
eBook - ePub
Thoracic Imaging
Illustrated Clinical Cases, Second Edition
- 212 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
About this book
The chest radiograph is a ubiquitous, first-line investigation and accurate interpretation is often difficult. Radiographic findings may lead to the use of more sophisticated imaging techniques, such as multidetector computed tomography (MDCT) and positive emission tomography. Containing 100 challenging clinical cases and illustrated with superb, h
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription.
At the moment all of our mobile-responsive ePub books are available to download via the app. Most of our PDFs are also available to download and we're working on making the final remaining ones downloadable now. Learn more here.
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 1000+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn more here.
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more here.
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS or Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Yes, you can access Thoracic Imaging by Sue Copley,David Hansell,Jeffrey Kanne in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Medicine & Cardiology. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.
Information
QUESTION 1
1 | A 21-year-old female from Zambia presented with a fever, night sweats and malaise. She had developed the symptoms several weeks before presentation. On examination she was not clubbed and had a slight pyrexia (37.5°C). She was not immunocompromised (CD4 count normal) and had a mild leucocytosis. Her chest radiograph is shown (1). |
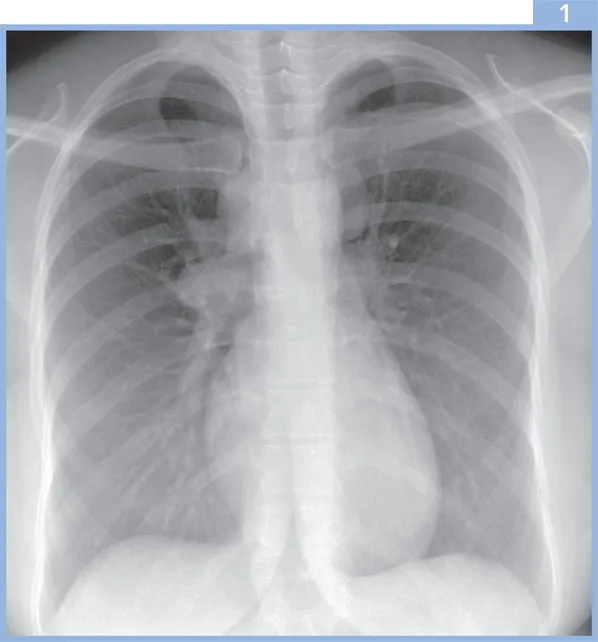
i. | What are the possible diagnoses? |
Answer 1
1i. | The chest radiograph shows right paratracheal, right hilar and left superior mediastinal lymphadenopathy. The diagnosis was primary tuberculosis (TB). The radiological differential also includes lymphoma, metastatic disease (less likely in view of the patient’s age) and sarcoidosis. |
The radiographic features typical of primary TB include a focal pneumonia and lymphadenopathy in the adjacent lymph drainage pathway. The hilar lymphadenopathy is often unilateral with contiguous mediastinal node involvement. Lymphadenopathy may be more prominent in patients of African or Asian origin. The right lung is more commonly involved than the left, and lymph nodes may cause airway narrowing, resulting in segmental or lobar atelectasis. Cavitation has been described in 10–30% of cases. Occasionally, when no cavitation is identified, the radiographic features of primary TB may be indistinguishable from other bacterial pneumonias; however, radiographic abnormalities tend to resolve fairly promptly with appropriate treatment in the latter, whereas radiographic resolution may be slow in TB. The pulmonary disease normally resolves completely, but in approximately 20% of cases, there may be a small calcified residual scar (Ghon focus). The finding may be associated with a calcified mediastinal lymph node (together termed Ranke complex). | |
The radiographic features of pulmonary TB in AIDS depend on the CD4 lymphocyte count. If the count is greater than 200/mm3, the features tend to be those of postprimary TB. However, if the CD4 count is less than 200/mm3, the features are usually those of primary TB, despite the circumstantial evidence that these cases represent reactivation of previously acquired infection. |
