
eBook - ePub
Data Science with Jupyter
Master Data Science skills with easy-to-follow Python examples
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
Data Science with Jupyter
Master Data Science skills with easy-to-follow Python examples
About this book
Step-by-step guide to practising data science techniques with Jupyter notebooks Key Features
- Acquire Python skills to do independent data science projects
- Learn the basics of linear algebra and statistical science in Python way
- Understand how and when they're used in data science
- Build predictive models, tune their parameters and analyze performance in few steps
- Cluster, transform, visualize, and extract insights from unlabelled datasets
- Learn how to use matplotlib and seaborn for data visualization
- Implement and save machine learning models for real-world business scenarios
-
Description
Modern businesses are awash with data, making data driven decision-making tasks increasingly complex. As a result, relevant technical expertise and analytical skills are required to do such tasks. This book aims to equip you with just enough knowledge of Python in conjunction with skills to use powerful tool such as Jupyter Notebook in order to succeed in the role of a data scientist. The book starts with a brief introduction to the world of data science and the opportunities you may come across along with an overview of the key topics covered in the book. You will learn how to setup Anaconda installation which comes with Jupyter and preinstalled Python packages. Before diving in to several supervised, unsupervised and other machine learning techniques, you'll learn how to use basic data structures, functions, libraries and packages required to import, clean, visualize and process data. Several machine learning techniques such as regression, classification, clustering, time-series etc have been explained with the use of practical examples and by comparing the performance of various models. By the end of the book, you will come across few case studies to put your knowledge to practice and solve real-life business problems such as building a movie recommendation engine, classifying spam messages, predicting the ability of a borrower to repay loan on time and time series forecasting of housing prices. Remember to practice additional examples provided in the code bundle of the book to master these techniques. Audience
The book is intended for anyone looking for a career in data science, all aspiring data scientists who want to learn the most powerful programming language in Machine Learning or working professionals who want to switch their career in Data Science. While no prior knowledge of Data Science or related technologies is assumed, it will be helpful to have some programming experience. Table of Contents
- Data Science Fundamentals
- Installing Software and Setting up
- Lists and Dictionaries
- Function and Packages
- NumPy Foundation
- Pandas and Dataframe
- Interacting with Databases
- Thinking Statistically in Data Science
- How to import data in Python?
- Cleaning of imported data
- Data Visualization
- Data Pre-processing
- Supervised Machine Learning
- Unsupervised Machine Learning
- Handling Time-Series Data
- Time-Series Methods
- Case Study – 1
- Case Study – 2
- Case Study – 3
- Case Study – 4
-
About the Author
Prateek is a Data Enthusiast and loves the data driven technologies. Prateek has total 7 years of experience and currently he is working as a Data Scientist in an MNC. He has worked with finance and retail clients and has developed Machine Learning and Deep Learning solutions for their business. His keen area of interest is in natural language processing and in computer vision. In leisure he writes posts about Data Science with Python in his blog.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
CHAPTER 1
Data Science Fundamentals
“Learning from data is virtually universally useful. Master it and you will be welcomed anywhere." - John Elder, founder of the Elder Research- America’s largest and most experienced analytics consultancy. With his vision about data, John has started his company in 1995 yet the importance of the finding information from the data is a niche and the most demanding skill of the 21st century. Today Data Science is everywhere.
The explosive growth of the digital world requires professionals with not just strong skills, but also adaptability and a passion for staying on the forefront of technology. A recent study shows that demand for data scientists and analysts is projected to grow by 28 percent by 2020. This is on top of the current market need. According to LinkedIn, there are more than 11,000 data scientist job openings in the US as of late August. Unless something changes, this skills gap will continue to widen. In this first chapter you will be familiar with data, your role as an aspiring data scientist and importance of Python programming language in Data Science.
Structure
- What is Data?
- What is Data Science?
- What a Data Scientist actually do?
