![]()
PART 1
Introduction
![]()
CHAPTER 1
Cost management
Introduction
This chapter:
• defines cost management in the context of building projects;
• describes the basic principles of cost management;
• explains the importance of cost management;
• identifies the objectives of cost management;
• outlines the role of the cost manager;
• describes the cost management cycle phases along with the activities needed to complete them;
• explains the role that the RICS [Royal Institution of Chartered Surveyors] New Rules of Measurement: Order of Cost Estimating and Cost Planning for Capital Building Works (NRM 1) has in effective cost management;
• explains the relationship of the documents that comprise the RICS suite of new measurement rules;
• explains how NRM 1 supports building information modelling (BIM); and
• summarises the key benefits of the rules.
1.1 What is cost management?
Cost management is all about achieving value for money (VfM). It is much more than simply maintaining records of expenditure and issuing cost reports. Management means control, so cost management means all those actions necessary to understand why costs occur and the necessary responses so that decisions controlling costs are taken promptly – in light of all relevant information.
In the context of building projects, cost management involves the overall planning, co-ordination, control and reporting of all cost-related aspects from initiation to operation and maintenance. It is the process of identifying all costs associated with the investment, making informed choices about the options that will deliver best value for money and managing those costs, including costs throughout the life of the building, where whole life costs are being considered.
Cost management of building projects is just one of the specialist services undertaken by the quantity surveyor.
1.2 Basic principles of cost management
Cost management is one of the cornerstones of project management. The establishment and implementation of effective cost management procedures at an early stage in the development of a building project will help ensure success. Established and effective cost control systems and procedures, understood and adopted by all members of the project team, entail less effort than ‘crisis management’ and will release management effort to other areas of the building project.
The principle areas of cost management can be described as follows:
• Scope – defining what is to be included within the building project and limiting expenditure accordingly.
• Programme – defining the programme for the building project from inception to completion and ensuring compliance. Estimates and cash flow projections should be consistent with the programme.
• Design – ensuring that designs meet the scope and budget (i.e. cost limit); delivering quality that is appropriate to the employer’s brief.
• Risk allowances – ensuring that all monies are appropriately allocated from risk allowances and are properly authorised. Monitoring the use of risk allowances to forecast the cost limit.
• Contracts and materials – ensuring that the contracts provide full and proper control and that all costs are incurred as authorised; ensuring that materials are properly specified so as to meet the scope and design, and that they can be procured effectively.
• Cash flow – planning and controlling both commitments and expenditure within budgets so that unexpected cost overruns or underruns do not occur.
• Cost records and reports – ensuring that all transactions are properly recorded and authorised and, where appropriate, decisions are justified; and that regular, consistent and accurate reports are available to the employer.
It must be emphasised that cost management procedures need to be varied and flexible. Cost managers should discuss and jointly agree appropriate controls and review mechanisms with the employer and, where appointed, the project manager.
1.3 Why is cost management important?
Cost management is an essential part of effective programme/project management, but when poorly performed can be a barrier to the successful delivery of the building project and can result in failure to achieve value for money. Cost overruns are often caused by the employer through objectives that are unclear and changed during the course of the building project. The other main reasons for cost increases are:
• unrealistic cost estimates (usually too optimistic);
• risk allocation that is ambiguous; and
• inadequate management control.
In building projects, additional problems are frequently caused by:
• design that does not meet planning or statutory requirements;
• design that lacks co-ordination; and
• design that is difficult to build and maintain.
1.4 Objectives of cost management
The objectives of cost management are:
• to deliver the building project at the lowest cost compatible with the specified quality and as closely as practicable to the cost limit (taking account of whole life costs, where appropriate);
• to ensure that, throughout the building project, full and proper accounts are maintained (and kept up to date at all times) of all transactions including commitments, payments and changes; and
• to ensure that all transactions fully accord with the requirements of the employer or, in the case of public sector organisations, with the requirements of public accountability, probity and propriety.
