
- 88 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Supporting Children with Sensory Impairment
About this book
This book provides a quick and easy reference guide to different types of sensory impairment, including causes, symptoms and the implications on teaching and learning. With most children and young people with hearing or visual impairments attending mainstream schools, this book explains the most effective and practical strategies for use in mainstream classrooms. Fully up to date with the 2014 SEND Code of Practice, this accessible resource is split into two sections: Supporting Children with a Hearing Impairment and Supporting Children with a Visual Impairment. The wide-ranging chapters include:
- Educational access for pupils with hearing loss
- Teaching phonics
- Teaching deaf pupils with English as a second language
- Identifying children with visual impairment
- Classroom management
- Adapting resources
This practical text provides strategies to use in schools to ensure that children with sensory impairments are fully supported. Featuring useful checklist and photocopiable resouces, it contains a wealth of valuable advice and tried-and-tested strategies for teachers and support staff working in early years settings, schools, academies and colleges.
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
Supporting children with a hearing impairment
1
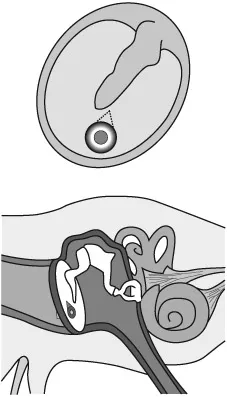
What is deafness?
2
Causes of deafness
3
Levels of deafness
Mild hearing loss
Definition
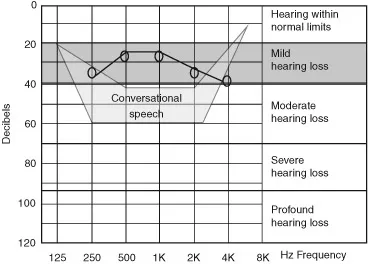
Implications
- This loss may go undetected as speech can be heard but it can be muffled.
- There may be difficulties in understanding speech in noisy environments.
- Where speech is misunderstood, this can cause confusion and lead to a breakdown in communication.
Strategies that should help
- A hearing aid may be prescribed but the disadvantages may outweigh the advantages.
- Background noise should be kept to a minimum.
- Advice from a teacher of the deaf.
- The development of appropriate communication skills.
- Deaf awareness training.
- Regular audiological reviews to monitor the hearing loss.
Moderate hearing loss
Definition
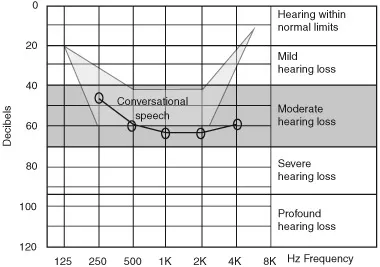
Implications
- The implications will depend on the age of onset and diagnosis. If it is from birth, there may be delayed language development.
- When listening to speech, all sounds may not be heard.
- Speech may lack clarity because of an inability to hear sounds clearly.
- There may be gaps in vocabulary and general knowledge.
- The loss may go undetected or the implications not fully appreciated if the person has good lip-reading skills and coping strategies.
Strategies that should help
- A hearing aid/s will probably be provided but they will not return hearing to normal.
- Occasionally a radio aid system will be provided for use in a school or learning situation.
- Advice and support from a teacher of the deaf.
- In class, a seating position where children are able to see the teacher’s face clearly whilst at the same time being able to see peers.
- The development of appropriate communication skills.
- Deaf awareness training.
- Speech therapy may be recommended.
- Regular audiological reviews to monitor the hearing loss.
Severe hearing loss
Definition
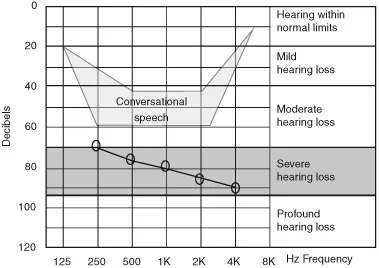
Implications
- The implications will depend on the age of onset and time of diagnosis. If the loss was from birth and/or late diagnosis, there may be severely delayed language development. There will be little spoken language acquired naturally without intervention.
- Speech may be unclear with omissions and unnatural rhythms.
- There may be difficulties acquiring new language and vocabulary.
- Acquiring early literacy skills may be difficult.
- There may be breakdowns in communication on both sides because of an inability to understand what is being said.
- There may be difficulties understanding situations and what is expected, resulting in frustration and temper tantrums in young children.
- There may be a need to rely on visual clues.
- Sign language may be considered as the method of communication.
Strategies that should help
- Hearing aids will be provided but hearing will not return to normal; they should be worn at all times.
- A cochlear implant may be considered.
- A radio aid system may be provided for use in a school or learning situation.
- Consideration may be given to a placement in a Resource Base for deaf pupils attached to a mainstream school.
- Advice and support from a teacher of the deaf from diagnosis and continuing throughout education.
- Speech therapy is likely to be recommended.
Profound hearing loss
Definition
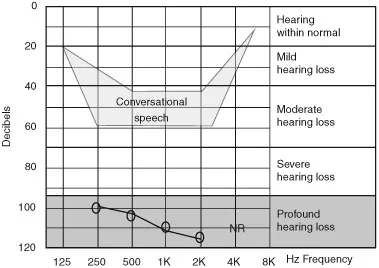
Implications
- The implications will depend on the age of onset and time of diagnosis. If the loss was from birth and/or late diagnosis, there may be severely delayed language development. There will be little spoken language acquired naturally without intervention.
- Speech development will probably be severely delayed and it may be difficult to understand.
- There may be difficulties understanding situations and what is expected resulting in frustration and temper tantrums in young children.
- Vocabulary and general knowledge will be restricted.
- Acquiring early literacy skills will be difficult.
- There may be breakdowns in communication on both sides because of an inability to understand what is being said.
- There are safety implications especially in hazardous situations such as crossing the road.
- There may be difficulties learning socially acceptable behaviour because of problems understanding what is expected.
- Concentrating on oral communication will be very tiring.
- There will be a need to rely on visual clues.
- Sign language may be considered...
Table of contents
- Cover Page
- Half Title Page
- Front Page
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Table of Contents
- Foreword
- Legislation and guidance
- Part A Supporting children with a hearing impairment
- Part B Supporting children with a visual impairment