
- 464 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
Optimal Control Systems
About this book
The theory of optimal control systems has grown and flourished since the 1960's. Many texts, written on varying levels of sophistication, have been published on the subject. Yet even those purportedly designed for beginners in the field are often riddled with complex theorems, and many treatments fail to include topics that are essential to a thorough grounding in the various aspects of and approaches to optimal control.
Optimal Control Systems provides a comprehensive but accessible treatment of the subject with just the right degree of mathematical rigor to be complete but practical. It provides a solid bridge between "traditional" optimization using the calculus of variations and what is called "modern" optimal control. It also treats both continuous-time and discrete-time optimal control systems, giving students a firm grasp on both methods. Among this book's most outstanding features is a summary table that accompanies each topic or problem and includes a statement of the problem with a step-by-step solution. Students will also gain valuable experience in using industry-standard MATLAB and SIMULINK software, including the Control System and Symbolic Math Toolboxes.
Diverse applications across fields from power engineering to medicine make a foundation in optimal control systems an essential part of an engineer's background. This clear, streamlined presentation is ideal for a graduate level course on control systems and as a quick reference for working engineers.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
Chapter 1
Introduction
In this first chapter, we introduce the ideas behind optimization and optimal control and provide a brief history of calculus of variations and optimal control. Also, a brief summary of chapter contents is presented.
1.1 Classical and Modern Control
The classical (conventional) control theory concerned with single input and single output (SISO) is mainly based on Laplace transforms theory and its use in system representation in block diagram form. From Figure 1.1, we see that
(1.1.1) |
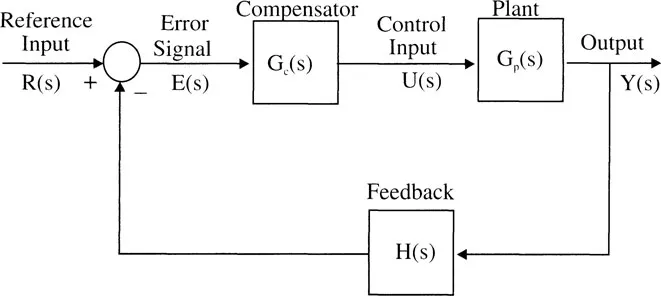
Figure 1.1 Classical Control Configuration
where s is Laplace variable and we used
(1.1.2) |
Note that
1. the input u(t) to the plant is determined by the error e(t) and the compensator, and
2. all the variables are not readily available for feedback. In most cases only one output variable is available for feedback.
The modern control theory concerned with multiple inputs and multiple outputs (MIMO) is based on state variable representation in terms of a set of first order differential (or difference) equations. Here, the system (plant) is characterized by state variables, say, in linear, time-invariant form as
(1.1.3) |
(1.1.4) |
where, dot denotes differentiation with respect to (w.r.t.) t, x(t), u(t), and y(t) are n, r, and m dimensional state, control, and output vectors respectively, and A is n×n state, B is nxr input, C is mxn output, and D is mxr transfer matrices. Similarly, a nonlinear system is characterized by
(1.1.5) |
(1.1.6) |
The modern theory dictates that all the state variables should be fed back after suitable weighting. We see from Figure 1.2 that in modern control configuration,
1. the input u(t) is determined by the controller (consisting of error detector and compensator) driven by system states x(t) and reference signal r(t),
2. all or most of the state variables are available for control, and
3. it depends on well-established matrix theory, which is amenable for large scale computer simulation.
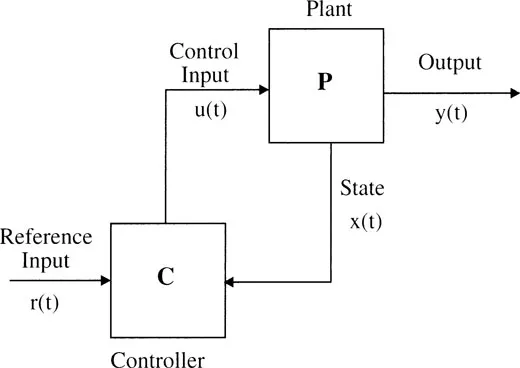
Figure 1.2 Modern Control Configuration
The fact that the state variable representation uniquely specifies the transfer function while there are a number of state variable representations for a given transfer function, reveals the fact that state variable representation is a more complete description of a system.
Figure 1.3 shows components of a modern control system. It shows three components of modern control and their important contributors. The first stage of any control system theory is to obtain or formulate the dynamics or modeling in terms of dynamical equations such as differential or difference equations. The system dynamics is largely based on the Lagrangian function. Next, the system is analyzed for its performance to find out mainly stability of the system and the contributions of Lyapunov to stability theory are well known. Finally, if the system performance is not according to our specifications, we resort to design [25, 109]. In optimal control theory, the design is usually with respect to a performance index. We notice that although the concepts such as Lagrange function [85] and V function of Lyapunov [94] are old, the techniques using those concepts are modern. Again, as the phrase modern usually refers to time and what ...
Table of contents
- Cover
- Half Title
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Dedication
- Table of Contents
- 1 Introduction
- 2 Calculus of Variations and Optimal Control
- 3 Linear Quadratic Optimal Control Systems I
- 4 Linear Quadratic Optimal Control Systems II
- 5 Discrete-Time Optimal Control Systems
- 6 Pontryagin Minimum Principle
- 7 Constrained Optimal Control Systems
- Appeddix A: Vectors and Matrices
- Appendix B:State Space Analysis
- Appendix C: MATLAB Files
- References
- Index
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription
No, books cannot be downloaded as external files, such as PDFs, for use outside of Perlego. However, you can download books within the Perlego app for offline reading on mobile or tablet. Learn how to download books offline
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 990+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn about our mission
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more about Read Aloud
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS and Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Yes, you can access Optimal Control Systems by D. Subbaram Naidu in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Technology & Engineering & Electrical Engineering & Telecommunications. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.