
- 766 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Model-Based Design for Embedded Systems
About this book
The demands of increasingly complex embedded systems and associated performance computations have resulted in the development of heterogeneous computing architectures that often integrate several types of processors, analog and digital electronic components, and mechanical and optical components—all on a single chip. As a result, now the most prominent challenge for the design automation community is to efficiently plan for such heterogeneity and to fully exploit its capabilities.
A compilation of work from internationally renowned authors, Model-Based Design for Embedded Systems elaborates on related practices and addresses the main facets of heterogeneous model-based design for embedded systems, including the current state of the art, important challenges, and the latest trends. Focusing on computational models as the core design artifact, this book presents the cutting-edge results that have helped establish model-based design and continue to expand its parameters.
The book is organized into three sections: Real-Time and Performance Analysis in Heterogeneous Embedded Systems, Design Tools and Methodology for Multiprocessor System-on-Chip, and Design Tools and Methodology for Multidomain Embedded Systems. The respective contributors share their considerable expertise on the automation of design refinement and how to relate properties throughout this refinement while enabling analytic and synthetic qualities. They focus on multi-core methodological issues, real-time analysis, and modeling and validation, taking into account how optical, electronic, and mechanical components often interface.
Model-based design is emerging as a solution to bridge the gap between the availability of computational capabilities and our inability to make full use of them yet. This approach enables teams to start the design process using a high-level model that is gradually refined through abstraction levels to ultimately yield a prototype. When executed well, model-based design encourages enhanced performance and quicker time to market for a product. Illustrating a broad and diverse spectrum of applications such as in the automotive aerospace, health care, consumer electronics, this volume provides designers with practical, readily adaptable modeling solutions for their own practice.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
Part I
Real-Time and Performance
Analysis in Heterogeneous
Embedded Systems
1
Performance Prediction of Distributed Platforms
1.1 System-Level Performance Analysis
1.1.1 Distributed Embedded Platforms
1.1.2 Role of Performance Analysis in the Design Process
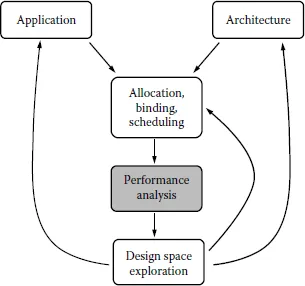
Performance analysis in the design space exploration cycle.
1.1.3 Approaches to Performance Analysis
Table of contents
- Cover
- Half Title
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Table of Contents
- Preface
- Introduction
- Contributors
- Part I Real-Time and Performance Analysis in Heterogeneous Embedded Systems
- Part II Design Tools and Methodology for Multiprocessor System-on-Chip
- Part III Design Tools and Methodology for Multidomain Embedded Systems
- Index
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app