
- 208 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
Investigative Rhinology
About this book
Rhinitis is the most common immunological disorder in man, with a marked effect on quality of life and significant co-morbid associations. Consequently, it is necessary to take rhinitis seriously and to attempt as precise a diagnosis as possible, if treatment is to be successful. This comprehensive text provides information on rhinitis, including such topics as the importance of rhinitis and its causes. It covers the most up-to-date methods of diagnosis such as airway testing, mucociliary clearance, imaging and more. Written by internationally respected experts, Investigative Rhinology provides a full and up-to-date guide to the investigations to be undertaken.
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription.
No, books cannot be downloaded as external files, such as PDFs, for use outside of Perlego. However, you can download books within the Perlego app for offline reading on mobile or tablet. Learn more here.
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 1000+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn more here.
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more here.
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS or Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Yes, you can access Investigative Rhinology by Glenis K. Scadding,Valerie J Lund in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Medicine & Clinical Medicine. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.
Information
1
The importance of rhinitis
Rhinitis which is defined clinically (Box 1.1), is the commonest immunological disorder in man. Recent figures suggest that it is a global problem affecting between 10 and 25% of individuals in different countries with increasing prevalence (Figure 1.1).
Box 1.1 Definition of rhinitis.
Rhinitis is an inflammatory disorder of the nasal mucosa characterized by two or more of the following symptoms:
rhinorrhoea (anterior and/or posterior)
blockage
itching/sneezing
Table 1.1 Rhinitis and asthma: quality of life.
Classically rhinitis has been described as a disease of no importance ‘except to those who suffer from it’. In fact the symptoms have a marked effect upon quality of life similar to that experienced by sufferers with mild to moderate asthma and chronic back pain (Table 1.1). It is also a cause of missed attendance at both workplace and school (3–4% of the United States population), and of reduced productivity at both places (30–40%). The economic impact of rhinitis, or rhinosinusitis as it should be known since the sinus mucosa is nearly always involved, is significant: an estimated $5 billion per annum in the United States in 1996.
Rhinitis has significant comorbid associations related to its intimate connections between the nose, the sinuses, the middle ear and the lungs (Figure 1.2). These include asthma, sinusitis, pharyngitis, otitis media with effusion and sleep problems. Most is known about the rhinitis–asthma link (Box 1.2 and Figure 1.3).
The mechanisms of interaction between the nose and chest are not fully elucidated – certainly the ciliated pseudocolumnar respiratory epithelium is continuous from just inside the nose to the smaller bronchi and is likely to react in similar fashion all along its length. Other factors probably include nasal obstruction leading to mouth breathing and loss of the normal filtration, warming and humidification of inspired air. The passage of postnasal secretions containing inflammatory or infectious mediators is unlikely to cause significant lower respiratory problems since it normally passes into the posterior pharynx and is swallowed rather than being inhaled. Naso-sino-bronchial reflexes exist; systemic connections between the nose and lungs involving the production and release of eosinophil precursors bearing high affinity IL-5 (interleukin-5) receptors have been demonstrated. Nitric oxide, predominantly produced in the sinuses and upper respiratory tract, may also be relevant (see Chapter 7).
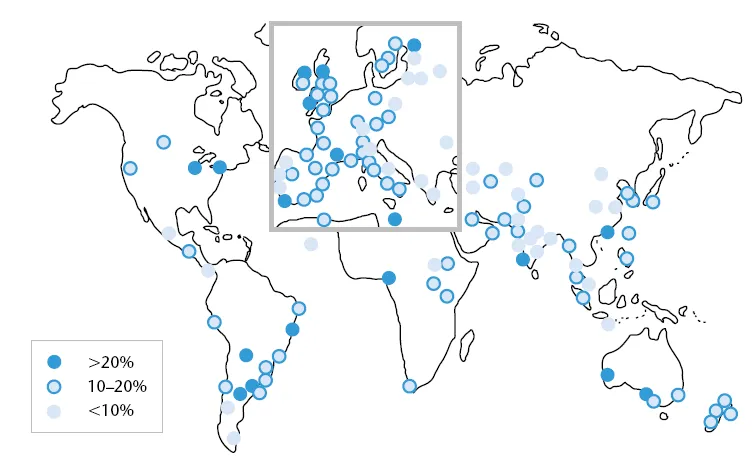
Figure 1.1 The global prevalence of seasonal allergic rhinitis in 13–14-year olds: ISAAC. Data from the International Study of Asthma and Allergies in childhood. (Source: Strachan et al. 1997.)
