
Ventilation and Airflow in Buildings
Methods for Diagnosis and Evaluation
- 210 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
About this book
Energy efficiency in buildings requires, among other things, that ventilation be appropriately dimensioned: too much ventilation wastes energy, and insufficient ventilation leads to poor indoor air quality and low comfort.
Studies have shown that ventilation systems seldom function according to their commissioned design. They have also shown that airflow measurement results are essential in improving a ventilation system. This key handbook explains why ventilation in buildings should be measured and describes how to measure it, giving applied examples for each measurement method.
The book will help building physicists and ventilation engineers to properly commission ventilation systems and appropriately diagnose ventilation problems throughout the life of a building. Drawing on over 20 years of experience and the results of recent international research projects, this is the definitive guide to diagnosing airflow patterns within buildings.
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
1
Airflow Rates in Buildings
Single-zone measurements
Mass conservation of tracer gas and air

m | is the mass of tracer gas in the zone (kg); |
I | is the injection rate of the tracer gas (kg/s); |
C | is the tracer gas mass concentration; |
Q | is the mass airflow rate (for example, Qio is airflow rate from indoor to outdoors); |
i | subscript for internal environment; |
o | subscript for external environment. |




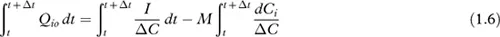
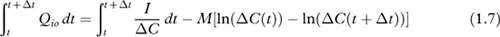
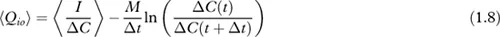
Tracer decay, no injection



Constant injection rate
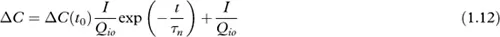


Constant concentration
Table of contents
- Front Cover
- Half Title
- Title Page
- Copyright
- Contents
- List of Figures and Tables
- Preamble
- Introduction
- 1 Airflow Rates in Buildings
- 2 Airflow Rates in Air Handling Units
- 3 Age of Air and Ventilation Efficiency
- 4 Airtightness
- 5 Measurements and Measures Related to Energy Efficiency in Ventilation
- 6 Contaminants in Air Handling Units
- 7 Common Methods and Techniques
- References
- Annexes
- Index