
- 414 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
Materials and Structures
About this book
The second edition of this highly informative book retains much original material covering the principles of structural mechanics and the strength of materials, together with the underlying concepts requisite to the theory of structure and structural design. Some of the material involving lengthy hand-drawing or hand-calculation has been replaced with more up-to-date relevant material and frequent reference is made to computer-aided learning techniques.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information



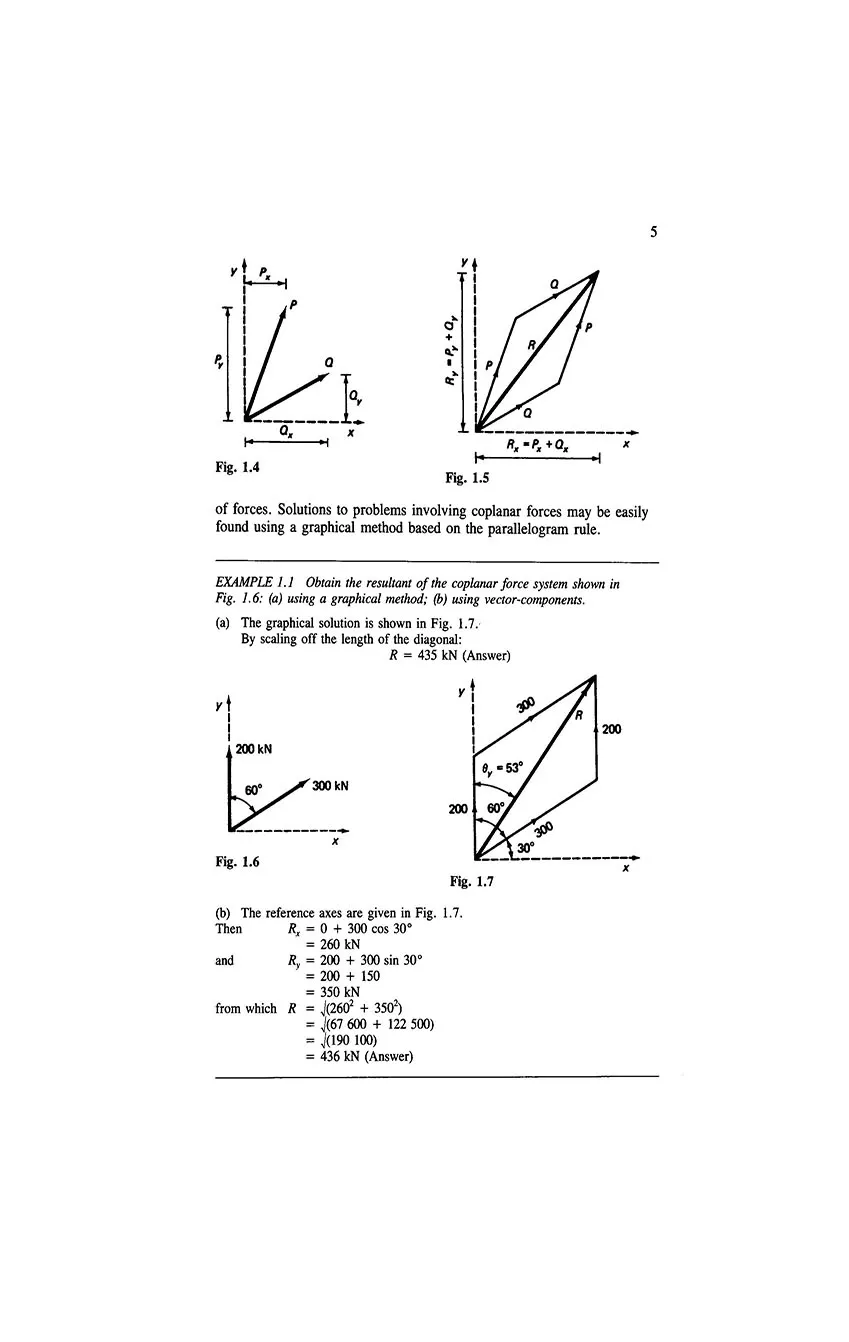
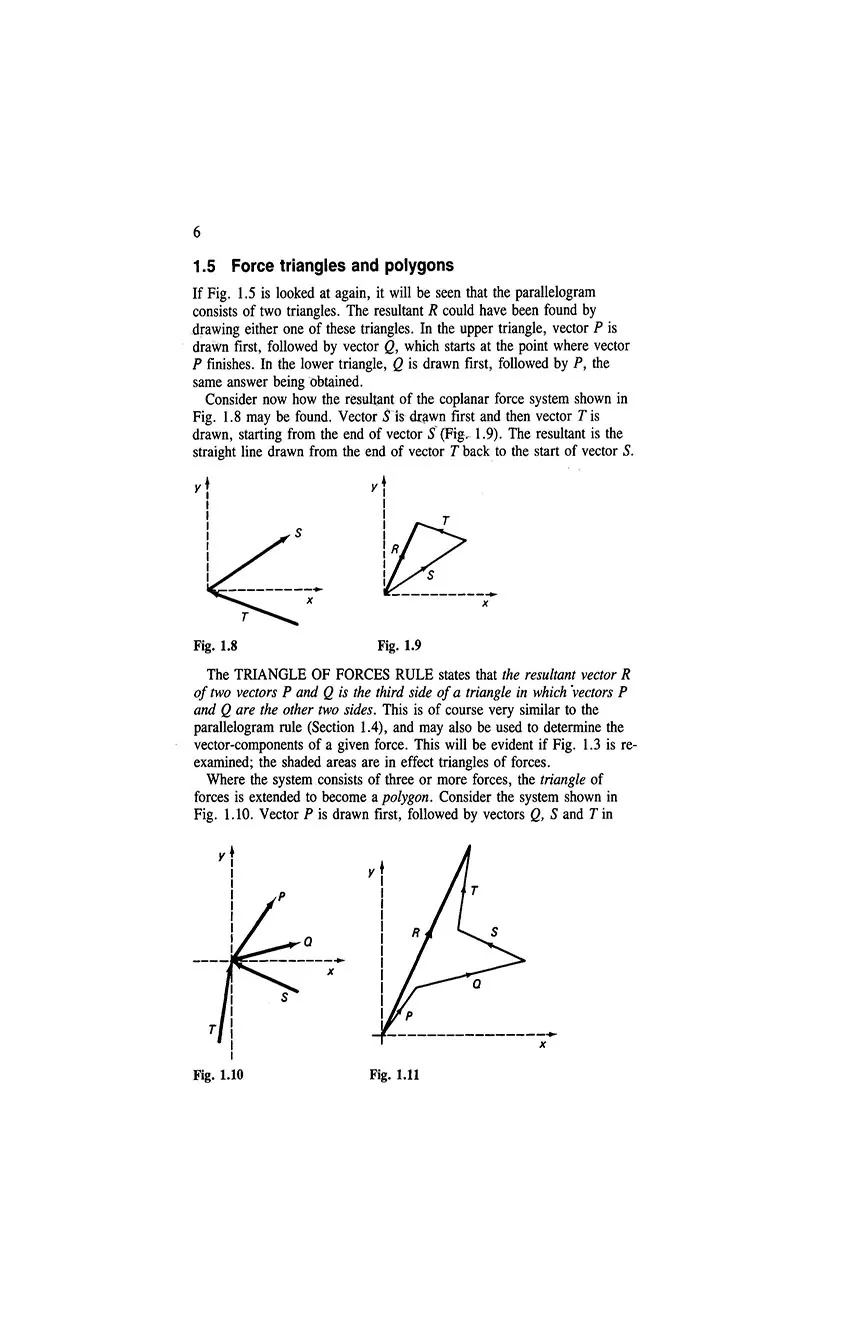


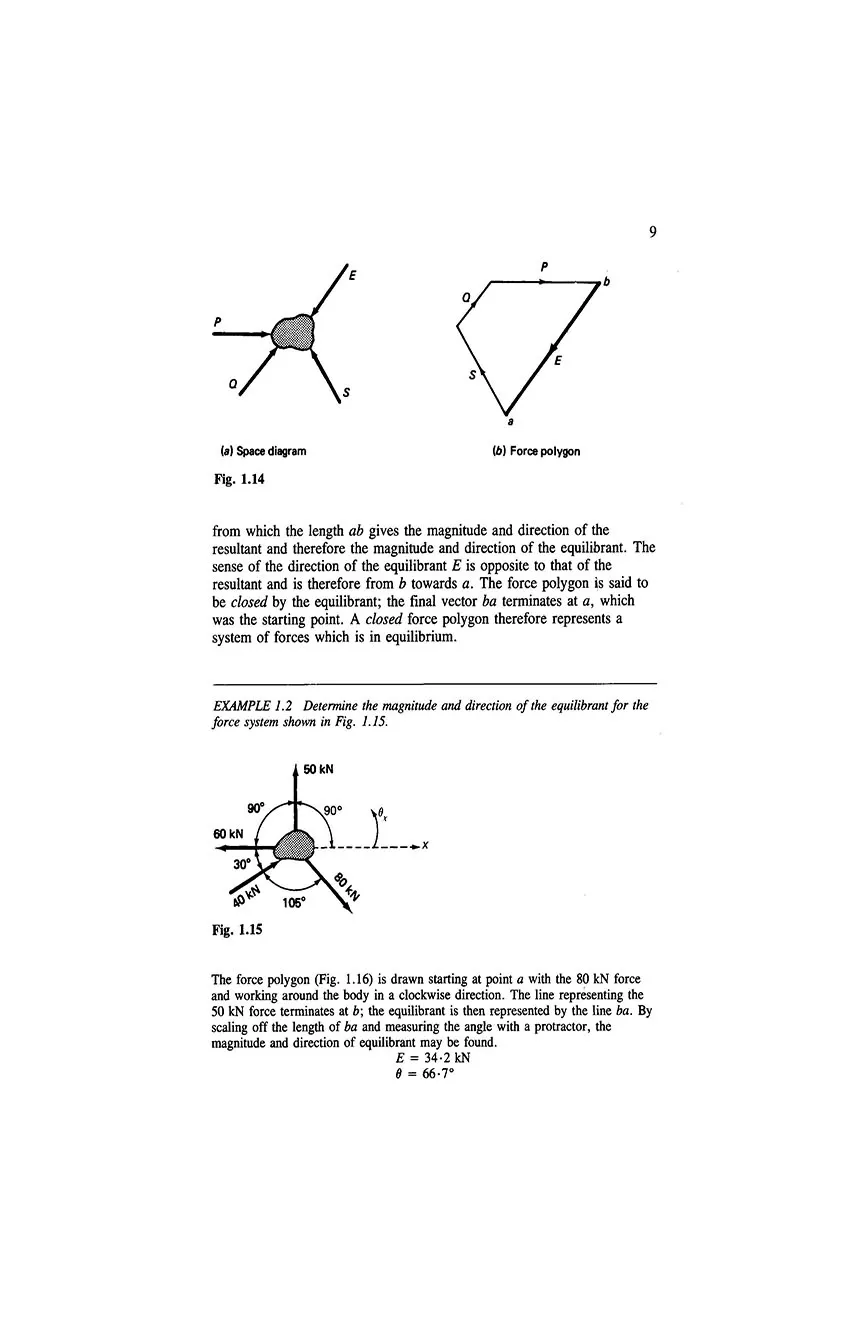
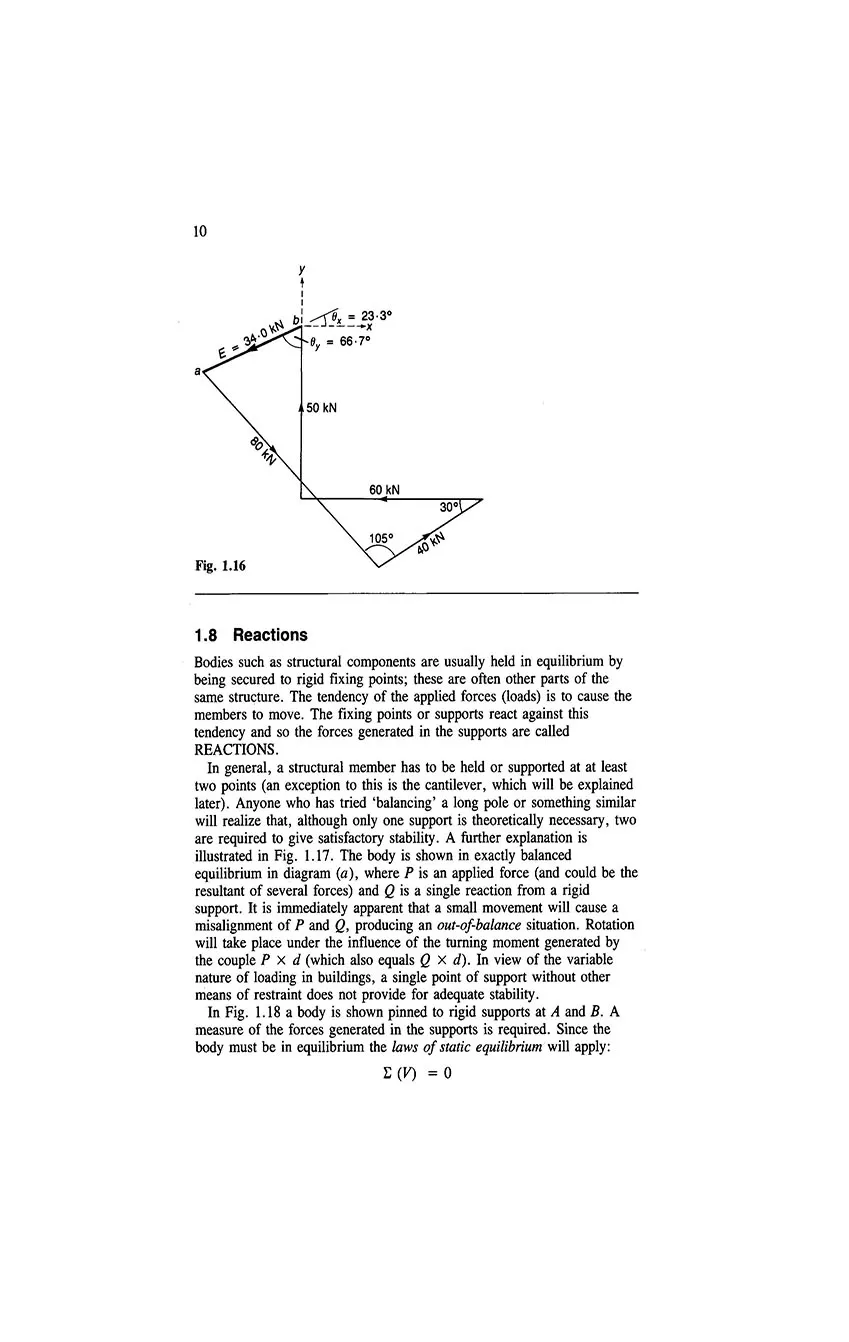
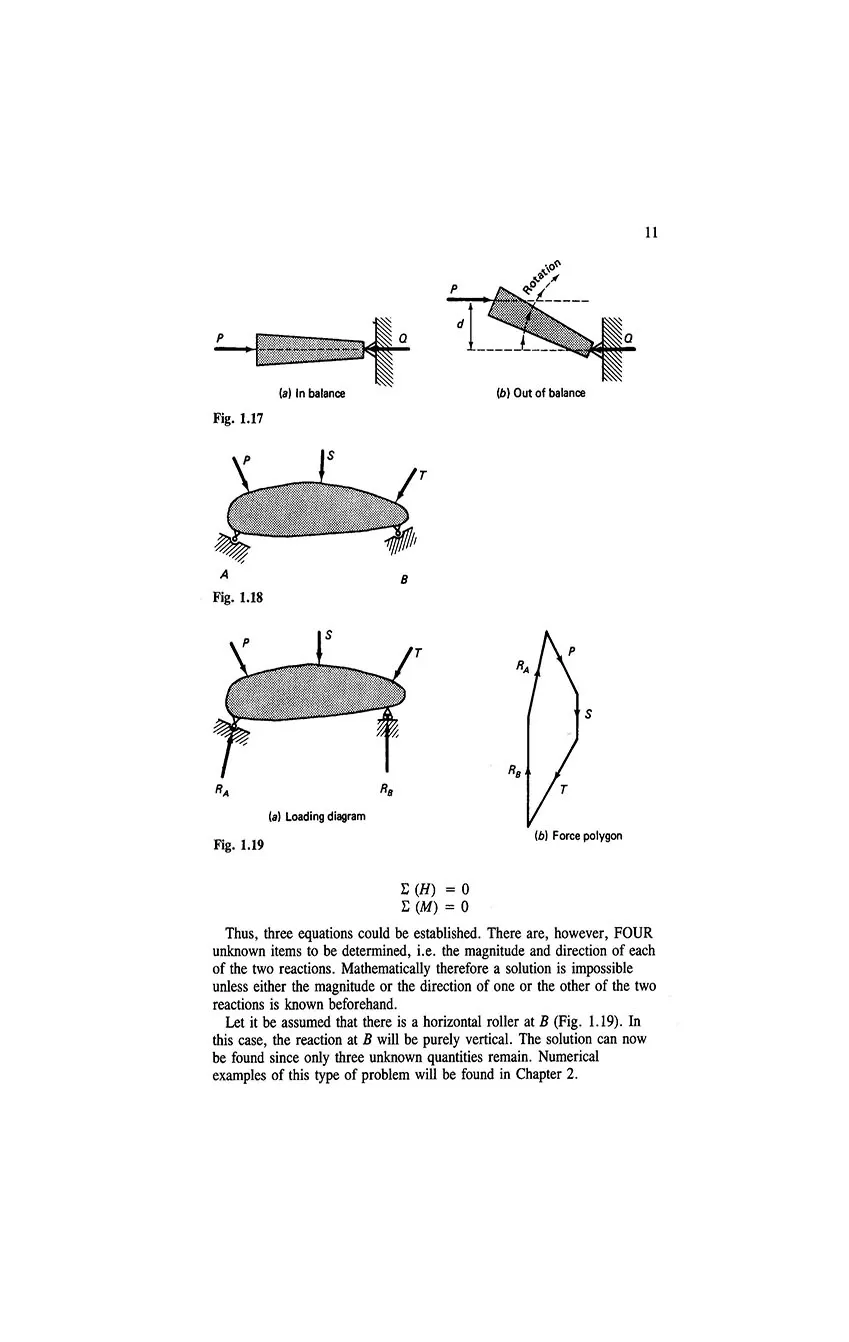
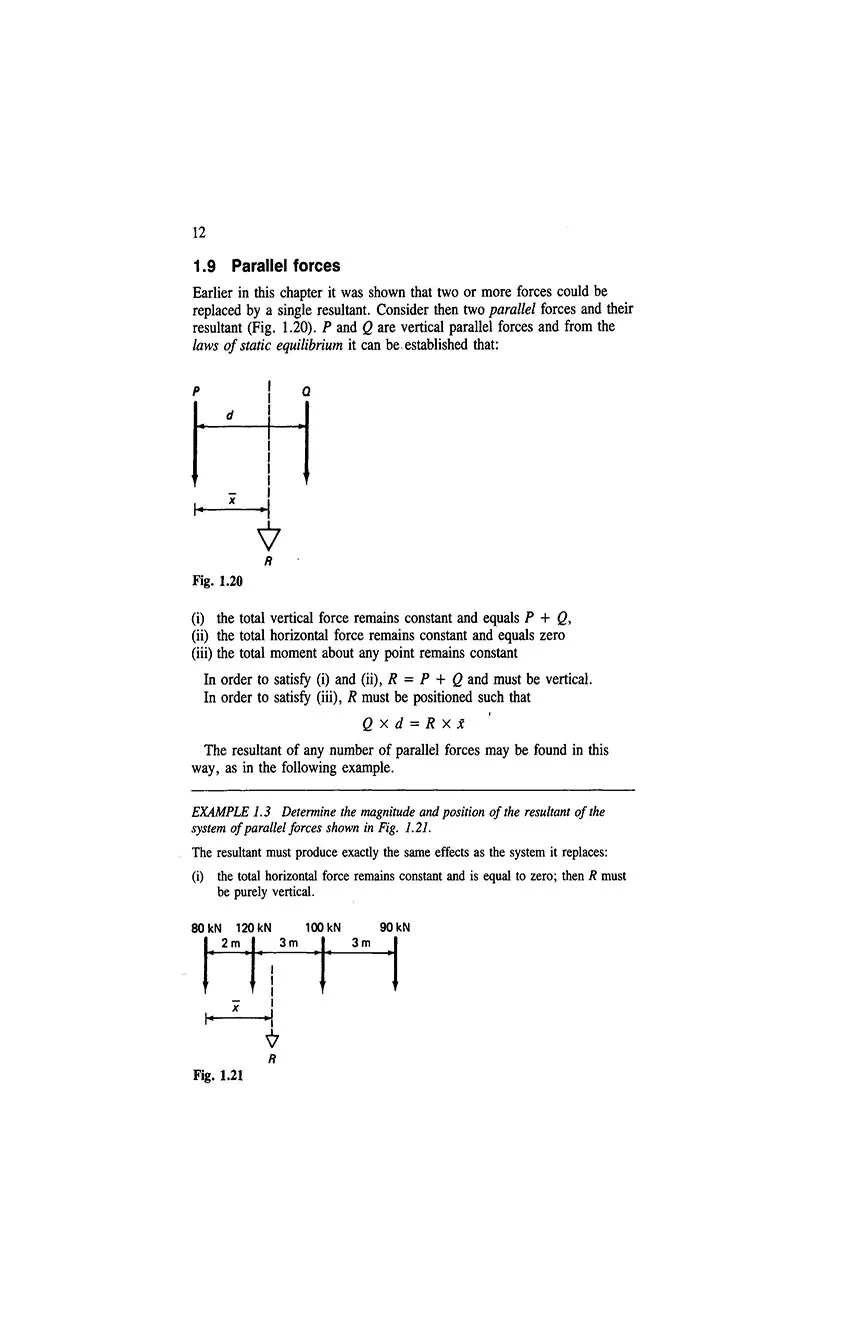
