Introduction
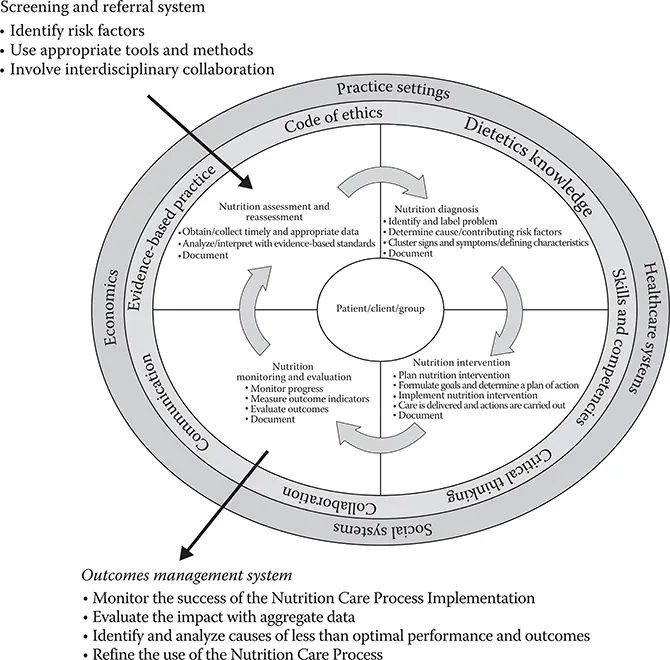
Nutrition screening and assessment are important steps in identifying individuals who may have nutrition-related health problem(s) and/or malnutrition. According to the American Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition (ASPEN), nutrition screening is defined as “a process to identify an individual who is malnourished or who is at risk for malnutrition to determine if a detailed nutrition assessment is indicated” [1]. Nutrition screening is mandated by the Joint Commission, and it must be completed within 24 h of admission in the acute care setting [2]. In most facilities, nursing staff complete the nutrition screen. A variety of nutrition screening tools have been developed and validated, including the Malnutrition Screening Tool (MST) and the Malnutrition Universal Screening Tool (MUST) [3]. In general, nutrition screening tools should be quick and easy to complete and validated for the population they will be used with. However, each healthcare system may establish institution-specific nutrition screening criteria that may not be exclusive to malnutrition. For example, some healthcare facilities may choose to include screening criteria to identify individuals who may benefit from nutrition education or who have food allergies. Individuals with a positive nutrition screen (i.e., presence of nutritional risk factors identified following completion of the screening) are selected to receive a nutrition assessment. ASPEN defines nutrition assessment as “a comprehensive approach to diagnosing nutrition problems that uses a combination of the following: medical, nutrition, and medication histories; physical examination; anthropometric measurements, and laboratory data” [1]. The Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics has created the Nutrition Care Process and Model (NCPM), with the first step being assessment. The Academy’s definition of assessment is more broad compared to the ASPEN criteria and is characterized as “a systemic approach to collect, record, and interpret relevant data from patients, clients, family members, caregivers, and other individuals and groups. Nutrition assessment is an ongoing, dynamic process that involves initial data collection as well as continual reassessment and analysis of the patient’s/client’s status compared to specific criteria” [4,5]. The four steps of the NCPM are described in Figure 1.1 [4].
FIGURE 1.1 Nutrition care process and model (NCPM). (From Lacey, K. and Pritchett, E., J. Am. Diet. Assoc., 103, 1061, 2003.)
Components of a Nutrition Assessment
Several validated nutrition assessment tools are widely referenced in the literature [6,7,8,9,10 and 11]. The Mini Nutritional Assessment (MNA®) has been validated among adults over age 65 who are malnourished or who are at risk for malnutrition [6,7 and 8]. The original MNA, now referred to the as the “full MNA,” consists of 18 questions and includes questions regarding dietary habits, living situation, use of prescription medications, self-view of nutritional status, mid-arm circumference (MAC), and calf circumference (CC) [8]. In addition to the “full MNA,” there is also the MNA-short form that has also been validated and only includes six questions. Due to increased ease of use, the MNA-short form is typically used in clinical practice and includes questions on food intake over the past 3 months, weight loss during the last 3 months, mobility, psychological stress over the past 3 months, neuropsychological problems (i.e., dementia or depression), and body mass index (BMI) [8]. Although the MNA has been validated among the elderly population, there is still debate about the sensitivity of this tool since its use has been associated with the “over-diagnosis” of malnutrition [7]. Although the ASPEN Clinical Guidelines for nutrition screening, assessment, and intervention in adults classify the MNA as a nutrition assessment tool [3], it is important to note, the MNA was originally developed as a screening tool to be used by non-RD practitioners. This is one reason debate exists whether the MNA is an appropriate assessment tool for “diagnosing” malnutrition.