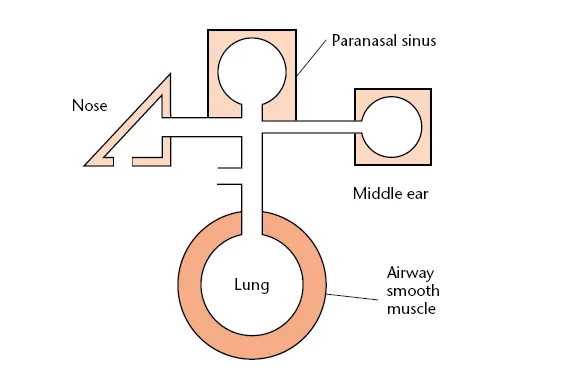
Figure 1.2 Nasal connections.
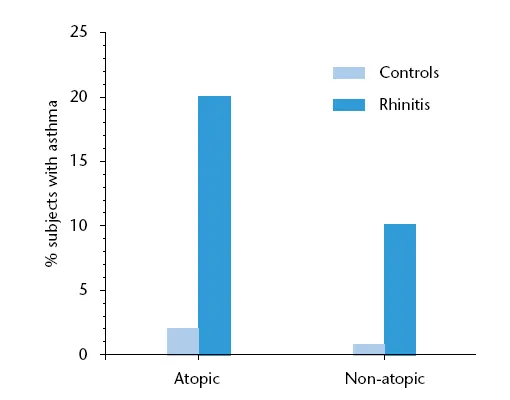
Figure 1.3 Rhinitis, both atopic and non-atopic, is a risk factor for subsequent asthma. (Source: Leynaert et al. 1999.)
Box 1.2 The rhinitis/asthma link.
Most asthma patients also suffer from rhinitis
Rhinitis, both allergic and non-allergic is a risk factor for the development of asthma (Figure 1.3)
Most asthma exacerbations start with upper respiratory tract inflammation – often viral, allergic or both
Rhinitis causes bronchial hyper-reactivity (BHR)
Treatment of rhinitis can decrease BHR and symptoms of asthma and reduce the need for emergency treatment
Thus, it is necessary to take rhinitis seriously to attempt as precise a diagnosis as possible, and to aim for successful treatment. The ARIA (Allergic Rhinitis and its Impact on Asthma, (Figure 1.4) guidelines provide a treatment plan for allergic rhinitis based on timing and severity (Figures 1.5 and 1.6).

Figure 1.4 The ARIA (Allergic Rhinitis and its Impact on Asthma) logo.