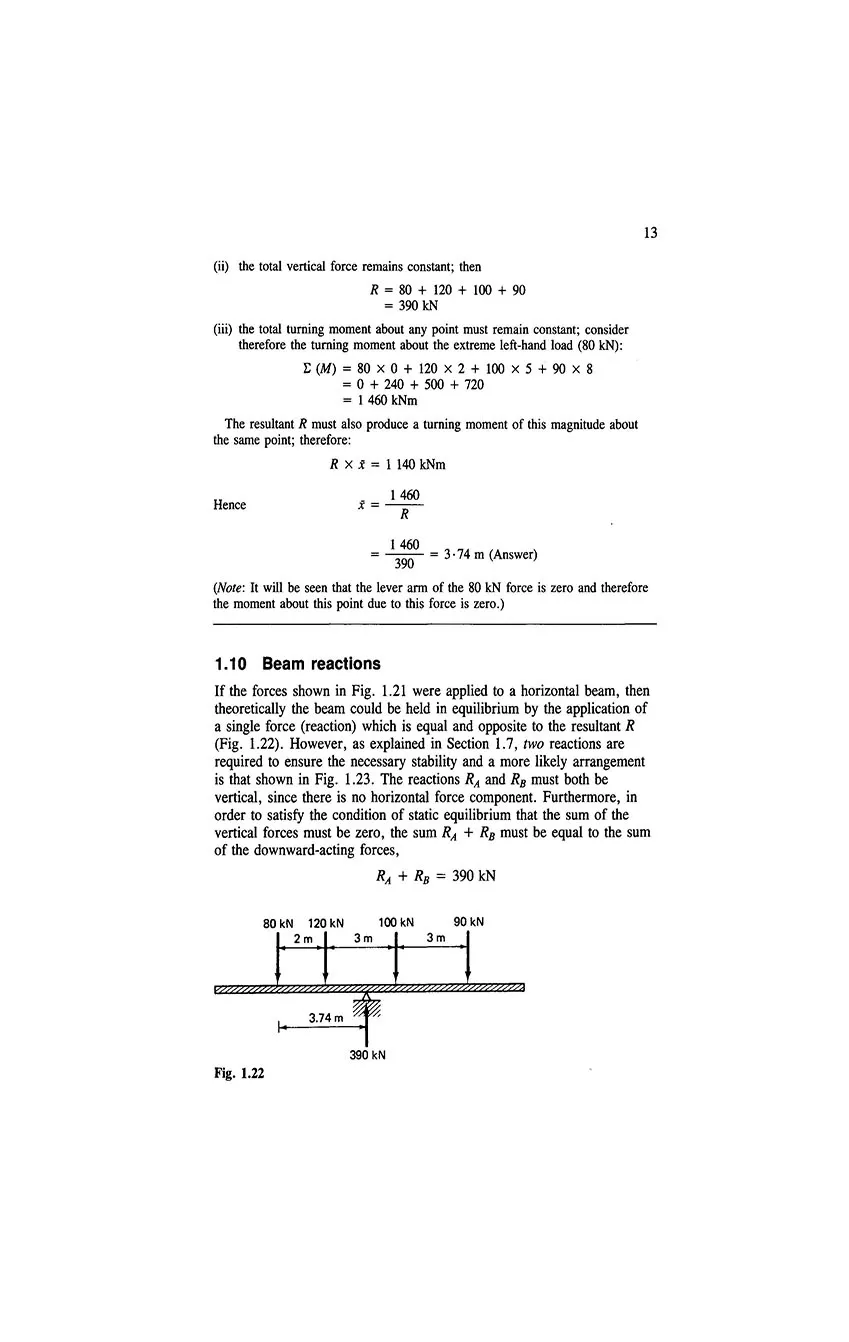
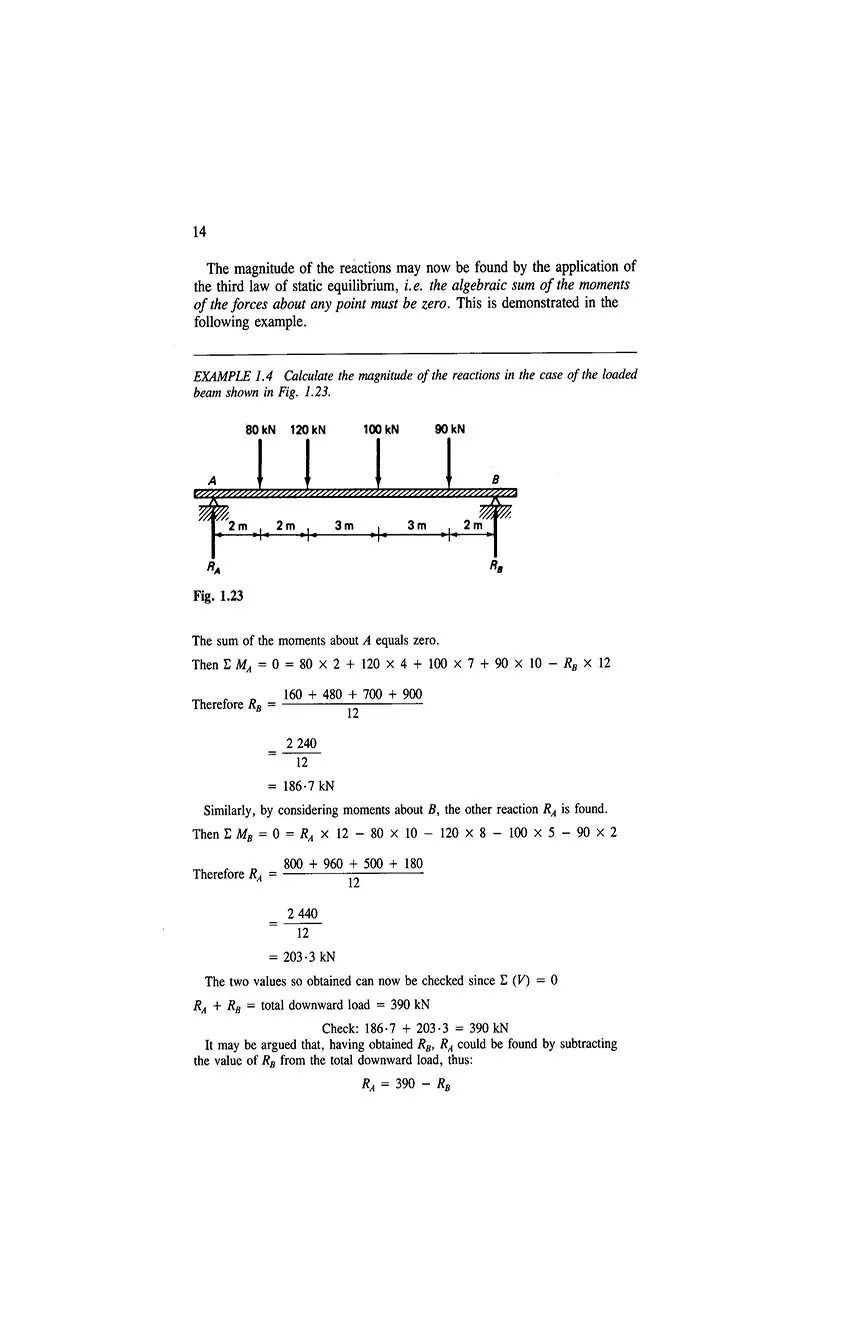

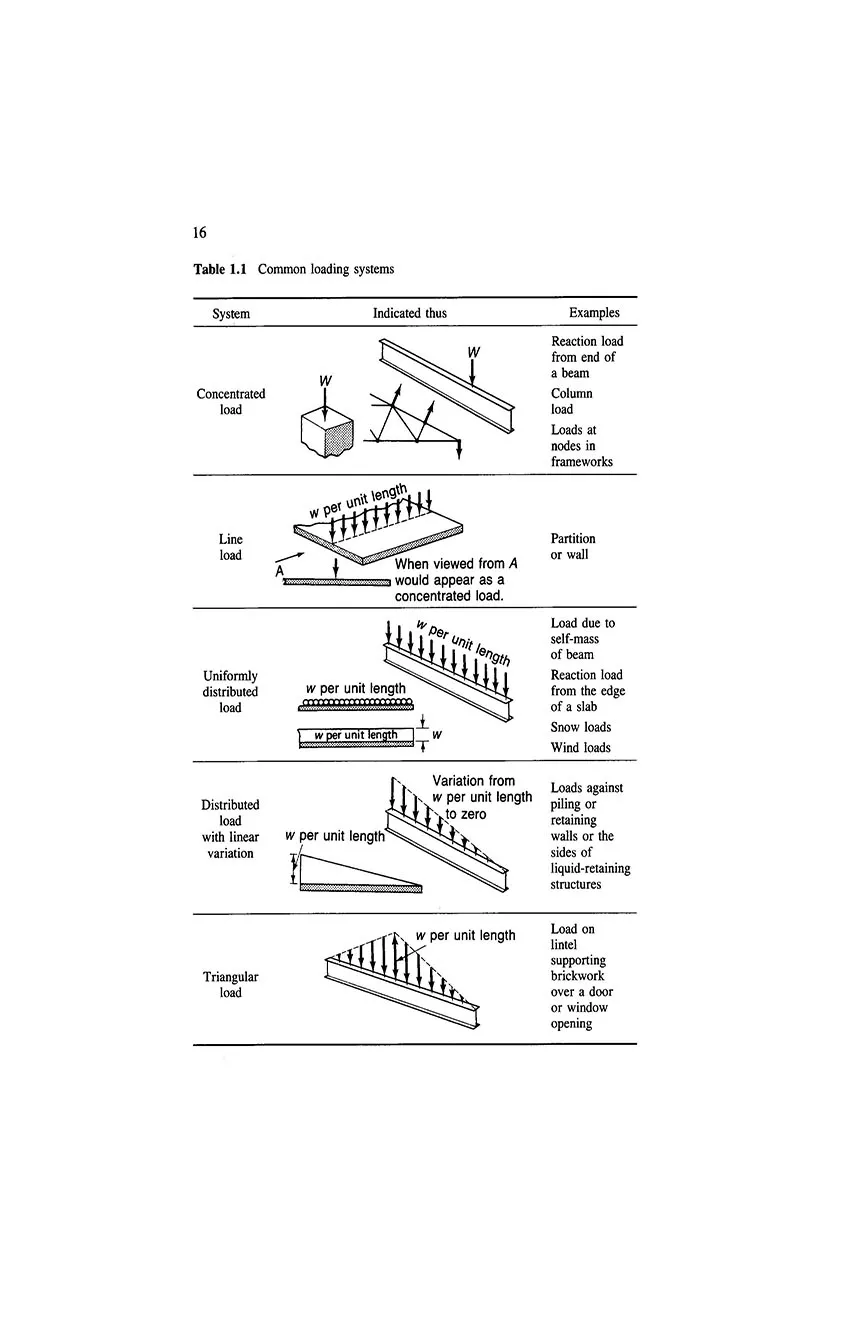
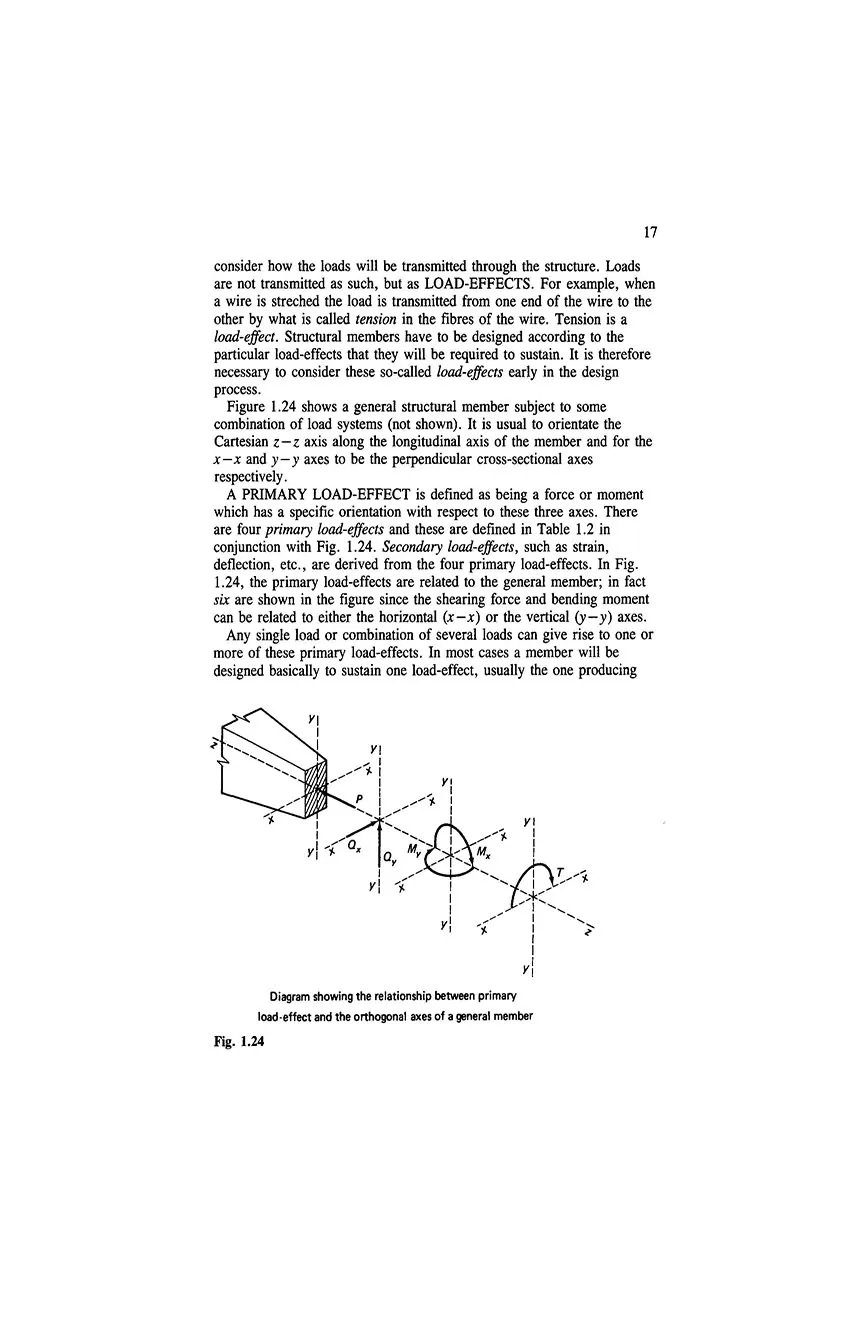

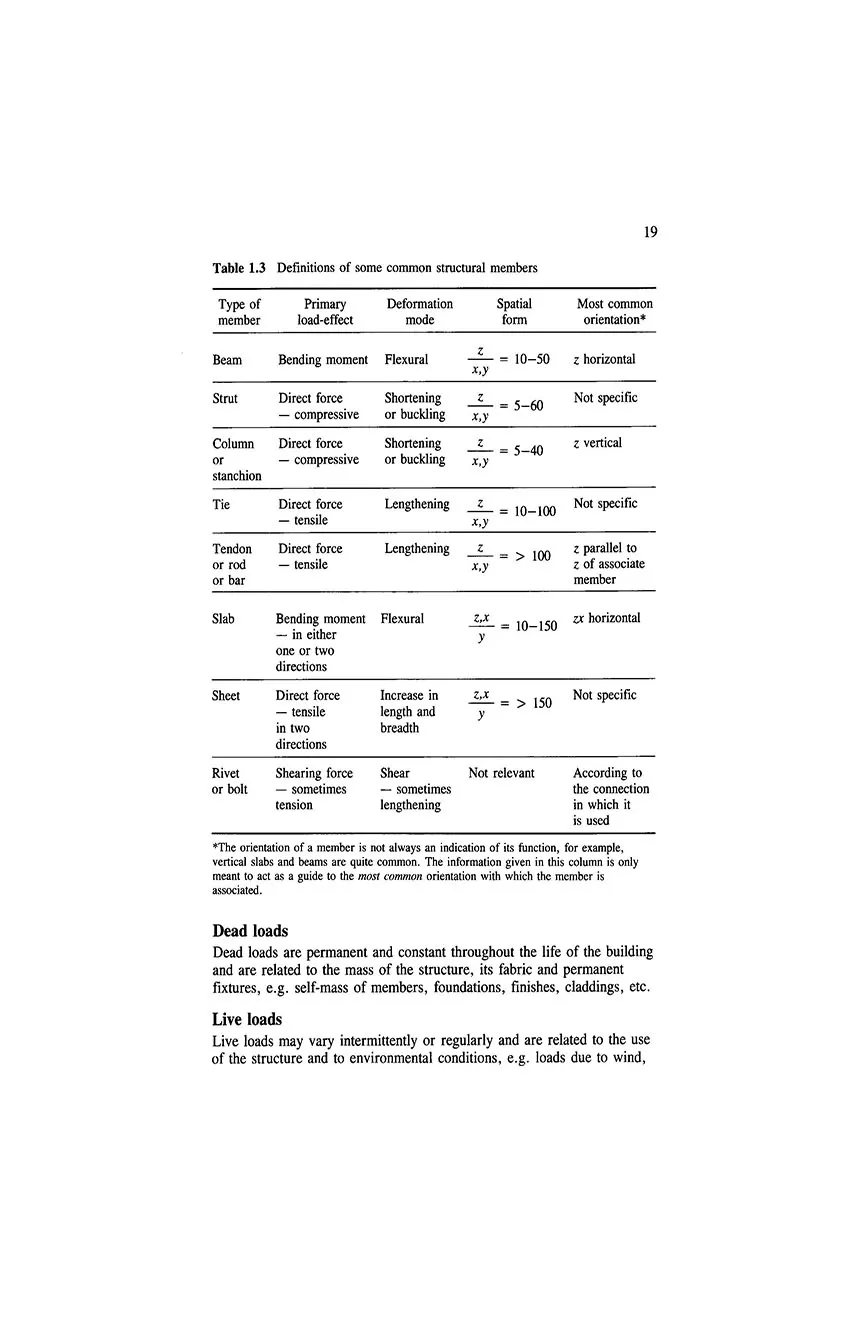

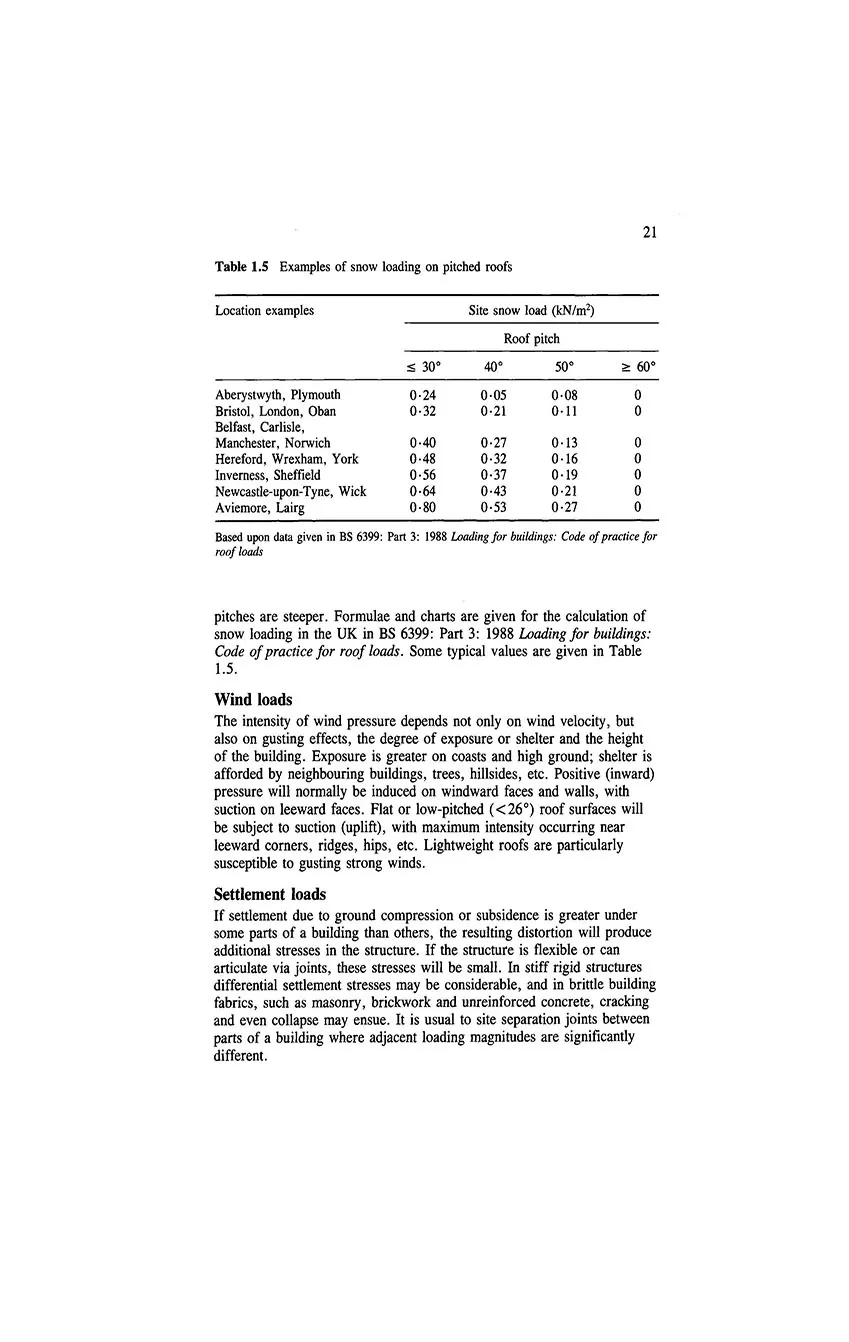


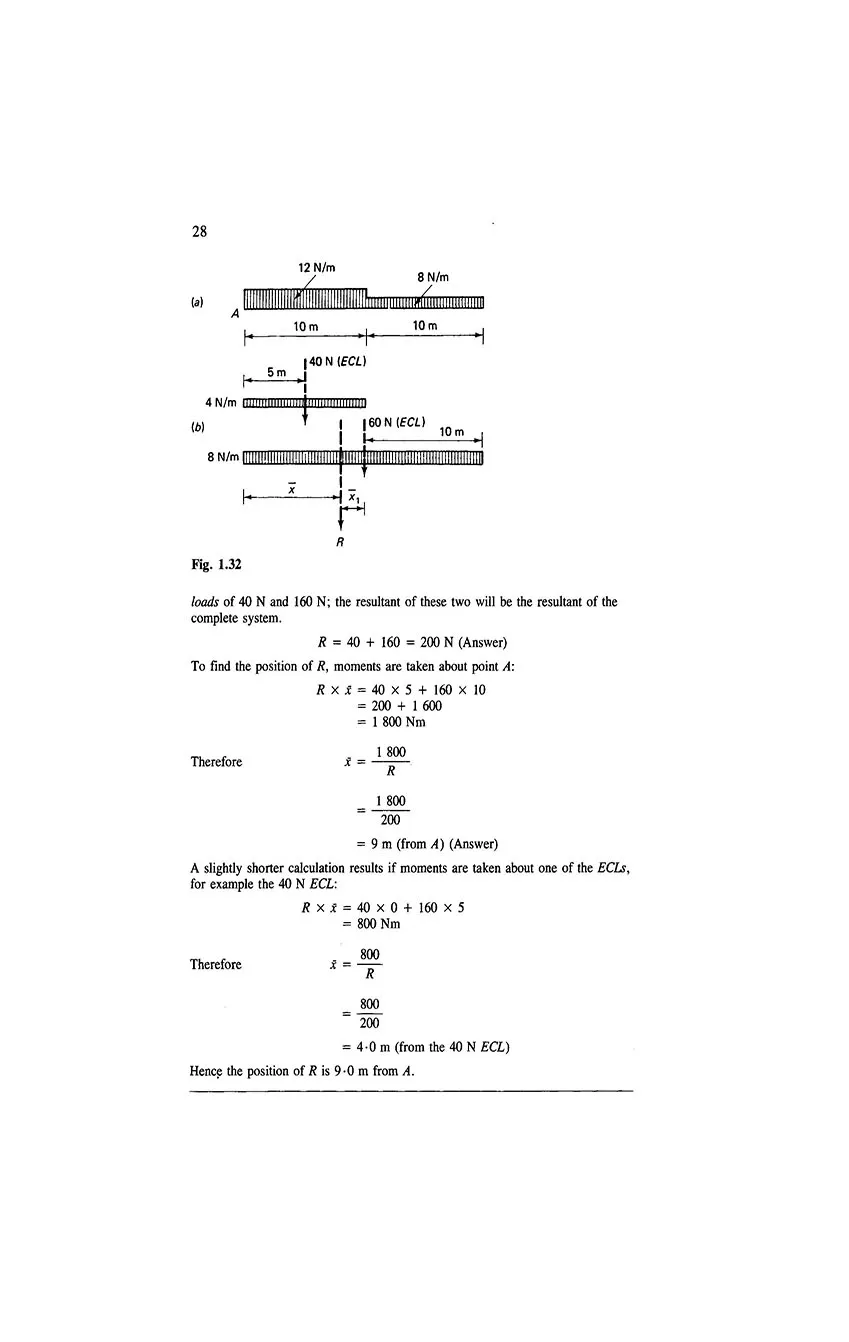
Table of contents
- Cover
- Half Title
- Title
- Copyright
- Contents
- Preface
- Preface to the second edition
- 1 Forces and reactions
- 1.1 Mass, force and gravity
- 1.2 Force is a vector
- 1.3 Vector components
- 1.4 Coplanar forces and resultants
- 1.5 Force triangles and polygons
- 1.6 Moments of forces
- 1.7 Equilibrium and equilibrants
- 1.8 Reactions
- 1.9 Parallel forces
- 1.10 Beam reactions
- 1.11 Loading systems
- 1.12 Effects of loading
- 1.13 Load types and sources
- 1.14 Using computers to aid learning
- 2 Forces in structural frameworks