1.5 Responsibility for cost management
The cost management of a building project is the joint responsibility of the whole project team; not the cost manager alone. Cost management requires continuing and active involvement from all project team members. Therefore, all project team members must remain mindful of their joint responsibility for cost management and draw to the attention of the employer, or project manager, anything that might affect cost. In view of this, it is important that the employer clearly sets out each consultant’s responsibility in respect of cost management in the consultant’s appointment.
1.6 The role of the cost manager
Management of the overall cost of the building project is the responsibility of the cost manager, maintaining effective financial control through the processes of evaluating, estimating, budgeting, monitoring, analysing, forecasting and reporting.
The main tasks of the cost manager are to:
• provide initial cost advice on capital investment costs;
• produce cost estimates and cost plans in respect of capital investment costs;
• advise on and estimate whole life costs;
• produce risk allowance estimates;
• manage the base cost estimate and risk allowance during design development and construction;
• undertake cost-in-use studies and option costs;
• produce cost reports, estimates and forecasts;
• maintain an up-to-date estimated outturn cost and cash flow;
• manage expenditure of the risk allowance;
• initiate action to avoid overspend;
• prepare pricing documents for the purpose of tender;
• evaluate tender bids;
• scrutinise actual cost of tenders;
• collect and analyse cost data;
• prepare interim valuations;
• value change instructions;
• ascertain cost implication of contractor’s financial claims;
• negotiate and agree final accounts; and
• issue financial reports or statements (i.e. throughout the building project to report the financial status).
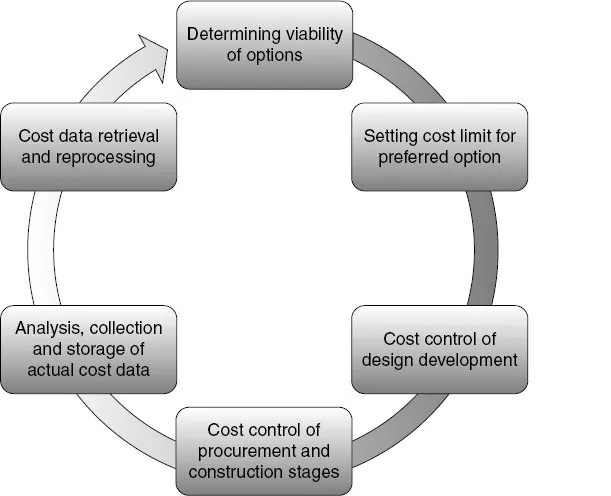
1.7 The cost management cycle (the Benge Cycle)
The cost management cycle is shown in Figure 1.1. Proactive cost management takes place throughout the cost management cycle (the Benge Cycle). Each cost management cycle phase is described below, along with the activities needed to complete it.
Where required, whole life costs will be considered during each phase of the cost management cycle.
1.8 Relationship of the documents that comprise the RICS suite of new measurement rules
NRM 1 forms part of the RICS suite of publications referred to as the ‘new rules of measurement (NRM)’. The RICS Quantity Surveying and Construction Group have developed the NRM suite of documents. The primary aim of the rules is to provide a consistent approach to the measurement and quantification of capital building works and maintenance, supported by a common means of analysing cost data for future use.
Although the NRM suite has principally been based on UK practice, the requirements for a co-ordinated set of rules and their underlying philosophy have worldwide application.
The NRM suite comprises the following three volumes (summarised in Figure 1.2):
NRM 1 – Order of cost estimating and cost planning for capital building works;
NRM 2 – Detailed measurement for building works; and
NRM 3 – Order of cost estimating and cost planning for building maintenance works.
These rules are supported by the BCIS (Building Cost Information Service) ‘Elemental Standard Form of Cost Analysis, (NRM) Edition’, which sets out the principles of analysing building costs. Together, these rules deal with the quantification of buildings from ‘cradle to grave’ – from inception to demolition.
Figure 1.1 The cost management cycle (the Benge Cycle)
Notes:
(1) Determining via...