A second nutrition assessment tool that has been validated and demonstrated to have excellent reliability is the Subjective Global Assessment (SGA) tool, described by Detsky and colleagues in 1987 [9]. This tool was designed to be easily used at the bedside without the need for specialized equipment to assess nutritional status [10 and 11]. This tool includes questions on weight and diet history, gastrointestinal symptoms, functional capacity, and physical assessment (subcutaneous fat or muscle loss, edema, and ascites [Figure 1.2]) [9]. Patients are classified as (1) well nourished, (2) moderately malnourished, or (3) severely malnourished [9]. This tool has been successfully used and validated in the surgical, oncology, HIV, acute kidney injury, chronic kidney disease, kidney and liver transplant, and elderly populations [10 and 11]. SGA has been positively regarded since it is simple and quick to administer, low-cost, requires no special equipment, and it assesses functional capacity [10,11]. It also has the advantage of excellent interobserver reproducibility [11]. Historically, some clinicians have been reluctant to use SGA due to unfamiliarity with conducting a nutrition-focused physical exam (NFPE), but this skill can be readily taught [10] and more training and standardized resources are available since NFPE is recognized as an important component of diagnosing malnutrition [12].
Jensen and colleagues have combined aspects of the MNA and SGA in their approach to nutrition assessment based on the joint ASPEN and Academy consensus guidelines on adult malnutrition [13,14] and our current understanding of inflammation in the pathogenesis of malnutrition [15]. The ASPEN and Academy consensus guidelines on adult malnutrition were developed to standardize the process for diagnosing malnutrition and to reduce confusion and possible misdiagnosis [14]. In addition, this approach is etiology based and criteria may change over time as validity evidence accrues. The identification of two or more of the following six criteria is needed for the diagnosis of malnutrition: insufficient energy intake, weight loss, loss of muscle mass, loss of subcutaneous fat, localized or generalized fluid accumulation that may mask weight loss, and diminished functional status measured by hand-grip strength [14]. Clinical characteristics for diagnosing malnutrition are defined in Table 1.1 [14].
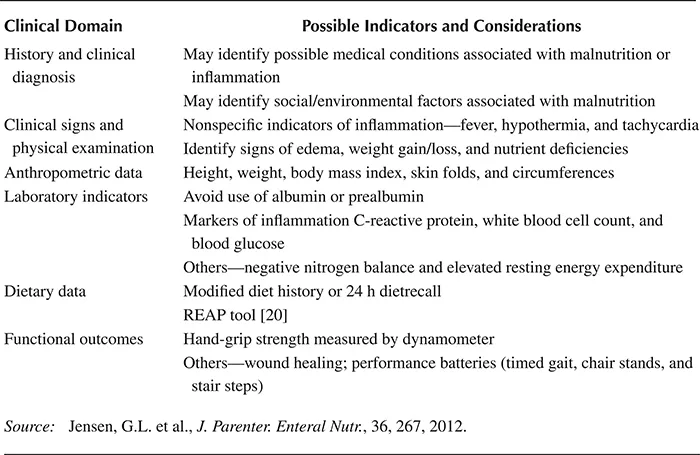
Jensen advocates a systematic approach to nutrition assessment based on six criteria, including history and clinical diagnosis, clinical signs and physical examination, anthropometric data, laboratory indicators of inflammatory response, dietary data, and functional outcomes (Table 1.2) [15]. The first step of the etiology-based approach to the diagnosis of malnutrition is identification of nutrition risk (compromised intake or loss of body mass), followed by the presence of inflammation (no/yes) [16]. Individuals identified at nutritional risk who are not experiencing inflammation are categorized as having starvation-related malnutrition (pure chronic starvation and anorexia nervosa) [16]. Individuals identified at nutritional risk who are experiencing inflammation are categorized into two groups based on the severity of the inflammatory response. Those identified with a mild-to-moderate degree of malnutrition are classified with chronic disease-related malnutrition (i.e., cancer, rheumatoid arthritis, and sarcopenic obesity), whereas those identified with a marked inflammatory response are classified with acute disease or injury-related malnutrition (i.e., major infection, burns, and trauma) [16]. A listing of acute and chronic conditions associated with the inflammatory response has been previously published [12]. Based on currently available data, the prevalence of malnutrition in the hospital setting is estimated to range from 15% to 60% [3].
FIGURE 1.2 Subjective global assessment (SGA). (From Detsky, A.S. et al., J. Parenter. Enteral. Nutr., 11, 8, 1987.)
TABLE 1.1
A.S.P.E.N./Academy Clinical Characteristics Supporting the Diagnosis of Malnutrition
TABLE 1.2
Systematic Approach to Nutrition Assessment
Many practitioners can proficiently review medical and dietary histories, anthropometric measurements, and laboratory indicators to determine the likelihood of nutritional problems. However, performing a nutrition-focused physical examination (NFPE) may be a new skill for some clinicians. Conducting a NFPE occurs after the other assessment criteria have been reviewed. This tool can be es...