
Wind Energy Pocket Reference
- 96 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Wind Energy Pocket Reference
About this book
Prepared and peer-reviewed by some of the foremost experts in the field, this easy-to-use pocket reference offers a wealth of information relating to wind energy and wind energy technologies.
Topics covered range from wind resources to wind turbines, covering offshore and onshore power, both stand-alone and grid-connected. The book also includes vital information on international economic support schemes and incentives and environmental issues and is peppered throughout with helpful illustrations, equations and explanations. Renewable energy professionals, students and wind energy entrepreneurs amongst others will find a host of answers in this essential book – a practical assimilation of data, fundamentals and guidelines for application.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
I. INTRODUCTION
| Year | 1235–1900 | Application | Comments | Regulation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1235–1900 | Wind roses, Dutch windmills | Mechanical energy in agriculture | Grinding mills, water pumping etc | |
| 1890–1910 | Horizontal axis turbines with 3–4 blades | Electricity production | Pioneered by Danish Poul la Cour at Askov Folk High School (Ref. I.1.) | Yawing control |
| 1910–1950 | Horizontal axis turbines with 3–4 blades | Electricity production | Pioneered by Danish Poul la Cour at Askov Folk High School (Ref. I.1.) | Yawing control |
| 1910–1950 | Horizontal axis, 3 blades. Turbine sizes of up to 5 MW | Electricity production in local power plants | Further developments in Denmark. UK, USA and USSR. Eventually outcompeted by cheap Oil | Spoiler rail for control |
| 1950–1967 | Horizontal axis, 3 blades. 200 kW stall controlled Danish Gedser Wind Turbine | Electricity production, utility demonstration prefect | The Gedser Mill (inventor Jons Juul) became the mother of modem Danish wind turbines | Stall control |
| 1974 | Start of modem phase of wind power pioneered by Danish manufacturers and developers | Grid-connected electricity production | Increasing turbine capacity from 22 kW in 1975 (inventor Chr. Riisager) Increasing sizes up to 6.5 MW in 2007 | Stall or pitch control |
| 1980 | Pitch controlled turbines | |||
| 1991 | First offshore wind farm in the Danish part of the Baltic Sea | Eleven 450 kW turbines about 2 km from the shore | Active stall control |
| Reference | Region | Potential Production | Comments |
| ETSU, Harwell, UK | Europe | 330TWh/year | Conservative estimate |
| Grubb and Meyer, in Renewable Energy, 1993 | World | 53,000 TWh/year | Surprisingly the same result as earlier by Grubb and Meyer |
1. GLOBAL DEVELOPMENT OF WIND ENERGY
1a. Global development of capacity (onshore and offshore)
1a1. Installed total wind turbine capacity globally
1a2. Installed capacity offshore
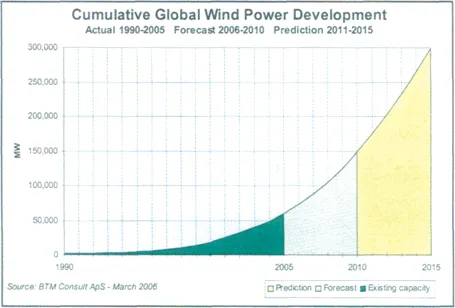

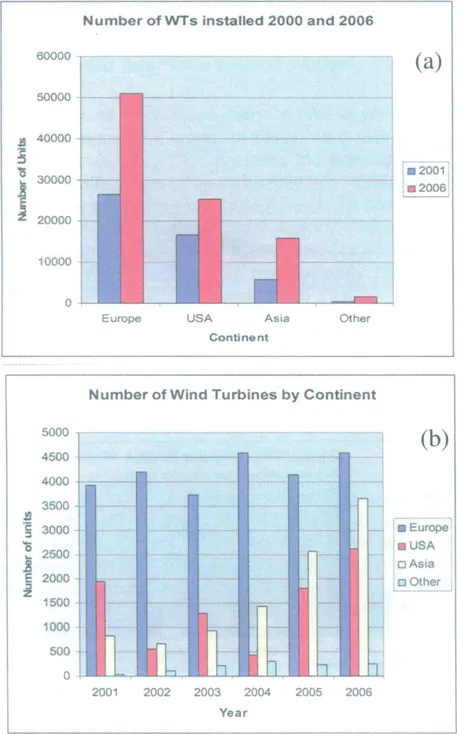
Table of contents
- Cover Page
- Title Page
- Preface
- Copyright Page
- Contents
- I Introduction
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app