
eBook - ePub
Improving Patient Safety
Tools and Strategies for Quality Improvement
- 284 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
Improving Patient Safety
Tools and Strategies for Quality Improvement
About this book
Based on the IOM's estimate of 44,000 deaths annually, medical errors rank as the eighth leading cause of death in the U.S. Clearly medical errors are an epidemic that needs to be contained. Despite these numbers, patient safety and medical errors remain an issue for physicians and other clinicians. This book bridges the issues related to patient safety by providing clinically relevant, vignette-based description of the areas where most problems occur. Each vignette highlights a particular issue such as communication, human facturs, E.H.R., etc. and provides tools and strategies for improving quality in these areas and creating a safer environment for patients.
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription.
No, books cannot be downloaded as external files, such as PDFs, for use outside of Perlego. However, you can download books within the Perlego app for offline reading on mobile or tablet. Learn more here.
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 1000+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn more here.
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more here.
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS or Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Yes, you can access Improving Patient Safety by Raghav Govindarajan, Harleen Kaur,Anudeep Yelam, Harleen Kaur, Anudeep Yelam in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Business & Operations. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.
Information
Chapter 1
Introduction to Patient Safety and Medical Errors
University of Missouri
Introduction
Patient safety and healthcare-related errors have now become an important healthcare issue worldwide. In recent years, there have been improvements in regard to improving the patient safety, and many quantifiable problems have been addressed such as medication errors, healthcare-associated infections, and postsurgical complications. Comparatively, diagnostic errors have received less attention, even though landmark patient safety studies have consistently found that diagnostic errors are widely prevalent. Many recent studies have reported on the incidence, scope, and cost of adverse events related to healthcare errors. In a Harvard Medical Practice Study, diagnostic errors accounted for 17% of preventable errors in hospitalized patients. In a medical chart review of 30,121 patients admitted to 51 acute care hospitals in New York State, in 1984, Brennan et al. reported that preventable adverse events occurred in 3.7% of admissions. Medication errors and adverse drug events have been extensively investigated because they are both relevant and preventable. In a study carried out by Bates et al. in two teaching hospitals in Boston, 1% of the events were noted to be fatal, 12% were life-threatening, 30% were serious, and 57% were significant. Of the adverse events, 42% classified as life-threatening or serious were preventable. The medication errors were associated with the use of analgesics, antibiotics, sedatives, chemotherapeutic agents, cardiovascular drugs, and anticoagulants.1 In a 2004 review of 25 years of malpractice claims, diagnostic errors were the leading cause of a claim (28.6%) and resulted in the highest proportion of total payments (35.2%). Further, diagnostic errors more often resulted in death than other causes (40.9% versus 23.9%) and were responsible for payments of US$38.8 billion.
Source of Errors in Healthcare
The literature identified two broad sources of error: human error and systemic error. Human error is further divided into random/personal error and systematic error. Random errors are those isolated personal errors that cannot be explained by underlying causes, external forces, or preceding events, and are due to personal behavior in a particular situation. Systematic errors, on the other hand, are those human errors that are not isolated but occur regularly due to some underlying undetected causes such as software or transfer errors. Figure 1.1 shows the sources and causes of errors in healthcare.2
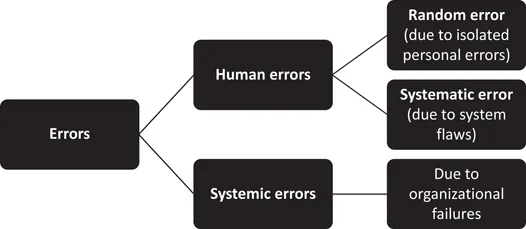
Figure 1.1 Sources and causes of errors in healthcare.
