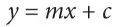1
Machine Learning Architecture and Framework
Nilanjana Pradhan* and Ajay Shankar Singh
School of Computer Science and Engineering, Galgotias University, Greater Noida, Uttar Pradesh, India
Abstract
Machine Learning is one of the fastest developing fields in computer science with wide range of applications. The machine learning architecture involves lot of complexity. The machine learning architecture will implement learning algorithm in the application engine which will perform the predictions, perform various complex queries in database and finally use analytics tools to produce predictions based on application areas. An effective machine learning architecture helps in designing better data centers, promote human welfare, solving critical system failures. A good architecture will cover all important risks involved with data privacy and security areas. In order to set up an effective machine learning architecture the problem area must be well defined. Training data (text, images, audio, video, structured data, user generated content etc.) must be collected for machine learning development process. In most cases data are incorrect and useless. The quality of the data matters in building and effective ML system. Good data visualization, data filtering, encryption tools and analytics tools are required. The machine learning system must be tested with test data. The model must get validated. In business domain ML algorithms are implemented on business processes, business services, people, skills, culture, risk management, partners, business functions, business organization.
Keywords: Machine learning, analytics, encryption, prediction, algorithm
1.1 Introduction
Machine learning is a branch of AI in which we require large volume of data and analyze those data with efficient algorithm. It aims at extracting knowledge or patterns from a large volume of observations. In supervised learning the observations contains data which trains the machine learning system to recognize certain rules.
ML systems recognize patterns from input data and predict or classify an object. In reinforcement learning, given evaluations help in distinguishing the situation. Examples are various types of ML applications which make a computer capable of playing games or drive vehicles. Machine learning emerged from artificial intelligence; however it focuses more on cognitive learning. AI attempts to model human function and intelligence which helps to resolve various problems. An important aspect of ML that makes it particularly appealing in terms of business is that it does not require as much explicit programming in advance to acquire intelligent insight. This ability uses various learning algorithms that simulate some human intelligence. Once data is collected and prepared for machine learning, algorithms are selected, modeled and interpreted [1]. Every learning system progresses through various learning iterations on its own to reveal hidden business value from data. Machine learning does not require too much of advance programming. Large amount of raw data is required coupled with high computing power on the execution platform to perform all the computations required for learning. However programming is still required for the application of machine learning, especially if it is applicable to automation.
The fundamental of ML involves large volumes of information data for the learning procedure. This information could emerge out of an assortment of sources, for example, venture frameworks, centralized server databases, and IoT edge gadgets. IT may be organized or unstructured in nature. Extremely high volumes of information are frequently nourished into machine since more information regularly yields better bits of knowledge. In this computerized business time, different sources and volumes of data are detonating. Learning in ML is commonly utilized for business reason for existing is either directed or unaided. In these classifications, be that as it may, there is a wide range of sorts of calculations and ML schedules, which are utilized to achieve different goals.
There are various eager learning methods which start computing before receiving new test data. They generally depend more on upfront evaluation of training data in order to predict without the need for new data. As a result, eager learning methods tend to spend more time on processing the training data. Another kind of learning method known as lazy learning method delays processing and data evaluation until it is fed with new test data. Machine learning is used to provide results that are either predictive, i.e. provide forecasts, or prescriptive, i.e. suggests recommended actions. Various data sets and feature regions are required for investigation using machine learning algorithm [1]. This yield information is by and large put away for examination and conveyed as reports and encouraged as contribution to other venture applications or frameworks.
The large volume of data that are collected from IoT sensors and other new information sources is increasing the capabilities of businesses to evaluate them and retrieve value and insights from them. Machine learning can relatively quickly and efficiently evaluate these mountains of data; many businesses are capturing the opportunity to discover the hidden insights that could deliver a competitive edge.
1.2 Machine Learning Algorithms
As of late individuals crosswise over various controls are exploring artificial intelligence to enhance their professional work. Artificial intelligence is used by economists to foresee future market costs in order to make a benefit. In restorative science [1], computer based intelligence is utilized to arrange whether a tumor is harmful or not. In meteorology AI is used for weather prediction. AI is used by human resource recruiters to analyze the résumé of applicants which helps in finding out if the applicant meets the minimum criteria for job. To achieve all these application of AI we need to implement machine learning algorithms. Every machine learning enthusiast begins with learning various ML algorithms and then moves toward building the ML architecture for various applications.
1.2.1 Regression
Regression is actually a method of building predictive model. This algorithm is mainly used for forecasting a predictive analysis. Here a set of predictor variables predicts an outcome, i.e. dependent variable. Regression estimates the relationship between one dependent and one independent variable and determines the strength of predictors and effect of forecasting. Various kinds of regressions are linear regression, multiple regression, logistic regression, ordinal regression, multinomial regression, and discriminant regression [2].
In the above figure the x hub speaks to autonomous variable and y— pivot speaks to subordinate variable. The dots represent the various observations. We need to minimize the error, i.e. the difference between estimated value and the actual value.
1.2.2 Linear Regression
One of the most well known algorithms in machine learning is linear regression. Machine learning helps in reducing the error of a predictive model resulting in making most accurate predictions. One of the examples of both statistical algorithm and machine learning algorithm is linear regression. Linear regression which is a linear model establishes a linear relationship between input variables and a single output variable [2]. If there are multiple input variables it is known as multiple linear regression. In simple regression problem the model is represented by
where x represents the in...