
eBook - ePub
Event Semantics of Verb Frame Alternations
A Case Study of Dutch and Its Acquisition
- 424 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
Event Semantics of Verb Frame Alternations
A Case Study of Dutch and Its Acquisition
About this book
Using both theoretical and language acquisition arguments, this study proposes a new model of the lexicon-syntax interface defined in terms of checking event-semantic features. The research is based on Dutch verbs and their possible verb frames (intransitive, transitive, etc.) and two studies of children's Dutch. The model developed from these cases represents more generally the way in which Universal Grammar organizes the lexicon of a language and the mapping system that associates a verb's lexical features with its syntactic projection.
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription.
No, books cannot be downloaded as external files, such as PDFs, for use outside of Perlego. However, you can download books within the Perlego app for offline reading on mobile or tablet. Learn more here.
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 1000+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn more here.
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more here.
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS or Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Yes, you can access Event Semantics of Verb Frame Alternations by Angeliek Van Hout in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Languages & Linguistics & Linguistics. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.
Information
CHAPTER 1
Lexicon Theories: State of the Art
This chapter reviews various models of the lexicon-syntax interface that have been proposed since the early eighties. Interface models analyze and explain the links between a verb's lexical specification and its appearance in verb frames. There are two major issues an interface model has to address: (i) Which features are relevant in the interface and how can they be formalized? (ii) How does the mapping algorithm associate these features with verb frames? On top of these basic issues comes the need to deal with a verb's flexible behavior, i.e., the phenomenon that it can appear in various frames. Several kinds of lexical specification have been proposed, ranging from subcategorization frames to θ-roles and from argument structures to lexical-conceptual and lexical-relational structures. Various kinds of mapping systems have been proposed as well, ranging from principles of projection and linking and procedures of θ-role assignment to mapping governed by aspectual considerations. Verbs' flexible behavior challenges lexicon-syntax models. Some models resolve this challenge by locating flexibility in the lexicon, i.e., via lexical rules; others deal with it as a syntactic phenomenon, i.e., the outcome of movement.
1.1 Goals of this chapter
In this chapter, I introduce the issues at play in the lexicon-syntax interface. Essentially, an interface theory defines how a verb's lexical specification determines the ways this verb appears in syntactic configurations. This is the so-called mapping problem; it is presented in section 1.2.
In the remainder of the chapter, I will discuss the main proponents of different views on the lexicon and the lexicon-syntax interface, thereby reviewing various concepts of lexical specification and various systems of mapping lexical information onto syntax (section 1.3). This review will serve as background for the research presented in this dissertation. It will be a point of departure for pointing out other lexical features that are relevant to mapping (see Chapter 3) and developing a new model of lexicon-syntax mapping (see Chapter 4). The empirical motivation of the new mapping system lies in the phenomenon of verbal flexibility. In section 1.4, I present various analyses of and approaches to this phenomenon.
Deviating from existing models and taking a different approach to flexibility, I will remodel the lexicon-syntax interface, using the Dutch data discussed in Chapters 2 and 3 as the empirical basis. The overview of the state of the art of the research on argument structure in this chapter will thus serve as a resonator against which my view on lexical specification and mapping can be evaluated.
1.2 The mapping problem
Basically, mapping is a relation between the verbal lexicon and a small set of syntactic configurations sentences can be made up of, (1).
(1) Mapping is a relation between the verbal lexicon and syntax:

If the verbal lexicon is viewed as a very large set of verbal meanings, each with its own specification, indicated with [..] in (1), then mapping relates each lexical specification to one or more verb frames. The set of verb frames is a small set of six or so different D-structure configurations, differing in the number and location of their argument positions. Six different types of verb frames are illustrated in (1) as various subcategorization frames; these must be seen as shorthand for different D-structure trees.
SU stands for subject position, typically the argument position outside of and predicated of by VP, or, alternatively, the specifier of V position in the VP internal Subject Hypothesis (see Koopman & Sportiche 1988). DO stands for direct object position, traditionally the argument position that is a sister of and directly governed by V, or, alternatively, the specifier position of the lower V in a VP-shell structure (see Larson 1988). OBL stands for the position for the oblique argument, i.e., the indirect object or PP complement. I use OBL as a neutral term to refer to the position the indirect internal argument is mapped onto in the syntatic configuration. There are many proposals as to where that position is situated: as a second sister of V in a ternary branching V' (Oehrle 1976), as a sister of V' (Chomsky 1981),withina small clause (SC) complement of V (Kayne 1984) or as sister of the lower V in a VP-shell structure (Larson 1988).1
The picture in (1) represents an abstract picture of the relation between lexicon and syntax. It is independent of how one formalizes lexical primitives and mapping, or of which syntactic configurations one chooses as the frames verbs can map onto. In fact, the picture is often more sophisticated, as several theories assume an intermediate level between lexicon and syntax: the level of argument structure. In these theories the mapping system splits up in a two-part algorithm (see (11) below): one part relates the lexical-semantic specifications and different argument structures, the so-called linking rules', the other part argument structures and syntactic configurations, the so-called projection rules.
