
Corrosion Protection for the Oil and Gas Industry
Pipelines, Subsea Equipment, and Structures
- 170 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Corrosion Protection for the Oil and Gas Industry
Pipelines, Subsea Equipment, and Structures
About this book
Corrosion Protection for the Oil and Gas Industry: Pipelines, Subsea Equipment, and Structures summarizes the main causes of corrosion and requirements for materials protection, selection of corrosion-resistant materials and coating materials commonly used for corrosion protection, and the limitations to their use, application, and repair.
This book focuses on the protection of steels against corrosion in an aqueous environment, either immersed in seawater or buried. It also includes guidelines for the design of cathodic protection systems and reviews of cathodic protection methods, materials, installation, and monitoring. It is concerned primarily with the external and internal corrosion protection of onshore pipelines and subsea pipelines, but reference is also made to the protection of other equipment, subsea structures, risers, and shore approaches. Two case studies, design examples, and the author's own experiences as a pipeline integrity engineer are featured in this book. Readers will develop a high quality and in-depth understanding of the corrosion protection methods available and apply them to solve corrosion engineering problems.
This book is aimed at students, practicing engineers, and scientists as an introduction to corrosion protection for the oil and gas industry, as well as to overcoming corrosion issues.
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
1 |
Introduction |
2 | Corrosion |
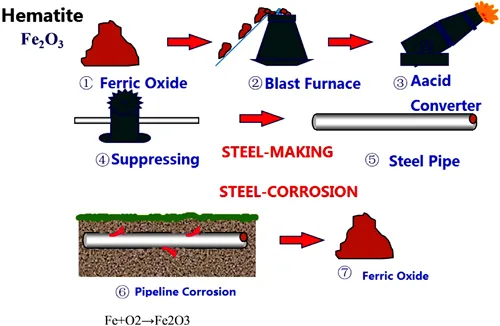
Table of contents
- Cover
- Half-Title
- Title
- Copyright
- Contents
- Preface
- Acknowledgements
- Author
- Chapter 1 Introduction
- Chapter 2 Corrosion
- Chapter 3 External Corrosion Protection
- 3.3 Cathodic Protection
- 3.4 Galvanic Zinc application
- Chapter 4 Internal Corrosion Protection
- Chapter 5 Atmospheric Corrosion
- Chapter 6 Stray Current Corrosion
- Chapter 7 Case Study
- Chapter 8 Corrosion Failures: Gas Pipeline Explosion
- References
- Key Terms and Definition
- Index