![]()
Chapter 1
PV technical sales: facts and figures
To make the most of your time, rather than digging deep into big paragraphs with a highlighter for important points, here is some material that is ripe for memorization or flash cards, which includes many acronyms.
NREL (National Renewable Energy Lab)Formerly the Solar Energy Research Institute, NREL is based in Golden, Colorado. Much of the research in the world on solar PV has been done at NREL. NREL also has many websites, including PVWATTS (pvwatts.nrel.gov) and System Advisor Model (sam.nrel.gov).
Pvwatts An NREL website that is used to predict output of PV systems. PVWATTS is very simple to use and is the most commonly used website for sizing PV systems. Other software that is used to predict outputs and do financial analysis of PV systems often uses information from PVWATTS.
SAM System Advisor Model is an NREL-designed software that can predict system outputs and will do financial analysis for PV and other renewable energy systems. SAM is more detailed and complicated to use than PVWATTS and can get information from different utility databases.
NREL Redbook Thirty years’ worth of solar radiation data for locations in the United States. This is a good place to compare the solar radiation as expressed in kWh/m2/day at flat tilt, latitude tilt, latitude +15 tilt and latitude –15 tilt for many locations.
FIT (feed-in tariff) A type of PBI. Typically a FIT is a 20-year fixed price for electricity produced by solar. The government requires the utility to pay the price. Introduced in Germany.
TOU (time of use) A utility rate schedule where the price of energy changes based on time. Typically weekday afternoons are most expensive due to an increased demand for electricity. This is why people that have a TOU schedule or expect to have a TOU schedule in the future would be better off facing their PV modules west than east. Some people expect that in the future, with electric cars, everyone will have a TOU rate schedule.
Tiered rate schedule A rate schedule where rates go up as more energy is used. Tiered rates are typically residential and based on monthly energy usage. Tiered rates penalize people for using a lot of energy; however, they benefit high energy users disproportionally for getting solar.
Derating factor A number that you multiply by to compute for losses. Often common “dc to ac” derating factors are in the range of 0.77 to 0.85.
In many places, including the NREL website, the derating factor is termed “dc to ac,” but it is actually a factor that will convert kWh per square meter per day to ac kWh per kW of PV per day. Sometimes we are given a loss factor and we would subtract that from 1 to get a derating factor. For instance, if we lose 20%, our loss factor would be 0.2 and our derating factor is going to be 0.8. The NREL PVWATTS calculator has transitioned from a derating factor to a loss factor.
PPA (power purchase agreement) An agreement to purchase electricity for a specified time, often about 20 years. As opposed to a lease, with a PPA you are paying for the amount of energy the system produces. A PPA typically has a buyout at the end and may have early buyout provisions. The owner of the system who sells the energy will take advantage of the tax credits, depreciation and other incentives.
10W/square foot An estimate that some people use to quickly determine how much PV will fit on a roof. This estimate is very conservative and in some cases it can be possible to get 20W/square foot with efficient PV. 10W/square foot can account for unused roof space, such as fire setbacks, other equipment on roofs and pathways.
Soh Cah Toa Used to memorize trigonometry, which can be used to calculate roof slopes and shadow lengths. Sine = opposite/hypotenuse; cosine = adjacent/hypotenuse; tangent = opposite/adjacent. Trigonometry uses relationships of right triangles to determine angles and side lengths of the triangle. (There is an entire chapter on solar trigonometry in the second book in this series, Solar PV Engineering and Installation and part of a chapter on trigonometry in this book.)
Voltage Electrical pressure. The dangers with higher voltage is arcing and sparking. Lightning is very high voltage. The hydraulic analogy for voltage is pressure.
Current Electrical flow. The dangers with high current are heat and stoppage of the heart. Current is what kills.
Power Voltage multiplied by current is power. Power is the instantaneous rate of electricity usage. If a utility charges for power, it is called a demand charge. The basic fundamental unit of power in the solar industry is the watt (W) or the kilowatt (kW).
Demand charge Charges for peak power usage. Often at 15-minute intervals or instantaneously, power is measured and the highest power measurement of the month determines the demand charge. When everything is on at once, that will cause a higher demand charge. Solar without energy storage typically does not lower demand charges, since it is not always sunny. Incorporating energy storage into a PV system can help offset demand charges by storing energy when demand is low and using the stored energy when the demand is high.
Energy Energy is power multiplied by time. Energy is the quantity of electricity used and is the main thing that utilities charge for, in kWh. When we design our PV systems, we are usually most interested in the energy they will make over time.
Irradiance Solar power, which can be measured in watts per square meter. This is a unit of power per unit area.
Peak sun Irradiance of 1000 watts per square meter.
Irradiation Solar energy, which is often measured in kWh per square meter.
PSH (peak sun hours) Solar energy measured in kWh/square meter. Typically PSH are measured for a day for a particular tilt angle and are a measurement of insolation.
Insolation (incident solar radiation) Solar radiation measured at a particular tilt angle, such as latitude tilt, and measured in kWh/m2/day. Insolation, PSH and irradiation can all be the same thing. Insolation is not a measurement of ac kWh (electricity), it is sunlight hitting a square meter.
Solar module A single unit of PV that people will purchase. An average solar module is 250W, has 60 cells and is about 39 inches (1m) × 66 inches (1.67m). Solar modules are often incorrectly called solar panels. Almost all solar modules have all of the solar cells arranged in series.
60-cell module Most 60-cell solar modules are arranged in a 6 × 10 cell format and have bypass diodes that divide the cells electronically into three groups of 20 cells.
72-cell module Most 72-cell modules are arranged in groups of 6 × 12 cells and have bypass diodes that divide the cells electronically into three groups of 24 cells each.
