Mobile Cellular Telephony is one of the greatest innovations of the twentieth century and today in the twenty-first century it can be safely said that it has brought nothing less than a revolution in the way communications take place across the globe.
The Mobile Cellular Telephony is enabled through a combination of cellular networks and mobile devices which communicate to each other by means of radio frequency spectrum (i.e. wirelessly). A cellular network consists of thousands of nodes that assist mobile device users in performing plethora of tasks. Mobile device has become the Third Screen after Television and Computer and is becoming more economical and powerful with continual technological advancements. There are more than 5 billion mobile subscribers in the world and for the very vast majority the mobile device has become a necessity and without it they can’t go about with their daily routine lives.
1.1Mobile Cellular Telephony Evolution
The cellular concept was conceived by Bell Laboratories in 1947 and enabled companies to provide wireless communications to a large population [1]. Like any other field of science and technology, mobile communications is continuously evolving and the sector has made astonishing progress in the last 70 years.
The first generation (1G) cellular networks was deployed in the 1980s, the second generation (2G) in the 1990s, while the third generation (3G) in the 2000s. Today, 4G (fourth generation) cellular networks are being deployed and the world is getting ready to embrace the fifth generation (5G) of mobile cellular telephony.
The 1G analog systems are no longer operational, which only provided voice services and had no support for data. The 2G digital systems are currently operational and support voice and limited data services. The 3G systems support voice, low speed data, and enable a number of data services. The 4G systems enable mobile broadband in the true sense, targeting 100 Mbps or higher on the move.
5G systems are expected to provide an enhanced mobile broadband targeting peak data rate of 20 Gbps, extend 4G’s Internet of Things capability, and enable mission-critical applications that require ultra-high reliability and low latency. 5G networks are expected to be designed by taking a user-centric approach.
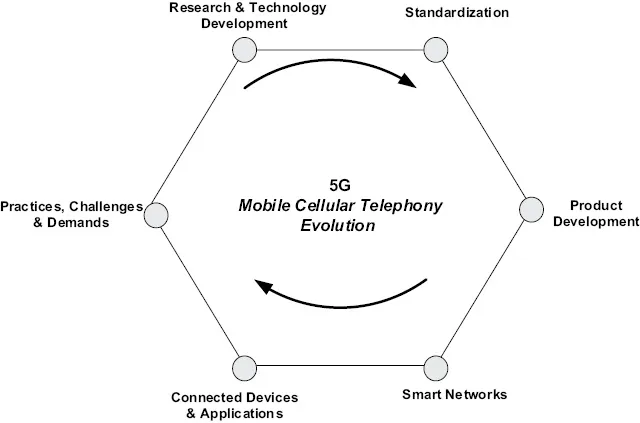
1.2Hexagon Based Mobile Cellular Telephony
A cellular network or mobile network is a wireless network spread over the land through a web of cell sites. Each of these sites or cell towers is comprised of a transceiver (transmitter/receiver) for communications with mobile devices. From a technological perspective, mobile devices rely on die hard cellular towers for communications and these cell sites or cell towers are designed to keep a hexagonal shape in mind. The use of hexagonal cells was invented by Bell Laboratories in the 1970s [2]. This shape was selected over other geometrical shapes since by using it the cells can be laid next to each other with no overlap, thus providing coverage theoretically to the entire service area without any gaps [3]. The hexagon design has been at least so far remained as necessary for mobile communications as cement for the construction of buildings or coal tar for carpeting the roads.
If we look at it from an end-to-end perspective, the key phases of the mobile cellular telephony can nicely fit on the six corners of the hexagon shape (Figure 1.1). These generic six phases are research and technology development, standardization, product development, network development, device and application development, and the sector’s practices and challenges.
Figure 1.1Key steps in mobile cellular telephony.
In a nutshell, though not necessary, research and technological development is the first step that leads into standardization followed by product development. Once telecom products are ready, they get deployed in the cellular networks. Device development usually lags behind network equipment production. Once networks are up and running and users are connected to networks through their devices, applications start to pour in; from there, the sectors begin to see the good or not-so-good practices, bottle necks and challenges, and new business demands which then leads back to the first step to start all over again.
1.3Manuscript Overview
This manuscript has been divided into the following six sections corresponding to the hexagonal cell.
Section I is on research, technology development, and the frequency spectrum. Like any field of science and technology, mobile communications also rely on research and technology development for progress and evolution. Chapter 2 discusses how these are currently capitalized in mobile networks and how these can be strengthened in the future. The topic of the radio frequency spectrum, which is controlled by governments, is discussed in Chapter 3. The ITU-R (International Telecommunications Union Radiocommunication Sector) process of frequency allocation and identification and some potential technical and financial solutions to address the spectrum needs of 5G are discussed in this chapter.
Section II looks into the element of standardization. Mobile communications is governed by global standards which are developed to achieve economies of scale and to attain many other benefits. Chapter 4 looks into the standardization of 5G along with the standardization processes of certain key standard development organizations (SDOs), ITU-T (ITU Standardization Sector) guidelines for establishing SDOs in developing nations, and a case study on the lack of research and standardization in OIC (Organization of Islamic Conference) member states. Chapter 5 summarizes certain key elements of 5G such as multiple access techniques, cognitive radio, massive cloud radio access network, vehicular communications, and network slicing. 5G is currently in the standardization phase and ITU is expected to approve the 5G standard in 2020.
Section III describes the key aspects of semiconductor development and product development. After standardization, the next step is to develop integrated circuits (ICs) conforming to standards, which is described in Chapter 6. Every piece of telecom equipment is equipped with ICs which is a set of electronic circuits on a small plate (chip) of semiconductor material, normally silicon. Various technologies for IC development along with a perspective on semiconductor business in Pakistan are presented in this chapter. The ICs along with components (shelves, chassis, nut, bolts, and so on) go into full scale product development. Chapter 7 presents a few such products, namely multimode base stations, 5G enabled base stations/small cells, and so on.
Section IV is all about networks covering the areas of radio access network, transport network, core network, and operation support systems. The section starts with defining the end-to-end cellular network architectures of 2G, 3G, 4G, and 5G in Chapter 8. The radio access network of 4G along with several advanced features of LTE-Advanced and LTE-Advanced Pro are discussed in Chapter 9. The requirements, architecture, and air interface of 5G NR (new radio) are also described in the same chapter. Chapter 10 starts off by defining traffic capacity requirements for 5G. It also discusses key technologies in three subareas of transport networks, namely mobile backhaul, metro transport network, and core transport network. A case study is also presented on the applicability of 80 GHz e-band microwave radios for the cellular and broadband providers of Pakistan. Chapter 11 provides an overview of the 4G Evolved Packet Core and evolving 5G NGC (Next Generation Core). CDN (Content Development Network), evolution of IMS (IP Multimedia Subsystem), and OSS (Operations Support Systems) are also discussed in the chapter.
Section V deals with connected devices and certain key mobile applications that are describ...