Types of Medical Errors
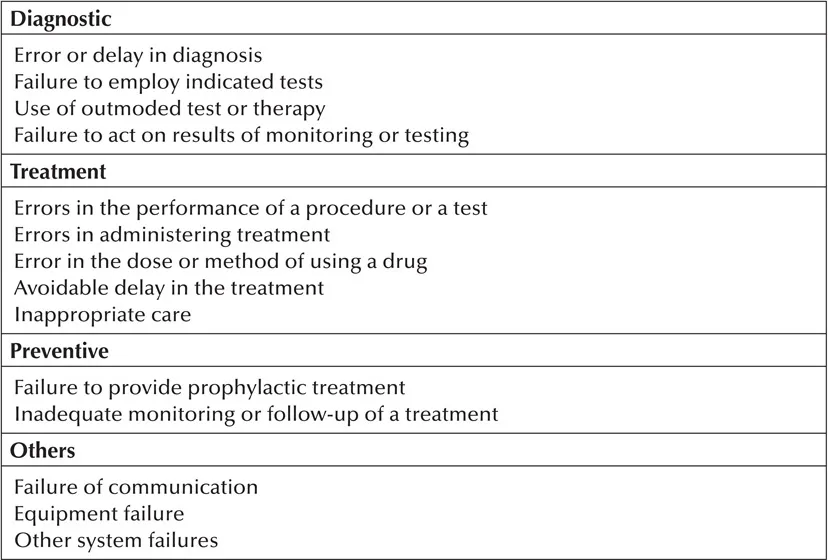
The most widely used classification in regards to medical errors is by the Institute of Medicine (IOM). Table 1.1 represents different types of medical errors as per the IOM approach.
Table 1.1 Type of Medical Errors Following IOM Approach
Terminologies in Patient Safety
The Hospital Survey on Patient Safety Culture, released in November 2004, was designed to assess hospital staff opinions about patient safety issues, medical errors, and event reporting. The survey includes 42 items that measure 12 areas, or composites, of patient safety culture.3 Each of the 12 patient safety culture composites is listed and defined in Table 1.2.
Healthcare Statistics
The first comparative database report, released in 2007, included data from 382 U.S. hospitals. The survey was designed to assess hospital staff opinions about patient safety issues, medical errors, and event reporting. The survey also included two questions that ask respondents to provide an overall grade on patient safety for their work area/unit and to indicate the number of events they reported over the past 12 months. The 2016 user comparative database report included data from 680 hospitals and 447,584 hospital staff respondents. The average hospital response rate was 55%, with an average of 658 completed surveys per hospital.3
Table 1.2 Patient Safety Culture Composites and Definitions
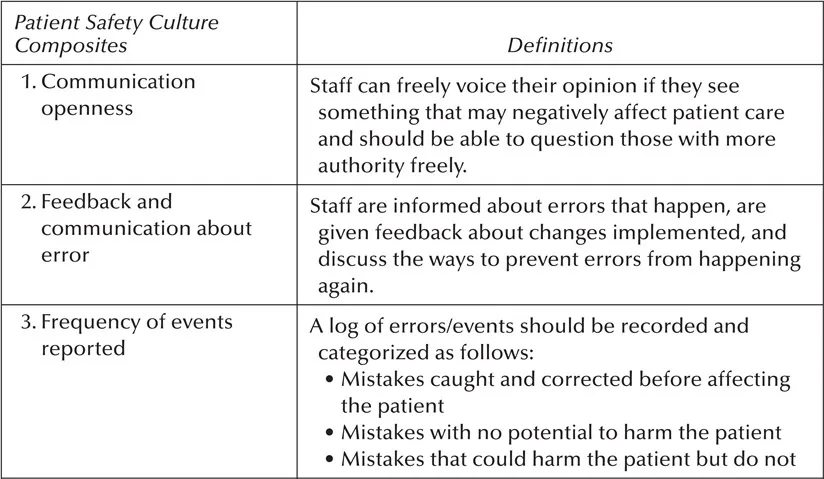
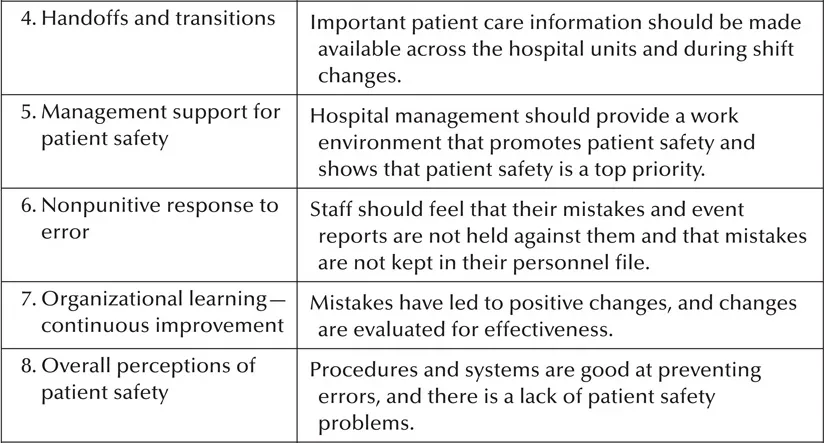
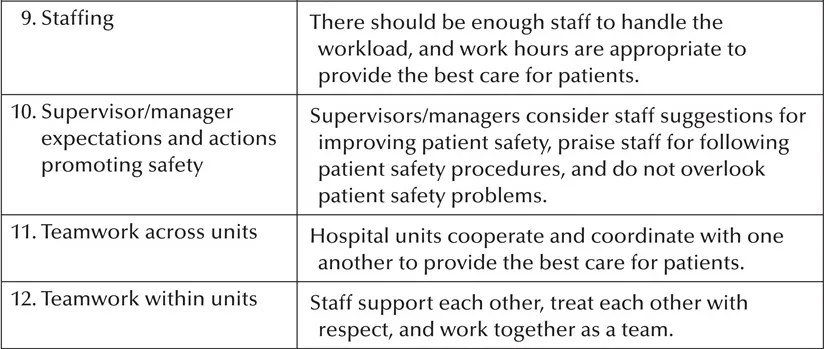
Table 1.3 shows the average percent positive response for each of the 12 patient safety culture composites across hospitals in the 2016 database.