Bypass diodes Bypass diodes can help current bypass shaded solar cells. When any cell in a group is shaded, the current will bypass the group of shaded cells. Bypassing the shaded cells will cause a decrease in voltage. If there were no bypass diodes, the current would have trouble bypassing the shaded cells and would create heat and resistance, which could be a fire hazard. When a bypass diode is broken, it will bypass cells, even without shade, and the module will typically see a one-third of a module decrease in voltage.
12-volt module In the early days of PV, modules had 36 cells and worked well for charging 12V batteries. We still see 12V modules for small battery charging systems and other small solar modules often have 36 cells.
Solar panel A group of solar modules connected together before installation. A solar panel technically is not a single solar module according to the National Electric Code, but most solar salespeople call a module a panel when speaking to their customers, since that is the common term that non-technical people use. For any technical exam, consider that a solar panel is a group of modules.
STC (standard test conditions) The way PV modules are tested, so that we will know their performance and can compare different modules to each other. The conditions are 1000W/m2 irradiance, 25C (77F) cell temperature (not ambient) and 1.5 air mass. Modules in reality perform at conditions that are considerably below STC most of the time. For example, 5kW of PV will never export 5kW of electricity.
AM (air mass) The thickness of the atmosphere, which filters sunlight and determines the spectrum of sunlight. PV is tested at STC with an air mass of 1.5. In theory, if someone is at sea level and the sun is straight overhead, the air mass will be 1.5. Every day, due to humidity, pollution and other atmospheric conditions, the air mass will be different. Air mass was standardized in Cape Canaveral, Florida, on an equinox day at solar noon.
Wp (watts peak) When people are referring to an amount of PV, they often use the term watts peak, which means the number of watts at STC. Also, we can refer to kWp for kW at STC.
Series Connected together electrically positive to negative, which will increase voltage, but not current. A thousand solar cells connected together in series will have 1000 times the voltage of one solar cell and will have the same current as a single solar cell. With series connections, when the current goes through one device, it will go through all of the other devices that it is in series with.
Parallel Connected together so that the positive terminals are all connected and the negative terminals are also connected together. Parallel connections do not increase voltage and only increase current. Parallel connections are done at a combiner box. Also, parallel connections can be done with alternating current at a service panel or a sub panel.
PV source circuit PV modules connected in series. Often a PV source circuit is called a “string.” PV modules or cells that are connected together in series will increase voltage.
PV output circuit Circuit at the output of a combiner box, often going to an inverter or charge controller. When PV source circuits are connected together in parallel at a combiner box, they will become a PV output circuit at the output of the combiner box.
Combiner box Where source circuits are combined to form a PV output circuit. Parallel connections are made at combiner boxes. Usually there will be fuses at a combiner box, unless only two strings are combined. (If strings are not combined, it is called a junction box or a transition box.)
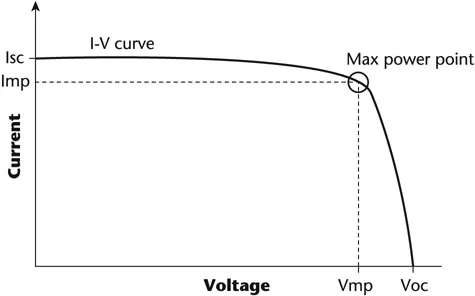
IV curve A curve in which current (I) is plotted on the y-axis (vertical) and voltage (V) is plotted on the x-axis (horizontal). Typical points plotted on a PV IV curve are Isc (upper left), Voc (lower right), and Vmp and Imp, which are both at the middle “knee” of the curve. MPPT takes place at Imp and Vmp.
MPPT (maximum power point tracking) Optimizing power from a PV array, a PV source circuit or a PV module by operating at the best combination of current and voltage for maximum power. MPPT will operate at Vmp and Imp on an IV curve and will adjust to different environmental conditions, such as irradiance and temperature, for maximum power in the given situation.
Figure 1.1 IV curve, courtesy of Solmetric.
Maximum power point tracker A part, often in an inverter, where MPPT takes place. Some inverters have two or more MPPT inputs and there should never be different PV source circuit lengths on a single maximum power point tracker.
Microinverter An inverter that operates underneath a single PV module. Microinverters are convenient, since they perform MPPT on each module individually. Microinverters can work with different module types, with different orientations; more modules can be added later and shading is less of an issue than with traditional string inverters. Microinverters are more expensive than string inverters.
Power optimizer Electronics underneath a module where dc to ac conversion and MPPT is done. Power optimizers are typically less expensive than microinverters, but they still need inverters to work with in order to produce ac power. Power optimizers can work with different module types, with different orientations; more modules can be added later and shading is less of an issue than with traditional string inverters.
Rafters The strong supporting parts of the roof, which the PV system is usually attached to. Rafters are underneath the roof deck and are oriented from the ridge top of the roof down to the lower eave of the roof. Wooden roofs often have rafters, which solar structures are attached to.
Purlins The strong supporting parts of the roof that go horizontally across the roof, from side to side. Purlins are usually what solar structures are structurally attached to on metal roofing systems.
Portrait Mounting modules with the long edges to the sides. Just like when you print portrait or a portrait painting in a museum. When the roof has rafters that are going from the ridge of the roof down, the rails are often mounted perpendicular to the rafters and the modules are usually mounted portrait with common rail systems.
Landscape Mounting modules with the short edges to the sides, like a landscape painting in an art gallery. With roofs that have purlins that are parallel to the ridge of a roof, which is common with metal roofing systems, then the rails are often mounted perpendicular to the purlins and will come from the ridge of the roof down. These systems usually have modules mounted landscape. There are al...