- 2.2 Pin-jointed plane frameworks
- 2.3 Statically determinate plane frameworks rule
- 2.4 Methods of analysis
- 2.5 Force diagrams for special cases
- 2.6 Wind loading
- 2.7 Forces in simple space frames
- 2.8 Solutions using computers
- 3 Direct stress and strain
- 3.1 Definition of stress
- 3.4 Direct axial stress
- 3.5 Definition of strain
- 3.6 Units of strain
- 3.7 Elasticity
- 3.9 Behaviour of mild steel in tension
- 3.10 Limiting values of stress. Factor of safety and load factors
- 3.11 Calculations involving direct stress and strain
- 3.12 Compound bars
- 3.13 Temperature stress
- 3.14 Strain energy
- 3.15 Suddenly applied loads
- 3.16 Falling loads
- 3.17 Creep under sustained loading
- 3.19 Solutions using computers
- 4 Properties of structural sections
- 4.1 Introduction
- 4.2 Area
- 4.3 Centre of area. Centroid
- 4.4 Graphical determination of centroids
- 4.5 Second moment of area
- 4.6 Second moment of area about a centroidal axis
- 4.7 The parallel axis principle
- 4.8 Compound sections
- 4.9 Radius of gyration
- 4.10 Polar second moment of area
- 4.11 Elastic section modulus
- 4.12 Principal axes and principal second moments of area
- 5 Shearing force and bending moment
- 5.2 The nature of shearing force and bending moment
- 5.3 Definitions for calculation purposes
- 5.4 Sign convention and units
- 5.6 Standard cases
- 5.7 Construction of parabolas
- 5.8 Properties of curves and diagrams
- 5.9 The mathematical relationship between load, shearing force and bending moment
- 5.10 Solutions using computers
- 6 Stresses in beams
- 6.1 Stresses induced by bending
- 6.2 Pure bending
- 6.4 Section modulus
- 6.5 Stresses due to simultaneous or asymmetric moments
