
This book is available to read until 12th May, 2026
- 288 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
Available until 12 May |Learn more
Basic Motorsport Engineering
About this book
Motorsport is not just about the spectacle of some of the world's most popular and famous sporting events - it also plays a crucial role in developing new techniques and technologies.
Each unit in the IMI and EAL level 2 courses are covered in full, and the chapters can be easily matched to the BTEC First course structure. The book covers introductory topics in motorsport from vehicle science and maths through the basics of vehicle maintenance to pre and post race inspections.
Written by an experienced teacher and author with decades of involvement with the industry, packed with detailed colour illustrations and learning tips, Basic Motorsport Engineering is the perfect textbook for you to make the first move into this most dynamic of industries.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information

Body and Chassis
KEY POINTS
- Most vehicles are front-wheel drive layout; alternative layouts are: conventional, mid-engine, and rear engine.
- The chassis is load bearing and must be free of corrosion.
- Jacking points and seat belt mounting points are specially reinforced.
- Air bags must only be handled following a special procedure.
- SIPS and crumple zones are sometimes added to give extra passenger protection.
On most popular cars the body and the chassis are one and the same. Trucks and buses, however, are likely to have the body and the chassis as separate components. Motorsport vehicles may use either arrangement. The chassis is the part to which the engine, gearbox, suspension and other components are attached. The body is the covering for the components, the passengers and the load. The chassis is load bearing, being made from strong steel. The body does not carry a load and may be made from aluminium alloy, or some form of plastic, as well as the more usual steel.
1. VEHICLE LAYOUT
By vehicle layout we mean the position of the engine and gearbox on the chassis in relation to the driving wheels.
Front-wheel drive (FWD) is the most common; the engine and the gearbox are mounted at the front of the car and short driveshafts take the power to the front wheels.
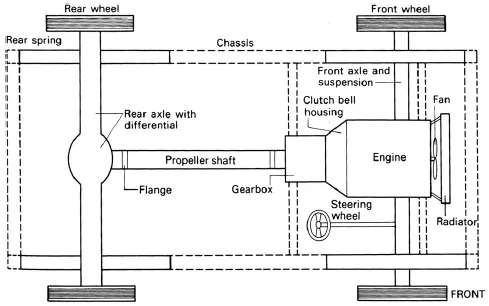
Conventional layout means that the engine is mounted at the front with a gearbox behind it and a propeller shaft takes the power to a rear axle so that the rear wheels are driven.
Rear-engined vehicles drive the rear wheels from a rear-mounted engine (RWD).
FIGURE 1.1 Front engine front wheel drive (FWD)
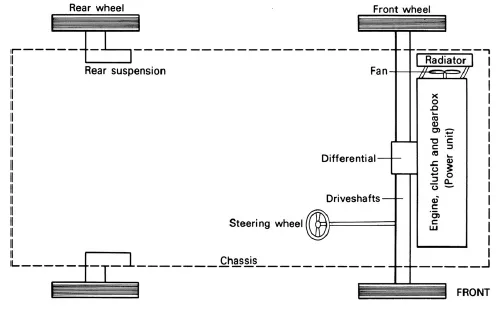
FIGURE 1.2 Front engine rear wheel drive
Increasingly mid-engine set-ups are becoming more popular in high performance cars, where the engine and the gearbox are mounted in the middle of the vehicle and the rear wheels are driven.
For off-road use four-wheel drive gives better grip. This can be with front or mid-engined layouts.
Nomenclature
4x4 means that the vehicle has a total of four wheels and that it is driven by all the four wheels. 4x4 vehicles may also be called all-wheel drive (AWD), off-road, or all-terrain vehicle.
FIGURE 1.3 Rear engine rear wheel drive (RWD)
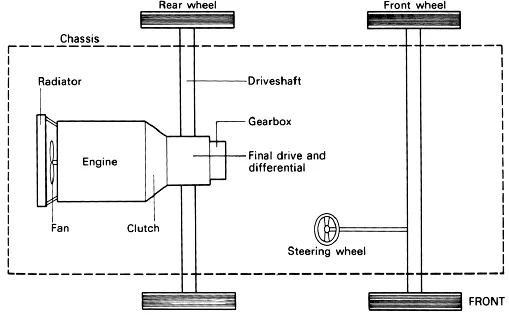
2. ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGES
OF DIFFERENT VEHICLE LAYOUTS
Each type of layout has certain advantages and disadvantages when compared to the others, see Table 1.1.
