
IoT
Security and Privacy Paradigm
- 381 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
IoT
Security and Privacy Paradigm
About this book
IOT: Security and Privacy Paradigm covers the evolution of security and privacy issues in the Internet of Things (IoT). It focuses on bringing all security and privacy related technologies into one source, so that students, researchers, and practitioners can refer to this book for easy understanding of IoT security and privacy issues.
This edited book uses Security Engineering and Privacy-by-Design principles to design a secure IoT ecosystem and to implement cyber-security solutions. This book takes the readers on a journey that begins with understanding the security issues in IoT-enabled technologies and how it can be applied in various aspects. It walks readers through engaging with security challenges and builds a safe infrastructure for IoT devices. The book helps readers gain an understand of security architecture through IoT and describes the state of the art of IoT countermeasures. It also differentiates security threats in IoT-enabled infrastructure from traditional ad hoc or infrastructural networks, and provides a comprehensive discussion on the security challenges and solutions in RFID, WSNs, in IoT.
This book aims to provide the concepts of related technologies and novel findings of the researchers through its chapter organization. The primary audience includes specialists, researchers, graduate students, designers, experts and engineers who are focused on research and security related issues.
Souvik Pal, PhD, has worked as Assistant Professor in Nalanda Institute of Technology, Bhubaneswar, and JIS College of Engineering, Kolkata (NAAC "A" Accredited College). He is the organizing Chair and Plenary Speaker of RICE Conference in Vietnam; and organizing co-convener of ICICIT, Tunisia. He has served in many conferences as chair, keynote speaker, and he also chaired international conference sessions and presented session talks internationally. His research area includes Cloud Computing, Big Data, Wireless Sensor Network (WSN), Internet of Things, and Data Analytics.
Vicente García-Díaz, PhD, is an Associate Professor in the Department of Computer Science at the University of Oviedo (Languages and Computer Systems area). He is also the editor of several special issues in prestigious journals such as Scientific Programming and International Journal of Interactive Multimedia and Artificial Intelligence. His research interests include eLearning, machine learning and the use of domain specific languages in different areas.
Dac-Nhuong Le, PhD, is Deputy-Head of Faculty of Information Technology, and Vice-Director of Information Technology Apply and Foreign Language Training Center, Haiphong University, Vietnam. His area of research includes: evaluation computing and approximate algorithms, network communication, security and vulnerability, network performance analysis and simulation, cloud computing, IoT and image processing in biomedical. Presently, he is serving on the editorial board of several international journals and has authored nine computer science books published by Springer, Wiley, CRC Press, Lambert Publication, and Scholar Press.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
1 Intrusion Detection and Avoidance for Home and Smart City Automation in Internet of Things
1.1 Introduction
- Smart city
- Smart roads
- Smart traffic lights
- Industrial applications
- Ozone presence
- Smart grids
- Industrial disaster prediction
- Smart home
- Wearables
- Smart water
- Chemical leakage detection
- Portable water monitoring
- Pollution-level analysis
- River floods
- Retail
- Industrial control systems
- Environment protection with sustainable resources
- Sea-based disaster prediction
- Air pollutions
- Forest fire detection
- Avalanche and landslide prevention
- Earthquake detection
- Snow-level monitoring
- Digital health and telemedicine
- Ultraviolet radiation
- Patient surveillance
- Smart agriculture
- Soil quality measurement
1.2 Key Modules and Components of an IoT Scenario
- Cloud
- Things or devices or gadgets
- User interface
- Gateway
- Interfacing modules
- Networks
- Storage panel
- Security mechanisms
- Communication platform
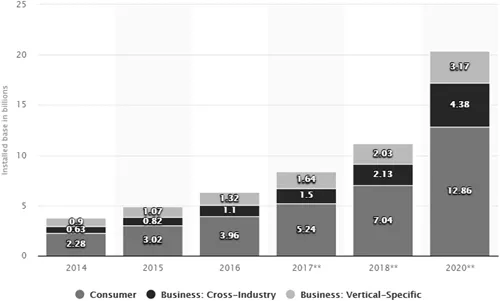
1.3 Global Scenario
1.4 Prominent Search Engines for Indexing IoT Devices
- shodan.io/
- iotcentral.io
- censys.io/
- thingful.net/
- iotcrawler.eu/
- iotscanner.bullguard.com/
- um.es/iotcrawler/
1.5 Shodan: An IoT Search Engine
Table of contents
- Cover
- Half-Title
- Series
- Title
- Copyright
- Contents
- Preface
- About the Book
- Editors
- Contributors
- Chapter 1 Intrusion Detection and Avoidance for Home and Smart City Automation in Internet of Things
- Chapter 2 Heterogeneous Intelligent Transportation Systems: Review of Cybersecurity Issues, EU Regulations, and Economics
- Chapter 3 Fog Platforms for IoT Applications: Requirements, Survey, and Future Directions
- Chapter 4 IoT-Based Smart Vehicle Security and Safety System
- Chapter 5 Smart Attendance Monitoring IoT-Based Device Using Cloud Services
- Chapter 6 Encryption of Data in Cloud-Based Industrial IoT Devices
- Chapter 7 Cyber Attack Analysis and Attack Patterns in IoT-Enabled Technologies
- Chapter 8 A Review of Cyber Attack Analysis and Security Aspect of IoT-Enabled Technologies
- Chapter 9 Authentication of Devices in IoT
- Chapter 10 Software-Defined Networks and Security of IoT
- Chapter 11 RSA-Based Remote User Authentication Scheme for Telecare Medical Information System
- Chapter 12 Illegitimate EPR Modification: A Major Threat in IoT-Based Healthcare System and Its Remedy through Blind Forensic Measures
- Chapter 13 IoT: Foundations and Applications
- Chapter 14 Physical Layer Security Approach to IoT
- Chapter 15 Tenable Irrigation System with Internet of Things
- Chapter 16 Privacy and Security Challenges Based on IoT Architecture
- Index
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app