- Real world use cases of Data Science
- Why Python for Data Science?
Objective
After studying this chapter, you should be able to understand the data types, amount of the data generated daily and need of data scientist with currently available real-world use cases.
What is Data?
The best way to describe the data is to understand the types of the data. Data is divided into following three categories.
1. Structured Data
A well-organized data in the form of tables that can be easily operated is known as structured data. Searching and accessing information from such type of data is very easy. For example, data stored in the relational database i.e. sql in the form of tables having multiple rows and columns. Spreadsheet is another good example of structured data. Structured data represent only 5 to 10% of all data present in world. Following image is an example of sql data where a sql table is holding the merchant related data.

2. Unstructured Data
Unstructured data requires advance tools and software’s to access information. For Example, images and graphics, pdf files, word document, audio, video, emails, PowerPoint presentations, webpages and web contents, wikis, streaming data, location coordinates etc fall under the unstructured data category. Unstructured data represent around 80% of the data. Following image shows various unstructured data types.
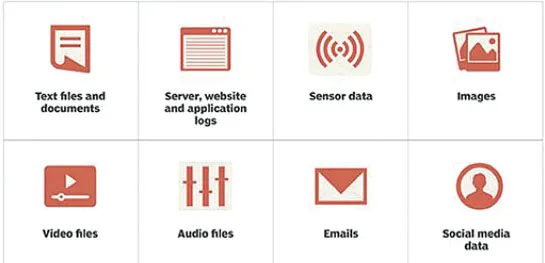
3. Semi-Structured Data
Semi-structured data is basically a structured data that is unorganised. Web data such JSON(JavaScript Object Notation) files, BibTex files, .csv files, tab-delimited text files, XML and other markup languages are the examples of Semi-structured data found on the web. Semi-structured data represent only 5 to 10% of all data present in world. Following image shows an example of JSON data.

What is Data Science?
It’s become a universal truth that modern businesses are awash with data. Last year, McKinsey estimated that big data initiatives in the US healthcare system "could account for $300 billion to $450 billion in reduced healthcare spending, or 12 to 17 percent of the $2.6 trillion baseline in US healthcare costs". On the other hand, though, bad or unstructured data is estimated to be costing the US roughly $3.1 trillion a year.
Data driven decision making is increasing in popularity. Accessing and finding information from the unstructured data is complex and cannot be done easily with some BI tools and here the Data Science comes in the picture.
Data Science is a field that extract the knowledge and insights from the raw data. To do so it uses Maths, Statistics, Computer Science and Programming Language knowledge. A person who has all these skills is known as a Data Scientist. Data scientist is all about being curious, self-driven, and passionate about finding answers. The following picture shows the skills a modern data scientist should have!
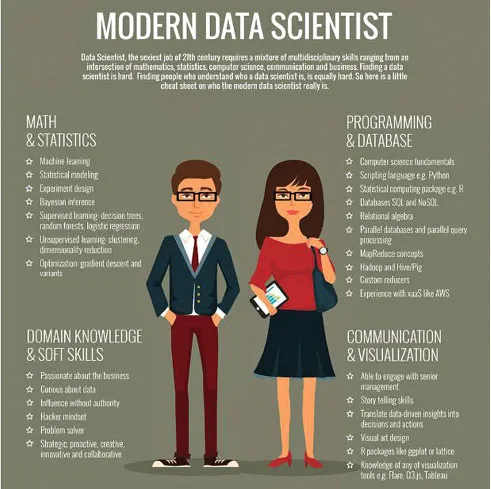
What a Data Scientist actually do?
Most data scientists in the industry have advanced and training in statistics, math, and computer science. Their experience is a vast horizon that also extends to data visualization, data mining, and information management. The primary job of a Data Scientist is to ask the right question- It’s about surfacing hidden insight that can help enable companies to make smarter business decisions.