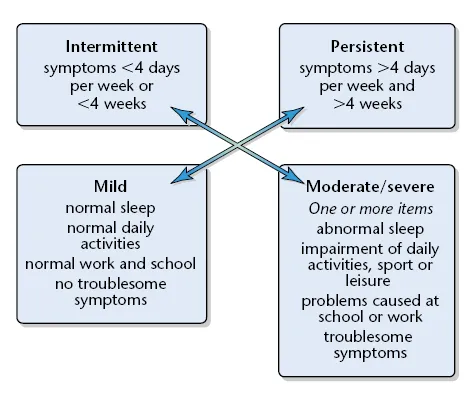
Figure 1.5 Classification of allergic rhinitis
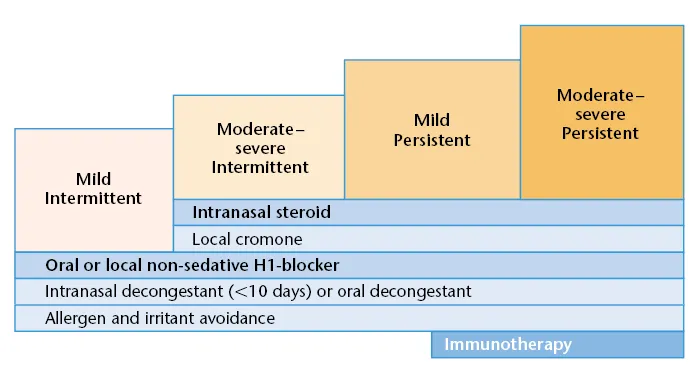
Figure 1.6 The treatment plan for allergic rhinitis based on severity and duration according to the ARIA guidelines.
References
Bousquet J, Bullinger M, Fayol C, Valentin B, Bustin B (1994a) Assessment of quality of life in patients with perennial allergic rhinitis with the French version of the SF-36 Health Status Questionnaire, J Allergy Clin Immunol 94(2pt1): 182–8.
Bousquet J, Khani J, Dhivert H et al. (1994b) Quality of life in asthma I. Internal consistency and validity of the SF-36 questionnaire, Am J Resp Crit Care Med 149(2Pt1): 371–5.
Leynaert B, Bousquet J, Neukirch C, Liard R, Neukirch F (1999) Perennial rhinitis: an independent risk factor for asthma in nonatopic subjects: results from the European Community Health Survey, J Allergy Clin Immunol 104(2Pt1): 301–4.
Strachan D, Sibbald B, Weiland S et al. (1997) Worldwide variations in prevalence of symptoms of allergic rhinoconjunctivitis in children: the International Study of Asthma and Allergies in Childhood (ISAAC), Pediatr Allergy Immunol 8: 161–76.
Further reading
Bousquet J, van Cauwenberge P, Khaltaev N and the ARIA workshop panel (2001) World Heath Organization Initiative: Allergic Rhinitis and its Impact on Asthma (ARIA), J Allergy Clin Immunol 108: 147–334.
Ray NF, Baraniuk JN, Thamer M et al. (1999) Healthcare expenditures for sinusitis in 1996: contribution of asthma, rhinitis and other airway disorders, J Allergy Clin Immunol 103: 409–14.
Table 1.1 Rhinitis and asthma: quality of life.
| Health concept | Mean quality of life score (scale: 1–100) | |
|---|---|---|
| Asthma (n = 252) | Rhinitis (n = 111) | |
| Physical functioning | 80 | 89 |
| Social functioning | 84 | 73 |
| Role limitation (physical) | 66 | 61 |
| Role limitation (emotional) | 70 | 64 |
| Mental health | 66 | 65 |
| Energy/fatigue | 59 | 55 |
| Pain | 74 | 77 |
| Change in health (1 year) | 55 | 50 |
| General health perception | 57 | 62 |
1. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1994; 149: 373
2. J Allergy Clin Immunol 1994; 94: 186
(Source: Bousquet et al. 1994a, b.)
2
Causes of rhinitis
The recent ARIA (Allergic Rhinitis and its Impact on Asthma)...
Table of contents
- Cover Page
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Preface
- 1 The importance of rhinitis
- 2 Causes of rhinitis
- 3 Making a diagnosis: history
- 4 Examination
- 5 Investigations
- 6 Airway tests
- 7 Tests of the mucociliary apparatus, inflammation and cystic fibrosis
- 8 Imaging
- 9 Other tests
- Appendix 1
- Appendix 2
- Appendix 3
- Appendix 4
- Appendix 5
- Appendix 6
- Appendix 7