
- 224 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
Quantitative Methods for Business and Economics
About this book
This book provides a brief yet rigorous introduction to various quantitative methods used in economic decision-making. It has no prerequisites other than high school algebra. The book begins with matrix algebra and calculus, which are then used in the book's core modes. Once the reader grasps matrix theory and calculus, the quantitative models can be understood easily, and for each model there are many solved examples related to business and economic applications.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
Topic
CommerceSubtopic
Commerce GénéralCHAPTER ONE
Vectors and Matrices
Vectors and matrices are very important tools in economic analysis. This chapter outlines the algebra of vectors. Students will not only be able to add and subtract vectors but also to multiply vectors. For economic modeling, linear independence is indispensable in that economic models must have unique solutions, and linear independence provides these solutions. Similarly, linear and convex combinations are also important for economics.
An extension of vector analysis is matrix algebra. The types of matrices and matrix operations are outlined in this chapter. A system of equations is solved by using matrix methods such as the inverse method, Cramer’s rule and the Gauss-Jordan method. Eigenvalues and vectors are explained and used for diagonalizing matrices. Finally, various economic applications of matrices are provided.
Vectors
A vector is a symbol used to refer to a set of variables or coefficients. For example,
Y = (y1, y2, y3, ..., yn),
where Y is used to represent n-variables. Vector A can be represented by
A = (a1, a2, a3,..., an),
where A contains a set of coefficients denoted by a’s. Also, vector Y can also be a set of real integer numbers such as Y = (3, 4, 6, 8).
Vector Y has a dimension as well. The dimension of a vector is the total number of elements (components) in that vector. For example, the above vector, Y, has four components and hence it is said to be of dimension four. Very compactly, a vector such as Y, where Y = (5, 6, 7), has one row and three columns. Accordingly, it is said to be a vector of dimension 1 by 3 or Y1 × 3 or Y1 3, where 1 and 3 indicate number of rows and columns, respectively. In general, Ym x n is said to be a vector of dimension m x n: with m rows and n columns.
Example:
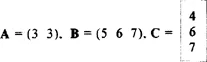
All these vectors have different dimensions: A is 1 × 2, B is 1 × 3, and A is 3 × 1. Vectors A and B are called row vectors, whereas vector C is a column vector.
The Transpose of a Vector
The transpo...
Table of contents
- Cover
- Half Title
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Table of Contents
- Preface
- Acknowledgments
- 1. Vectors and Matrices
- 2. Derivatives and Applications
- 3. The Input-Output Model
- 4. Optimization Theory: The Calculus Approach
- 5. The Inventory Model
- 6. Dynamic Techniques
- 7. Linear Programming I: The Simplex Method
- 8. Linear Programming II: Sensitivity Analysis, Duality, and Integer Programming
- 9. Decision Analysis
- 10. Game Theory
- 11. Markov Chains
- 12. The General Linear Model
- References
- Index
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription
No, books cannot be downloaded as external files, such as PDFs, for use outside of Perlego. However, you can download books within the Perlego app for offline reading on mobile or tablet. Learn how to download books offline
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 990+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn about our mission
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more about Read Aloud
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS and Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Yes, you can access Quantitative Methods for Business and Economics by Adil H. Mouhammed in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Commerce & Commerce Général. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.