
- 568 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
About this book
This is a one-stop book for knowing everything important about building structures. Self-contained and with no prerequisites needed, it is suitable for both general readers and building professionals.
- follow the history of structural understanding;
- grasp the concepts of structural behaviour via step-by-step explanations;
- apply these concepts to a simple building;
- see how these concepts apply to real buildings, from Durham Cathedral to the Bank of China;
- use these concepts to define the design process;
- see how these concepts inform design choices;
- understand how engineering and architecture have diverged, and what effect this had;
- learn to do simple but relevant numerical calculations for actual structures;
- understand when dynamics are important;
- follow the development of progressive collapse prevention;
- enter the world of modern structural theory;
- see how computers can be used for structural analysis;
- learn how to organise and design a successful project.
With more than 500 pages and over 1100 user-friendly diagrams, this book is a must for anyone who would like to understand the fascinating world of structures.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
CHAPTER 1 Loads and load paths
A structure’s main function is to transfer loads, but before considering the form of a structure, a clear idea of what loads it has to transfer is required: in other words an answer to the question what are the loads?
The sources of loads can be divided into natural, useful and accidental loads. Natural loads occur due to the existence of the structure in the world; useful loads are ones that occur from the purpose of the structure; and accidental loads occur from the misuse of the structure.
1.1 Natural loads
All structures on the surface of the Earth have to resist the force of gravity. This force acts through a body in a line joining the body with the centre of the Earth. However, at the local level these forces can be considered vertical.
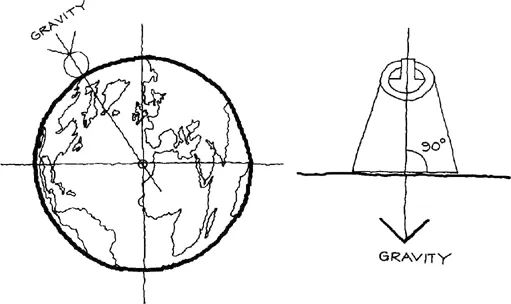
Fig.1.1
So the first source of natural loads is the gravity load. For the example of the plank across the stream - see Fig. 0.17 – this means that the plank has to transfer its own weight, usually called self-weight, to the support points.
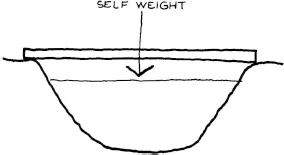
Fig.1.2
Due to regular and continuous changes in atmospheric pressure from place to place on the Earth’s surface air flows across the surface of the Earth, that is, wind. All structures built on the Earth’s surface have to resist forces from wind. Near to ground level the wind can be considered to blow along the surface: this is not true for the whole of the atmosphere, as any pilot knows.
Fig.1.3
If an obstruction is placed in the path of the wind it alters the pattern of the wind flow. This is why kites and planes fly and boats sail. If the object is fixed to the Earth’s surface, like a building, the wind must flow around and over it.
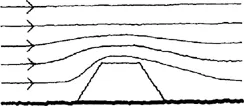
Fig.1.4
How the wind flows around and over an object depends both on the wind speed and the shape of the object. These are the basic questions considered by the complex subject known as aerodynamics. But the alteration in wind flow pattern will always cause a force on the interrupting object.
It is an intellectual feat to see the alteration of the wind flow pattern around and over a building as a force or wind load. But this view allows the action of the wind on a building to be clear.
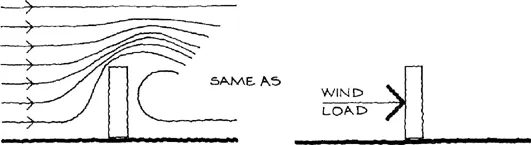
Fig.1.5
This effect can readily be felt by holding a flat object in the flow of a stream. This is why canoes and people can propel themselves through water.
Although the pattern of wind flow around buildings is complex (very!) the resulting loads from the alteration of wind flow are predominately at right angles to the surfaces of the building.
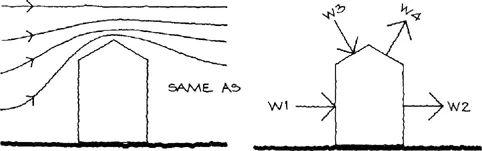
Fig.1.6
So, for the pitched roofed building shown in Fig. 1.6, the alteration in wind flow will cause four loads. The loads W1 and W2 are on, and at right angles to the walls, and the loads W3 and W4 are on, and at right angles to the roof slopes. These are wind loads.
As far as buildings and their supporting structures are concerned, gravity and wind loads are two types of natural loads they always have to resist.
There are other natural loads that the structure may have to resist. These are earth or water pressure, earthquakes, temperature, and ground movement.
If the local shape of the Earth’s surface is altered to site the building, as it often is, then parts of the building and its structure may be subject to loads from earth pressure. This is because the natural surface has found a shape that is at rest (not over geological time of course). So, rather like the wind flow, an alteration will cause forces. If dry sand is piled into a heap, there is a maximum slope for the sides.

Fig.1.7
What is happening inside the heap is complex, and is further complicated by the addition of water (which is why sand castles can be made). If, however, a heap with a vertical side is required, forces are needed to keep the heap in the unnatural shape.
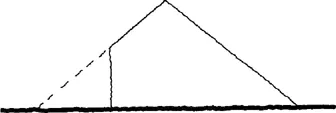
Fig.1.8
This is usually done by building a (retaining) wall. Because the heap wants to return to a natural shape, s...
Table of contents
- Cover
- Half Title
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Table of Contents
- Preface to the Third Edition
- Introduction
- Chapter 1 Loads and load paths
- Chapter 2 Internal forces
- Chapter 3 Structural element behaviour
- Chapter 4 Advanced concepts of stress
- Chapter 5 Structural materials
- Chapter 6 Safe structures and failure
- Chapter 7 Geometry and structural behaviour
- Chapter 8 Below-ground structures
- Chapter 9 Behaviour of a simple building
- Chapter 10 Real structures
- Chapter 11 Structural conception
- Chapter 12 Structures and built form
- Chapter 13 Structures in existing buildings
- Chapter 14 A simple approach to calculations
- Chapter 15 Dynamic behaviour
- Chapter 16 Progressive collapse and robustness
- Chapter 17 The mathematical basis
- Chapter 18 The basis for computer calculations
- Chapter 19 The successful structural project
- Index
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription
No, books cannot be downloaded as external files, such as PDFs, for use outside of Perlego. However, you can download books within the Perlego app for offline reading on mobile or tablet. Learn how to download books offline
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 990+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn about our mission
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more about Read Aloud
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS and Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Yes, you can access Building Structures by Malcolm Millais in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Architecture & Architecture General. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.