Table 1.3 Composite-Level Average Percent Positive Response—2016 Database Hospitals
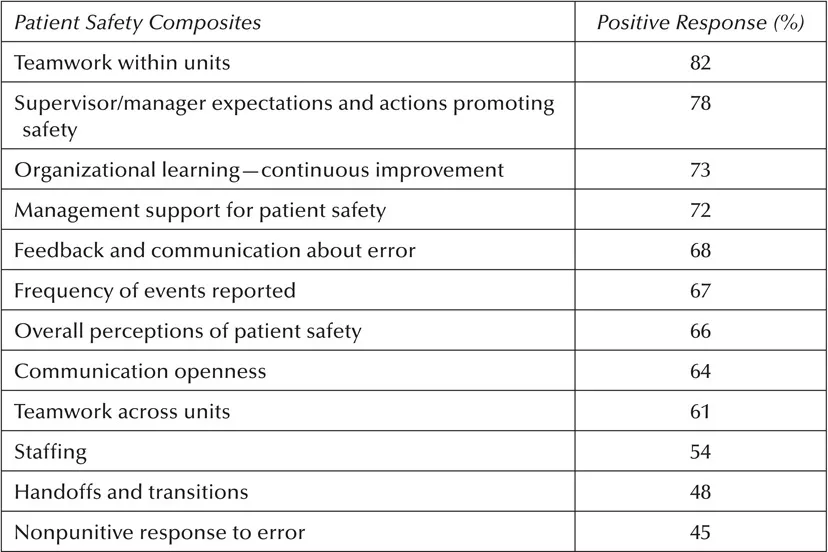
The areas of strength or the composites with the highest average percent positive responses were as follows: teamwork within units (82% positive), supervisor/manager expectations and actions promoting patient safety (78% positive), and organizational learning—continuous improvement (73% positive).
The areas with potential for improvement or the composites with the lowest average percent positive responses were as follows: nonpunitive response to error (45% positive), handoffs and transitions (48% positive), and staffing (54% positive).
REFERENCES
1. La Pietra, L., et al., Medical errors and clinical risk management: State of the art. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital, 2005. 25(6): pp. 339–346.
2. Maamoun, J., An introduction to patient safety. J Med Imaging Radiat Sci, 2009. 40(3): pp. 123–133.
3. Study. Available at: www.ahrq.gov/professionals/quality-patient-safety/index.html. Accessed on July 25, 2018.
Chapter 2
Developing an Outline for Patient Safety Curriculum
University of Missouri
ACGME Standards for Quality Improvement and Patient Safety Curriculum
The past decade has seen remarkable changes in healthcare system with an extensive focus on the need for quality improvement and patient safety (QI/PS).1 This focus has resulted in the introduction of newer innovations in QI/PS education among U.S. medical schools and teaching hospitals. Resident participation is critical in quality improvement projects as they have the firsthand knowledge of the areas that need improvement.1 Moreover, educational quality improvement projects can teach them core improvem...
Table of contents
- Cover
- Half Title
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Table of Contents
- Preface
- Editors
- List of Contributors
- 1 Introduction to Patient Safety and Medical Errors
- 2 Developing an Outline for Patient Safety Curriculum
- 3 Understanding System Errors
- 4 Understanding Diagnostic Errors
- 5 Understanding Human/Provider Errors
- 6 Tools and Strategies for Quality Improvement and Patient Safety: A Primer for Healthcare Providers
- Index