
Data Analytics for Pandemics
A COVID-19 Case Study
- 88 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Data Analytics for Pandemics
A COVID-19 Case Study
About this book
Epidemic trend analysis, timeline progression, prediction, and recommendation are critical for initiating effective public health control strategies, and AI and data analytics play an important role in epidemiology, diagnostic, and clinical fronts. The focus of this book is data analytics for COVID-19, which includes an overview of COVID-19 in terms of epidemic/pandemic, data processing and knowledge extraction. Data sources, storage and platforms are discussed along with discussions on data models, their performance, different big data techniques, tools and technologies. This book also addresses the challenges in applying analytics to pandemic scenarios, case studies and control strategies. Aimed at Data Analysts, Epidemiologists and associated researchers, this book:
- discusses challenges of AI model for big data analytics in pandemic scenarios;
- explains how different big data analytics techniques can be implemented;
- provides a set of recommendations to minimize infection rate of COVID-19;
- summarizes various techniques of data processing and knowledge extraction;
- enables users to understand big data analytics techniques required for prediction purposes.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
1
COVID-19 Outbreak
1.1 Introduction
- (i) Case-fatality rate: It is defined as the ratio of the number of patients who die due to the disease to the number of people affected by it.
- (ii) Observed survival rate: It is the prediction of the probability of survival.
- (iii) Relative survival rate: It is defined as the percentage of the observed survival to the survival rate expectation.
- (i) Congenital diseases
- (ii) Acquired diseases
- (i) Infectious diseases
- (ii) Non-infectious diseases
- (i) Direct transmission
- (ii) Indirect transmission
- Coming in contact with the infected person.
- Via droplet infection (coughing, sneezing, and spitting).
- Coming in contact with the soil.
- If pathogens are transmitted through food, water, etc., it is known as vehicle-borne disease.
- If pathogens are transmitted through the air, then it is known as airborne disease.
- If pathogens are transmitted through contaminated items like clothing, utensils, books, etc., it is known as fomite-borne disease.
- (i) Prevention
- (ii) Cure
1.2 Epidemic and Pandemic Overview
1.2.1 Stages of Disease
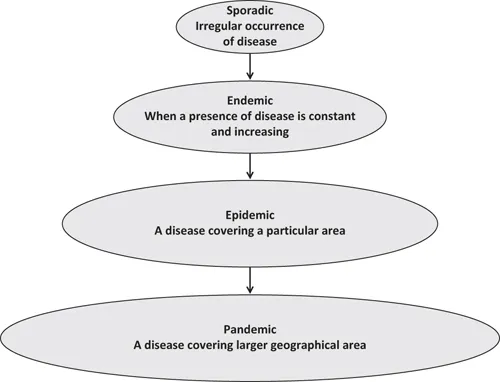
- (i) Sporadic
When the occurrence of the disease is not regular and is infrequent, it is termed as sporadic. - (ii) Endemic
When the presence of the disease is constant in a particular geographical area, it is known as endemic. Endemic turns into a hyperendemic situation when a high level of disease occurrence is observed. - (iii) Epidemic
When there is a sudden rise in the number of patients with the same disease and within a particular area, it is termed as an epidemic. - (iv) Pandemic
When epidemics affect larger geographical areas (including multiple countries and continents), it is known as a pandemic.
1.2.2 Pandemic Phases
- Phase 1: A pathogen/virus that exists in animals has not caused any kind of infection to humans.
- Phase 2: A pathogen/virus has infected humans.
- Phase 3: Small groups of people or random persons are infected with the virus.
- Phase 4: Human to human transmission is observed due to the outbreak at the community level.
- Phase 5: The disease has spread in multiple WHO regions.
- Phase 6: There is an outbreak of the disease in one or more regions different from the ones enlisted in Phase 5 [2].
1.2.2.1 Pandemic Risk Factors
Table of contents
- Cover
- Half-Title
- Series
- Title
- Copyright
- Contents
- Preface
- Acknowledgment
- Authors
- 1 COVID-19 Outbreak
- 2 Data Processing and Knowledge Extraction
- 3 Big Data Analytics for COVID-19
- 4 Mitigation Strategies and Recommendations
- Index
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app