
Soft Computing Applications and Techniques in Healthcare
- 260 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Soft Computing Applications and Techniques in Healthcare
About this book
This book provides insights into contemporary issues and challenges in soft computing applications and techniques in healthcare. It will be a useful guide to identify, categorise and assess the role of different soft computing techniques for disease, diagnosis and prediction due to technological advancements.
The book explores applications in soft computing and covers empirical properties of artificial neural network (ANN), evolutionary computing, fuzzy logic and statistical techniques. It presents basic and advanced concepts to help beginners and industry professionals get up to speed on the latest developments in soft computing and healthcare systems. It incorporates the latest methodologies and challenges facing soft computing, examines descriptive, predictive and social network techniques and discusses analytics tools and their role in providing effective solutions for science and technology.
The primary users for the book include researchers, academicians, postgraduate students, specialists and practitioners.
Dr. Ashish Mishra is a professor in the Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Gyan Ganga Institute of Technology and Sciences, Jabalpur, Madhya Pradesh, India. He has contributed in organising the INSPIRE Science Internship Camp. He is a member of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers and is a life member of the Computer Society of India. His research interests include the Internet of Things, data mining, cloud computing, image processing and knowledge-based systems. He holds nine patents in Intellectual Property, India. He has authored four books in the areas of data mining, image processing and LaTex.
Dr. G. Suseendran is an assistant professor, Department of Information Technology, School of Computing Sciences, Vels Institute of Science, Technology & Advanced Studies (VISTAS), Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India. His research interests include ad-hoc networks, the Internet of Things, data mining, cloud computing, image processing, knowledge-based systems, and Web information exploration. He has published more than 75 research papers in various international journals such as Science Citation Index, Springer Book Chapter, Scopus, IEEE Access and UGC-referred journals.
Prof. Trung-Nghia Phung is an associate professor and Head of Academic Affairs, Thai Nguyen University of Information and Communication Technology (ICTU). He has published more than 60 research papers. His main research interest lies in the field of speech, audio, and biomedical signal processing. He serves as a technical committee program member, track chair, session chair, and reviewer of many international conferences and journals. He was a co-Chair of the International Conference on Advances in Information and Communication Technology 2016 (ICTA 2016) and a Session Chair of the 4th International Conference on Information System Design and Intelligent Applications (INDIA 2017).
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
- 1.1 Introduction
- 1.2 Literature Review
- 1.3 Data Collection and Processing
- 1.4 Classification and Model Evaluation
- 1.4.1 K-Nearest Neighbours
- 1.4.2 Support Vector Machine
- 1.4.3 Kernels in Support Vector Machine
- 1.4.4 ADABoost
- 1.4.5 Random Forest
- 1.5 Logistic Regression
- 1.5.1 Naive Bayes
- 1.6 Results
- 1.7 Conclusion
- References
1.1 Introduction
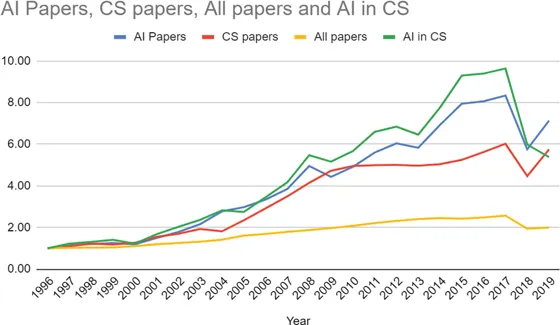
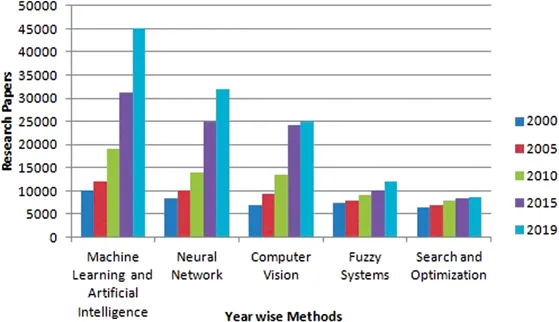
1.2 Literature Review
Table of contents
- Cover
- Half Title
- Series Page
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Contents
- Preface
- Acknowledgements
- Editors
- Contributors
- Chapter 1 Analytical Approach to Genetics of Cancer Therapeutics through Machine Learning
- Chapter 2 A Study on Behaviour of Neural Gas on Images and Artificial Neural Network in Healthcare
- Chapter 3 A New Approach for Parkinson’s Disease Imaging Diagnosis Using Digitized Spiral Drawing
- Chapter 4 Modelling and Analysis for Cancer Model with Caputo to Atangana-Baleanu Derivative
- Chapter 5 Selection of Hospital Using Integrated Fuzzy AHP and Fuzzy TOPSIS Method
- Chapter 6 Computation of Threshold Rate for the Spread of HIV in a Mobile Heterosexual Population and Its Implication for SIR Model in Healthcare
- Chapter 7 Application of Soft Computing Techniques to Heart Sound Classification: A Review of the Decade
- Chapter 8 Fuzzy Systems in Medicine and Healthcare: Need, Challenges and Applications
- Chapter 9 Appliance of Machine Learning Algorithms in Prudent Clinical Decision-Making Systems in the Healthcare Industry
- Chapter 10 Technique of Receiving Data from Medical Devices to Create Electronic Medical Records Database
- Chapter 11 Universal Health Database in India: Emergence, Feasibility and Multiplier Effects
- Chapter 12 Cluster Analysis of Breast Cancer Data Using Modified BP-RBFN
- Index