QUESTION 2
2 | A 60-year-old male presented with dyspnoea, wheeze and stridor occurring several months previously. He had a history of intermittent painful swelling of his auricular cartilage. He had no other relevant past medical history. His blood tests were normal. Lung function tests showed an obstructive defect. The chest radiograph was normal. An inspiratory CT was performed (2a), viewed on soft tissue windows, supplemented with end-expiratory images (2b), viewed on lung windows. |
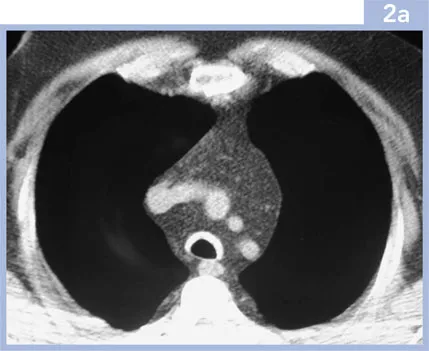
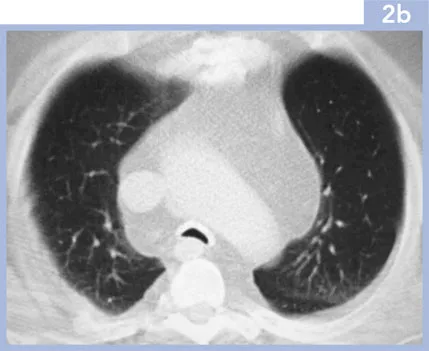
i. | What is the abnormality? |
ii. | What is the likely diagnosis? |
iii. | What are the treatment options? |
Answer 2
2i. | The CT images show abnormality of the trachea, which is thick-walled and calcified, with sparing of the posterior tracheal membrane. On the end-expiratory images there is tracheal collapse with the posterior membrane bowed anteriorly. Note the excessive mediastinal fat in this patient, who had been treated with corticosteroids for several months. |
ii. | The appearances are those of relapsing polychondritis, a rare disease of unknown aetiology characterised by recurrent inflammation of cartilage. The differential diagnosis includes tracheobronchopathia osteochondroplastica and amyloidosis (which also affects the posterior tracheal membrane, which is spared in this patient). Structures that are most often affected by relapsing polychondritis include the nasal cartilage, the pinna and the cartilage-containing large airways. The disease is commonest in the fifth decade and there is an equal sex incidence. There is an association with other autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis. Histopathological findings are chondral and perichondral inflammation with chondrolysis. |
Respiratory tract involvement is a common and potentially life-threatening complication and may involve the large, cartilage-containing airways from the trachea to the segmental bronchi. The stenoses may be multiple, single, dynamic or fixed, and diffuse involvement may occur. The chest radiograph is often normal, although areas of atelectasis may be seen. CT demonstrates airway thickening, calcification and collapse on end-expiration. Multiplanar reconstructions may be useful to guide treatment such as stenting. | |
iii. | The treatment options include long-term steroids (as in this patient) to reduce airway inflammation, although more invasive techniques, such as tracheostomy or airway stenting, may be required. |
QUESTION 3
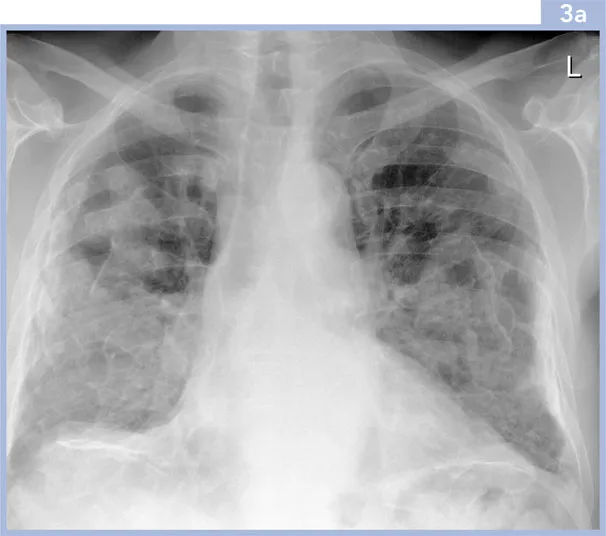
3 | A 67-year-old male presented with a productive cough. He had worked as a packer in an asbestos factory. He had never smoked and did not keep any pets. The patient was well on examination with no abnormal physical signs. Serum biochemistry and full blood count were normal. Spirometric and plethysmographic lung function indices were normal. |
i. | What does the chest radiograph (3a) show? |
ii. | What is the likely cause? |
Answer 3
3i. | The chest radiograph shows irregular confluent opacities projected over both lungs and the diaph... |
Table of contents
- Cover
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Table of Contents
- Preface
- List of Abbreviations
- Glossary
- Clinical Cases
- Further Reading & Useful Websites
- Index