on the Internet] to their IP addresses) is introduced. By the end of the year, there are over 1,000 hosts.
- 1986: The Internet Engineering Task Force and the Internet Research Task Force are established.
- 1987: By the end of the year, there are over 10,000 Internet hosts.
- 1989: With seventeen countries online in the National Science Foundation Network (NSFNET), the number of Internet hosts breaks 100,000.
- 1991: The World Wide Web (WWW) is released, and the National Science Foundation (NSF) lifts restrictions on commercial access to the Internet.
- 1995: Mobile code, such as Java (a programming language developed by Sun Microsystems, designed to run on any computer or computing device regardless of the specific microprocessor or operating system it uses) is developed, adding online interactivity to e-commerce.
- 2000: ASP technology comes of age. Microsoft unveils its .Net Strategy (a new way to deliver applications), expected to turn many of its applications into ASP services by utilizing XML (eXtensible Markup Language) protocol-based Web communication code, which makes information in documents usable in computer programs.
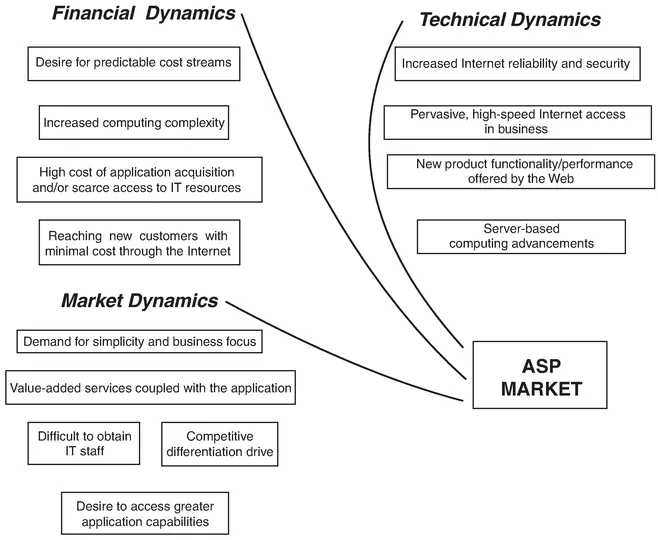
ASP Drivers
Financial Dynamics
- Desire for predictable cost streams at business level
- Increased computing complexity
- Escalating IT infrastructure and application costs; rapidly evolving business environments; rapidly changing technology
- Ability to reach new customers with minimal cost through the Internet
Technical Dynamics
- Increased reliability and security of the Internet (on which software, IT services, and telecommunications industries have converged)
- Pervasive, high-speed access from virtually every computer anywhere in the world, which allows users to link into a massive network, backed up by growing standards
- A user interface—the Web browser—widely embraced by end users everywhere thanks to new, higher-level functionality/performance
- Server-based computing advancements
Market Dynamics
- Demand for simplicity and business focus driven by the e-business transformation
- Desire to access greater application capabilities and value-added services around the application
- Difficulty in hiring IT staffs
- Competitive differentiation drives
- Recognition of value-added services tied to outsourced software applications
- Focus: Executives know that anything that distracts the company from its core expertise should ideally be moved outside the organization. Such operational freedom is probably the most fundamental justification underlying the adoption of the ASP model in any industry or company. ASP contracts put the...
Table of contents
- Cover
- Title
- Copyright
- Contents
- Preface
- Acknowledgments
- Chapter 1. Application Service Providers: An Overview
- Chapter 2. The ASP Marketplace: Structure and Overall Dynamics
- Chapter 3. ASP Performance Experiences: A Contingency Approach
- Chapter 4. Emerging Best Practices
- Chapter 5. The Future of ASPs
- References
- Index