- 6.6 Bending due to oblique loading and moments
- 6.7 Beams of two materials — composite beams
- 6.8 Reinforced concrete beams — elastic theory
- 6.9 Plastic bending theory
- 6.10 Reinforced concrete beams — plastic theory
- 6.11 Shearing stresses in beams
- 6.12 A general expression for the distribution of shearing stress
- 6.13 Distribution of shearing stress in a rectangular section
- 6.14 Distribution of shearing stress in I-sections
- 7 Deflection of beams
- 7.1 Binding and stiffness
- 7.3 Mathematical relationship between bending moment, slope and deflection
- 7.4 Sign convention and units
- 7.5 Mohr’s area moment theorems
- 7.6 Deflection formulae — standard cases
- 7.7 Macaulay’s method and superposition
- 8 Further work on stress and strain. Combined stresses
- 8.1 Introduction
- 8.3 Lateral strain. Poisson’s ratio
- 8.4 Biaxial stresses and strains
- 8.5 Triaxial stress and volumetric strain
- 8.6 Oblique stresses and resultants
- 8.7 Normal and tangential stresses on an oblique plane
- 8.8 Oblique planes and biaxial normal stresses
- 8.9 Oblique planes and a general two-dimensional stress system
- 8.10 Principal planes and principal stresses
- 8.11 Mohr’s stress circle
- 8.12 Triaxial stress systems
- 8.13 Failure of brittle materials in compression
- 8.14 Cracking in concrete beams and the principle of shear reinforcement
- 9 Torsion in circular shafts
- 9.2 Solid circular shafts
- 9.3 Hollow circular shafts
- 9.4 Torsional stiffness
- 9.5 Work done and power transmitted
- 10 Combined direct and bending stress
- 10.1 Bending in struts and ties
- 10.3 Position of neutral axis for combined direct and bending stress
- 10.4 Eccentrically applied longitudinal load
- 10.5 Load applied eccentrically to both axes