A theory of mapping then links verbal specifications in the lexical domain to frames (or configurations) in the syntactic domain. In more prosaic terms, a verb's lexical specification goes through a mapping "transformer" and comes out with a syntactic configuration with a certain number of argument positions. The mapping relation is complicated by the fact that one and the same verb can appear in more than one frame; I will refer to this phenomenon as lexical-syntactic flexibility. Lexical-syntactic flexibility can be pictured in (1) as a one-to-many relation between verbal meanings and verb frames. The mapping problem is this: how does a verb's lexical specification transform into a set of syntactic configurations?
1.3 Lexical primitives and mapping theories
In many of the present-day theories, the mapping from lexical information onto syntax is exclusively and exhaustively determined by the lexical-semantic arguments of the verb. Projection of different syntactic configurations, i.e., the various frames, depends on the number and kinds of a verb's arguments. Each verb is lexically characterized with a certain number of various kinds of arguments. The mapping algorithm more or less directly "translates" the lexical-semantic structure to a syntactic structure. I will refer to such systems as argument-centered mapping approaches.
The argument-centered conception has been formalized in a number of different ways. Theories differ in their assumptions about what kind of information about the arguments must be specified in a lexical entry. Basically, there are three major semantic kinds of lexical primitives: θ-roles listed in a θ-grid, arguments ordered in an argument structure and variables in lexical conceptual structures. Furthermore, there is one syntactic kind of lexical primitive: subcategorization frames. I will discuss their properties and the mapping algorithms defined on them in subsection 1.3.1.
In recent years, however, there have been other views around. The basic motivation behind these alternatives is that an argument-centered perspective misses important mapping generalizations as it turns out that other semantic features play a role as well, in particular event type features. In subsection 1.3.2, I will discuss how aspectual considerations play a role in three of these alternative theories: Tenny's (1987, 1994) aspectual interface hypothesis, Grimshaw's (1990) theory of aspectual prominence and the associations between argument structure and event structure and Hale & Keyser's (1992, 1993) lexical-relational structures and their association with different event types.
1.3.1 Argument-centered mapping
Subcategorization frames
The traditional kind of formalization of a verb's arguments is of a completely syntactic nature. It specifies verbs for their subcategorization frames (see Chomsky 1965). A subcategorization frame specifies the number of complements a verb takes, the syntactic category of those complements and whether they are optional or obligatory. Additional selection restrictions further specify the semantics of the complements. Consider transitive drink in (2a) and ditransitive put in (2b) with subcategorization frames (adopting the notation used by Emonds 1991a).
(2)
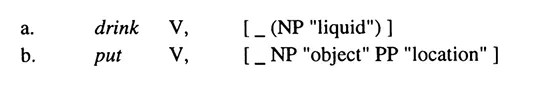
The lines in (2) indicate the position of the verb, NP and PP indicate the category of the complements and the semantic notions in quotes indicate selection restrictions on these complements. The brackets around the NP complement in (2a) indicate optionality of the object of drink; the absence of such brackets in (2b) implies obligatoriness of both complements of put. Notice that subjects are not mentioned in subcategorization frames; they do not require subcategorization as the subject position always needs to be projected. A subcategorization frame contains purely syntactic information in a lexical shorthand notation; it translates directly to a syntactic projection. Hence, mapping is a trivial operation.
Throughout all of his research, Emonds explores in great depth the notion of subcategorization frame and shows applications of its use for a large number of affixes and syntactic constructions (cf. Emonds 1976, 1985, 1987, 1991a,b, 1992).
θ-roles
Gruber (1965) has introduced the concept of thematic relations to examine the semantic relations involved in interpreting the NP arguments of verbs. Gruber considers the theme of a sentence to be the central and fundam...
Table of contents
- Cover
- Title
- Copyright
- Contents
- Preface
- 1 Lexicon Theories: State of the Art
- 2 Verb Frame Alternations in Dutch
- 3 Event Type-Shifting
- 4 The Lexicon and the Lexicon-Syntax Interface: the CHESS Model
- 5 Learning Verbs: Learning Light Verbs
- 6 Learning Verbs: Learning Intransitive Verbs
- Conclusions
- Appendices
- Appendix 2
- Appendix 3
- References
- Index