
Freeze Drying of Pharmaceutical Products
- 192 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Freeze Drying of Pharmaceutical Products
About this book
Freeze Drying of Pharmaceutical Products provides an overview of the most recent and cutting-edge developments and technologies in the field, focusing on formulation developments and process monitoring and considering new technologies for process development.
This book contains case studies from freeze dryer manufacturers and pharmaceutical companies for readers in industry and academia. It was contributed to by lyophilization experts to create a detailed analysis of the subject matter, organically presenting recent advancements in freeze-drying research and technology. It discusses formulation design, process optimization and control, new PAT-monitoring tools, multivariate image analysis, process scale-down and development using small-scale freeze-dryers, use of CFD for equipment design, and development of continuous processes.
This book is for industry professionals, including chemical engineers and pharmaceutical scientists.
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
1 The Freeze-Drying of Pharmaceutical Products
Introduction and Basic Concepts
Contents
- 1.1 Introduction
- 1.2 Freeze-Drying Equipment
- 1.3 Process Objectives and Constraints
- 1.4 Mathematical Modelling and Process Design
- 1.5 Open Issues
- 1.5.1 Formulation Design
- 1.5.2 Process Monitoring and Control
- 1.5.3 Small-Scale Freeze-Dryers
- 1.5.4 Continuous Freeze-Drying
- 1.5.5 Equipment Design
- References
1.1 Introduction
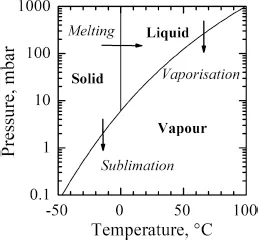
1.2 Freeze-Drying Equipment
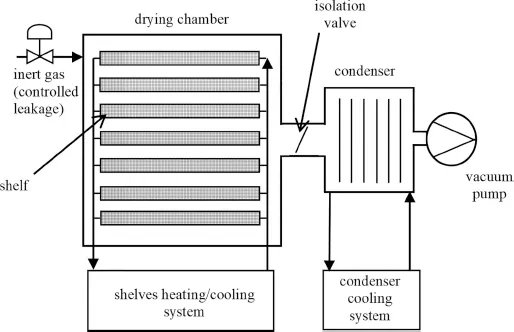
- The “ice fog” technique: ice crystals are formed in the drying chamber when a flow of nitrogen at very low temperature is introduced in the humid drying chamber (Patel et al. 2009). As an alternative, the ice fog may be obtained in the condenser where a certain amount of water is atomized, provided that the temperature of the condenser has been lowered (Ling 2011; Thompson 2013; Wollrath 2019). Once the ice crystals are obtained, they enter the vials, causing nucleation. The main concern of this technique is related to obtaining a uniform distribution of the ice crystals in the chamber, in such a way that ice nucleation occurs effectively at the same time in all the vials.
- Ultrasonic vibrations (at frequencies above 10 kHz): they can cause the formation of small-size gas bubbles that rapidly grow and collapse. This causes very high pressure and temperature fluctuations that induce ice nucleation (Morris et al. 2004; Nakagawa et al. 2006)
- Pressurization/depressurization: Konstantinidis et al. (2011) proposed a method based on the creation of a pressure fluctuation as a method to induce ice nucleation. The chamber of the freeze-dryer, after vials loading, is pressurized with argon to about 2.80–2.95 bar (26–28 psig) at the beginning of the run. Then, when the target nucleation temperature is reached, the pressure is rapidly reduced to almost atmospheric pressure (about 1 psig) to induce nucleation.
- Vacuum-induced surface freezing: when the desired nucleation temperature is reached, chamber pressure is reduced for a short time interval. This causes water evaporation at the top of the product and causes ice nucleation (Kramer et al. 2002; Liu et al. 2005; Oddone et al. 2014).
1.3 Process Objectives and Constraints
1.4 Mathematical Modelling and Process Design
Table of contents
- Cover
- Half Title
- Series
- Title
- Copyright
- Contents
- Series Preface
- Preface
- Editors
- Contributors
- Chapter 1 The Freeze-Drying of Pharmaceutical Products: Introduction and Basic Concepts
- Chapter 2 Formulation Design and Optimization Using Molecular Dynamics
- Chapter 3 Established and Novel Excipients for Freeze-Drying of Proteins
- Chapter 4 Infrared Imaging and Multivariate Image Analysis (MIA): A New PAT for Freeze-Drying Monitoring and Control
- Chapter 5 Through-Vial Impedance Spectroscopy (TVIS): A New Method for Determining the Ice Nucleation Temperature and the Solidification End Point
- Chapter 6 Innovations in Freeze-Drying Control and In-Line Optimization
- Chapter 7 Use of a Micro Freeze-Dryer for Developing a Freeze-Drying Process
- Chapter 8 Continuous Manufacturing in Lyophilization of Pharmaceuticals: Drawbacks of Batch Processing, Current Status, and Perspectives
- Chapter 9 Use of CFD for the Design and Optimization of Freeze-Dryers
- Index