3. CHASSIS
The chassis is the load bearing part of the vehicle. That is to say it carries the weight of the load and the passengers, and locates the engine, transmission, steering and suspension. On most popular cars the chassis and the body are one and the same; but on specialized cars and goods vehicles separate chassis are used. There are three main types of chassis: these are ladder chassis, cruciform chassis and backbone chassis.
TABLE 1.1
Type of Layout | Advantages | Disadvantages |
| FWD |
|
|
| Conventional |
|
|
| Mid-engine |
|
|
| RWD |
|
|
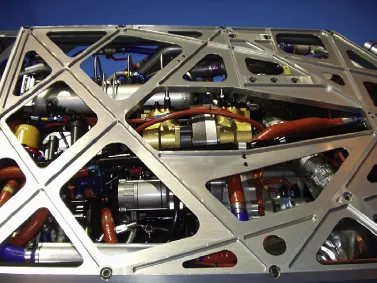
FIGURE 1.4 CNC machined chassis of the JCB Diesel record holder car
RACER NOTE
If you look underneath a popular car you will see square sections, like little box girders, connecting the main suspension and transmission parts. These are called the chassis sections; although the vehicle does not have a separate chassis these give extra strength. It is important that the chassis sections are in good condition for the car to be safe.
Ladder chassis — it is called this because of its shape: it looks vaguely like a builder's ladder. It has two side rails connected by cross-members. Ladder chassis are used on trucks and buses as well as vehicles like Land Rovers and some kit cars. The rails which run lengthwise are called longitudinal members; those which go across the vehicle are transverse members. Generally the suspension is attached to the longitudinal rails and the engine will sit between these rails. The gearbox tail housing is attached to a transverse member.
FIGURE 1.5 Ladder chassis
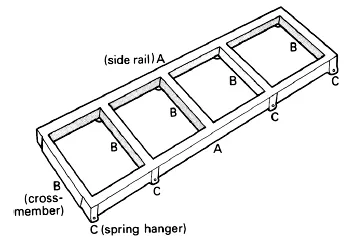
FIGURE 1.6 Cruciform chassis
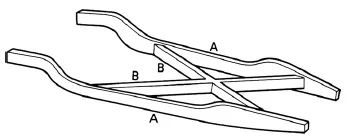
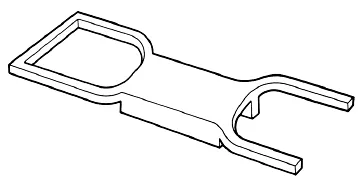
FIGURE 1.7 Backbone chassis
Cruciform chassis — it is cross-shaped in the middle to give resistance to twisting. This type of chassis is used on some old rare sports cars such as Lea-Francis.
Backbone chassis — it looks roughly like a person's skeleton — a backbone with arms and legs. Lotus and Mazda use this design on their small sports cars (Elise and MX-5); the propeller shaft can fit through the middle of the hollow backbone section.
4. INTEGRAL CONSTRUCTION
Integral construction is also known as unitary construction or monocoque. This is when the chassis and the body are made as one integral unit, that is, as one piece from parts welded together, not as a separate body and chassis. These are often referred to as body shells. The floor, the sills, the roof and the quarter panels are all spot-welded together to form an assembly to which the engine and the running gear are attached. The integral body/chassis is much ligh...
Table of contents
- Cover
- Title Page
- FOREWORD
- PREFACE
- ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- ABBREVIATIONS AND SYMBOLS
- CHAPTER 1 Body and Chassis
- CHAPTER 2 Engine Technology
- CHAPTER 3 Fuel System
- CHAPTER 4 Ignition System
- CHAPTER 5 The Cooling System
- CHAPTER 6 Lubrication System
- CHAPTER 7 Clutch
- CHAPTER 8 Transmission System
- CHAPTER 9 Suspension and Steering
- CHAPTER 10 Wheels and Tyres
- CHAPTER 11 Braking System
- CHAPTER 12 Electrical and Electronic Systems
- GLOSSARY
- APPENDIX 1: Vehicle Maintenance and Repair Level 2
- APPENDIX 2: Answers to Multiple-Choice Questions
- BIBLIOGRAPHY
- INDEX
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription
No, books cannot be downloaded as external files, such as PDFs, for use outside of Perlego. However, you can download books within the Perlego app for offline reading on mobile or tablet. Learn how to download books offline
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 990+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn about our mission
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more about Read Aloud
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS and Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Yes, you can access Basic Motorsport Engineering by Andrew Livesey in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Technology & Engineering & Automotive Transportation & Engineering. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.