- 10.6 The middle-third rule for rectangular sections
- 10.7 The middle-quarter rule for circular sections
- 10.8 Buckling of slender columns and struts
- 10.9 Practical buckling criteria
- 10.10 Effective length of struts
- 10.11 Proof of the Euler formula
- 10.12 Other buckling formulae
- 11 Retaining walls and other gravity-dependent structures
- 11.1 Gravity-dependent structures
- 11.2 Failure criteria
- 11.3 Lateral pressure and thrust
- 11.4 Wind pressure
- 11.5 Liquid pressure
- 11.6 Pressure due to retained soil and other granular materials
- 11.7 Rankine’s theory of lateral earth pressure
- 11.8 Stepped wall faces
- 11.9 Inclined wall faces
- 11.11 Coulomb’s wedge theory
- 11.12 Stability calculations
- 11.13 Determination of the position of the ground reaction
- 11.14 Ground bearing pressures
- 11.15 The middle-third rule
- 11.16 Sliding
- Answers to exercises
- Index
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription
No, books cannot be downloaded as external files, such as PDFs, for use outside of Perlego. However, you can download books within the Perlego app for offline reading on mobile or tablet. Learn how to download books offline
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 990+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn about our mission
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more about Read Aloud
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS and Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Yes, you can access Materials and Structures by R. Whitlow in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Technology & Engineering & Civil Engineering. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.