The job of a Data Scientist is not bonded to a particular domain. Apart from the scientific research they are working in various domain including shipping , healthcare, e-commerce, aviation, finance, education etc. They start their work by understanding the business problem and then they proceed with data collection, reading the data, transforming the data in required format, visualizing, modelling, evaluating the model and then deployment. You can imagine their work cycle as mentioned in below image

80 percent of a data scientist’s time is spent in simply finding, cleansing, and organizing data, leaving only 20 percent to actually perform analysis. These processes can be time-consuming and tedious. But it’s crucial to get them right since a model is only as good as the data used to build it. And because models generally improve as they are exposed to increasing amounts of data, it’s in data scientists’ interests to include as much data as they can in their analysis.
In the later chapter of this book you will learn all above required skills to be a data scientist.
Real world use cases of Data Science
Information is the oil of the 21st century, and analytics is the combustion engine. Whether you are uploading a picture on Facebook, posting a tweet, emailing anybody or shopping in e-commerce site, the role of Data Science is everywhere. In modern workplace Data Science is applied to many problems to predict and calculate outcomes that would have taken several times more human hours to process. Following are some list of real-world examples where Data Scientists are playing a key role.
- Google’s AI research arm is taking help of Data Scientists to build the best performing algorithm for automatically detecting objects.
- Amazon has built a product recommendation system to personalize their product.
- Santander Group of Bank has built a model with the help of Data Scientists to identify the value of transactions for each potential customer.
- Airbus in maritime industry is taking help of Data Scientists to build a model that detects all ships in satellite images as quickly as possible to increase knowledge, anticipate threats, trigger alerts, and improve efficiency at sea.
- You tube is using an automated video classification model in a limited memory.
- Data Scientists at the Chinese internet giant Baidu Inc. released details of a new deep learning algorithm that they claim can help pathologist identify tumors more accurately.
- The Radiological Society of North America (RSNA®) is using an algorithm to detect a visual signal for pneumonia in medical images which automatically locate lung opacities on chest radiographs.
- The Inter-American Development Bank is using an algorithm that considers a family’s observable household attributes like the material of their walls and ceiling, or the assets found in the home to classify them and predict their level of need.
- Netflix data using data science skill on the movie viewing patterns to understand what drives user interest and uses that to make decisions on which Netflix original series to produce.
Why Python for Data Science?
Python is very beginner-friendly. The syntax (words and structure) is extremely simple to read and follow, most of which can be understood even if you do not know any programming. Python is a multi-paradigm programming language: a sort of Swiss Army knife for the coding world. It supports object-oriented programming, structured programming, and functional programming patterns, among others. There’s a joke in the Python community that "Python is generally the second-best language for everything."
Python is free, open-source software, and consequently anyone can write a library package to extend its functionality. Data science has...
Table of contents
- Cover
- Data Science with Jupyter
- Copyright
- About the Author
- Preface
- Acknowledgements
- Erratta
- Contents
- 1. Data Science Fundamentals
- 2. Installing Software and Setting up
- 3. Lists and Dictionaries
- 4. Function and packages
- 5. NumPy Foundation
- 6. Pandas and Dataframe
- 7. Interacting with Databases
- 8. Thinking Statistically in Data Science
- 9. How to import data in Python?
- 10. Cleaning of imported data
- 11. Data Visualization
- 12. Data Pre-processing
- 13. Supervised Machine Learning
- 14. unsupervised Machine Learning
- 15. Handling time-Series Data
- 16. Time-Series Methods
- 17. Case Study-1
- 18. Case Study-2
- 19. case Study-3
- 20. Case Study-4
- Index
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription
No, books cannot be downloaded as external files, such as PDFs, for use outside of Perlego. However, you can download books within the Perlego app for offline reading on mobile or tablet. Learn how to download books offline
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 990+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn about our mission
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more about Read Aloud
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS and Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Yes, you can access Data Science with Jupyter by Prateek Gupta in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Computer Science & Computer Science General. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.