
- 166 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
About this book
"A systematic review of the structure and context of the blockchain-derived economic model... (the book) describes cryptoeconomics in connection with the game theory, behavioral economics and others in simple understandable language."—Wang Feng, founder of Linekong Interactive Group and Mars Finance, partner in Geekbang Venture Capital
Blockchain technology has subverted existing perceptions and is the start of an economic revolution, called, cryptoeconomics. Blockchain is a key component of cryptoeconomics. Vlad Zamfir, a developer of Ethereum, defines this term as "a formal discipline that studies protocols that governs the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services in a decentralized digital economy. Cryptoeconomics is a practical science that focuses on the design and characterization of these protocols".
This book explains the structures of blockchain-derived economic models, their history, and their application. It uses real-world cases to illustrate the relationship between cryptoeconomics and blockchain.
Blockchain technology solves trust issues. A blockchain application can restrict behavior on the blockchain through a reward and punishment system that enables consensus in an innovative way. The greatest significance of cryptoeconomics lies in guaranteeing safety, stability, activity, and order in a decentralized consensus system. Security and stability are achieved mainly by cryptographical mechanisms. Activity and order are achieved through economic mechanisms.
Cryptoeconomics and Blockchain: Ignighting a New Era of Blockchain discusses the most popular consensus algorithms and optimization mechanisms. With examples explained in clear and simple terms that are easy to understand, the book also explores economic mechanisms of blockchain such as game theory and behavioral economics.
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
Chapter 1
What Is Cryptoeconomics?
1.1 The Basics of Cryptography
1.1.1 Hash Algorithm
- Cryptographic hash functionA cryptographic hash function has the following characteristics:
- – Definiteness: no matter how many times are parsed in the same hash function, if the input is the same, the resulting output is always the same.
- – Efficiency of the calculations: the process of calculating hash values is very efficient.
- – Anti-preimage attack: for a given output, the input is irreversible.
- – The influence of subtle changes: subtle changes in any input can have a dramatic effect on the output of the hash function.
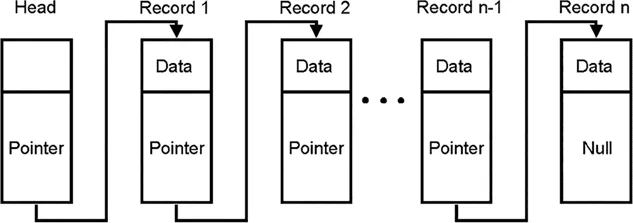
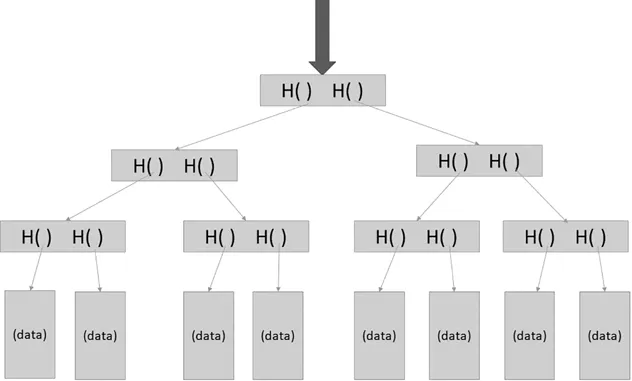
The cryptographic hash function is very important for the security on blockchain and the mining. - Data structureIn cryptography, there are two kinds of data structures which are important for understanding blockchains: linked list and hash pointer.The linked list is a data block that is sequentially connected in order, as shown in Figure 1.1.A blockchain is essentially a linked list in which each new block contains a hash pointer. The pointer points to the hash of the previous block and all the data it contains. With it, the blockchain has great features that cannot be changed.So how does the blockchain achieve immutability?If someone tries to tamper with the data in the block, let’s look at the third feature of the cryptographic hash function: “The effect of subtle changes is that any slight change in the input will have a dramatic impact on the output of the hash function”. So, even if someone tries to rewrite the data in the block subtly, it will also cause a huge change in the hash value of Block 1 stored in Block 2, which will cause changes in the hash value of Block 2. The change, in turn, affects the hash value stored in Block 3. No. 3 affects No. 4, No. 4 affects No. 5…. Eventually, the data on the entire blockchain will change. This way of modifying data by freezing the entire chain is almost impossible. Therefore, the blockchain is considered as immutable.Each block has its own Merkle root. If multiple transactions are included in each block and these transactions are stored linearly, the process of finding a particular transaction in all transactions can become very complicated. That’s why we use the Merkel tree.As it is shown in Figure 1.2, in the Merkel tree, all individual transactions can be traced back to the same root through a hash algorithm, which makes searching very easy. Therefore, if we want to get a specific data in the block, we can search directly through the hash value in the Merkel tree without linear access.
- MiningThe hash algorithm is very important for mining new encrypted blocks, and its working principle is the adjustment of the difficulty value. A random string named “nonce” is added to the hash of the new block and then hashed again. Next, check if it is lower than the set difficulty level. If it is lower, the resulting new block will be added to the chain, and the miner responsible for mining will be rewarded. If it is not lower, then the miner continues to modify the random string “nonce” until the value appears below the difficulty level.
1.1.2 Key Encryption
1.1.3 Digital Signature
- ■ Verifiability: this signature should prove that it is indeed your handwriting.
- ■ Unforgeability: no one else can forge your signature.
- ■ Non-repudiation: if you sign your document with your own signature, the validity of the file will not be reclaimed, and you can’t claim that someone else is signing you instead.
Table of contents
- Cover
- Half Title
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Table of Contents
- Foreword
- Preface
- Authors
- 1 What Is Cryptoeconomics?
- 2 Mechanisms of Consensus
- 3 Optimized Consensus Mechanism