
- 208 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
Economics, Philosophy and Physics
About this book
This book traces the relationship between ideas and methodological perspectives in economics to the fields of philosophy and the physical sciences. It is aimed at students of economics who want to learn about the philosophical underpinnings and scientific foundations of contemporary economic theory. The authors show how advances in scientific knowledge have had an impact on philosophy that in turn influenced the development of economic thought.
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription.
At the moment all of our mobile-responsive ePub books are available to download via the app. Most of our PDFs are also available to download and we're working on making the final remaining ones downloadable now. Learn more here.
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 1000+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn more here.
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more here.
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS or Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Yes, you can access Economics, Philosophy and Physics by Ching-Yao Hsieh,Meng-Hua Ye in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Business & Business General. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.
Information
Chapter 1
Newtonian Physics, Philosophy, and Economics
The medieval world view was severely damaged by two revolutions: the Copernican Revolution in astronomy (1543) and the Cartesian Revolution in philosophy (1637). "The pernican Revolution," as pointed out by Thomas S. Kuhn, "was a revolution in ideas, a transformation in man’s conception of the universe and of his own relation to it. Again and again this history of Renaissance thought has been proclaimed an epochal turning point in the intellectual development of Western man."1 In other words, the Copernican Revolution paved the way for the conception of the mechanical world view.
There had been two strands of thought in the quest for new certainty before Newton. In his Novum Organum (1620), Francis Bacon (1561–1626) launched a skillful attack on scholasticism and urged philosophers to adopt the empirical method. The other strand was Réné Descartes’s (1596–1650) rationalist quest for certain knowledge. In Discourse upon Method (1637), Descartes started with radical doubt of everything and ended with a firm belief in the view that nature was a perfect machine governed by exact mathematical laws (Descartes’s "universal mathematics"). Thus, a new order of the universe was established and a new language had to be developed for the description of this new order. Descartes invented analytical geometry (the Cartesian coordinates) for this purpose. David Bohm observes:
To use coordinates is in effect to order our perception and our thinking . . . . [O]nce men were ready to conceive of the universe as a machine, they would naturally tend to take the order of coordinates as a universally relevant one, valid for all basic descriptions in physics.2
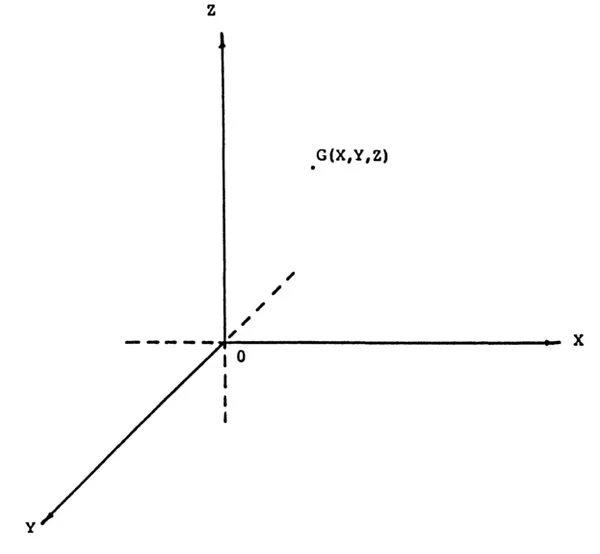
This idea is depicted by Figure 1.1: in order to specify the position of a particle it is necessary to know three distances (space has three dimensions), namely (a) length, represented by the Cartesian axis X in Figure 1.1, (b) breadth, represented by Cartesian axis Y, and (c) height, represented by the Cartesian axis Z. The three distances, X, Y, and Z, are called Cartesian coordinates. The position of the particle G is expressed in the form of (X, Y, Z). The use of the Cartesian coordinates was implicit in Newtonian physics. The introduction of the Cartesian coordinates was indeed an important contribution of the Cartesian Revolution.
Another salient feature of the Cartesian Revolution, which is relevant to the subsequent development of economic analysis, was the so-called “reductionist methodology.” According to Descartes, certain knowledge should be achieved through intuition and deduction. This methodology is succinctly summarized by Fritjof Capra:
Descartes’ method is analytic. It consists of breaking up thoughts and problems into pieces and in arranging these in their logical order. This analytic method of reasoning is probably Descartes’ greatest contribution to science. It has become an essential characteristic of modem scientific thought and has proved extremely useful in the development of scientific theories and the realization of complex technological projects.3
A third feature of Cartesian philosophy was the so-called “mind-matter duality.” According to Descartes, there are two independent and separate realms of nature. One of the realms is the realm of mind; he referred to this as “res cognitas.” The other realm is the realm of matter, which he called “res extensa.” This Cartesian duality led to two tenets of Western sciences: (a) the observer of the physical universe only observes but never disturbs; and (b) the physical universe is a machine governed by exact mathematical laws.
Figure 1.1. The use of Cartesian coordinates to fix the position of a particle in space
In the realm of natural sciences, the Copemican heliocentric astronomy was subsequently refined by Johann Kepler (1571–1630). Among other things, Kepler emphasized that the path of each planet is not circular as depicted by Copernicus, but rather is an ellipse with the sun slightly off center at a point known as the focus of the ellipse.
The most famous contemporary of Kepler was Galileo Galilei (1564–1642). It is interesting to note that William Shakespeare was born in the same year as Galileo and that Isaac Newton was born in the year he died. It was Galileo who finally broke the lingering bondage of Aristotelian physics and medieval scholasticism. Thus, Galileo, more than any other single person, was responsible for the birth of modern science.
Galileo’s devotion to obtain quantitative description of nature may be best illustrated by his law of falling bodies: d = 1/2gt2, where d denotes the number of feet the body falls; g stands for the constant acceleration of a body dropped in a vacuum (g = 32 feet per second); and t is time in seconds. Thus, the law may be rewritten as d = 16t2.
Galileo did not offer explainations for why phenomena occur, such as Heron’s famous explanation that “nature abhors a vacuum.” His formula is precise and quantitatively complete in a way that is characteristic of modern science.
It may be said that it was Galileo who planted the seed of what John Hicks called the “New Causality”:
Causality can only be asserted, i n terms of New Causality, if we have some theory, or generalization, into which observed events can be fitted; to suppose that we have theories into which all events can be fitted, is to make a large claim indeed.4
Frangois Quesnay’s tableau economique (1758), the quantity theory of money elucidated by John Locke (1632–1704), David Hume (1711–76), and Richard Cantillon (1680–1734), as well as David Ricardo’s one-sector “corn model” (1815) brought forth during the so-called “corn laws controversy” were all in line with the “New Causality.” Even today economists are still attempting to fit observed events into some mathematical models.
Newton’s Grand Synthesis
The climax of the intellectual revolution in phi...
Table of contents
- Cover
- Half Title
- Title
- Copyright
- Dedication
- Contents
- List of Figures
- Acknowledgments
- Introduction
- Chapter 1 Newtonian Physics, Philosophy, and Economics
- Chapter 2 The Romantic Protest against the Newtonian Mechanistic World View
- Chapter 3 Thermodynamics and the Newtonian World View
- Chapter 4 Relativity, Philosophy, and Economics
- Chapter 5 Quantum Mechanics, Philosophy, and Economics
- Chapter 6 Chaos Theory, Philosophy, and Economics
- Chapter 7 The Revolutions in Physics and the Future of Economics
- Bibliography
- Index