
- 391 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
About this book
Although the Internet of Things (IoT) is a vast and dynamic territory that is evolving rapidly, there has been a need for a book that offers a holistic view of the technologies and applications of the entire IoT spectrum. Filling this void, The Internet of Things in the Cloud: A Middleware Perspective provides a comprehensive introduction to the Io
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
I
The Internet of Things
Chapter 1
The Third ICT Wave
1.1 Rise of the Machines
Over the past decades, billions of people have hooked themselves up to the Internet via the computer, and more recently mobile devices such as smartphones. This communication revolution is now extending to objects as well as people. Machine-to-machine (M2M) communication has long been predicted, and now it is rushing into the present. According to Parks Associates, the number of smartphones (excluding feature phones) worldwide is expected to top 1.1 billion in 2013. However, this is just the tip of the iceberg. Smart grid devices will reach 244 million; e-readers and tablets will be 487 million; networked office devices, 2.37 billion; networked medical devices, 86 million; connected automobiles, 45 million; connected appliances, 547 million; connected military devices, 105 million; information technology (IT) system devices, 431 million; connected supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA)/industry automation devices, 45 million; and other connected consumer electronic devices minus smartphones, e-readers, and tablets will reach a whopping 5+ billion and counting.
“Rise of the machines” became a popular catchphrase after Terminator 3: Rise of the Machines, a 2003 science-fiction action film directed by Jonathan Mostow and starring Arnold Schwarzenegger. The movie demonstrates the power of machines or robots that could potentially overpower human beings.
During the first decade of the twenty-first century, big U.S. defense budgets financed the deployment of thousands of service robots, including unmanned aerial and underwater vehicles, to Iraq and Afghanistan. IEEE Spectrum [1] estimated a million industrial robots toiling around the world in 2008, and Japan is where they’re the thickest on the ground. In 2011, the world’s industrial robot population was estimated to be 1.2 million. Also, according to the Frankfurt-based International Federation of Robotics, the service robot market is expected to double in size by 2013 from 2011 [2].
A robot is a kind of tightly coupled cyber-physical system (CPS) [4,165]. A CPS (Figure 1.1) is an embedded sensor network and control system featuring a tight combination of, and coordination between, the system’s computational and physical elements. Cyber-physical systems or robots can be found in areas as diverse as aerospace, automotive industry, chemical processes, civil infrastructure, energy, healthcare, manufacturing, transportation systems, entertainment, and consumer appliances. A real-world example of such a system is the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) CarTel project where a fleet of taxis collects real-time traffic information in the Boston area. Together with historical data, this information is then used for calculating the fastest route for a given time of the day.
Figure 1.1
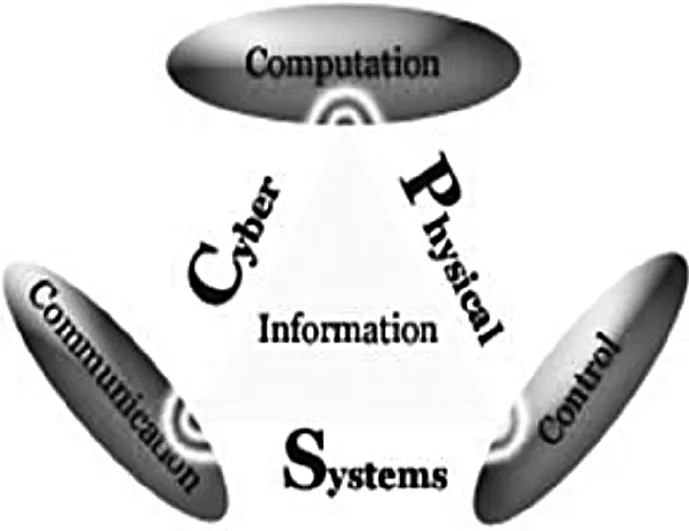
Cyber-physical system (CPS).
The U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) has identified cyber-physical systems as a key area of research, proposed by Helen Gill at the High Confidence Software and Systems conference [28] in 2008. In 2007, the President’s Council of Advisors on Science and Technology listed CPS as one of the top eight key technologies of the future, and a $4 billion budget was allocated for the Networking and Information Technology Research and Development [29] project. The expectation is that in the coming years, ongoing advances in science and engineering will improve the...
Table of contents
- Foreword
- Preface
- Author
- Section I - The Internet of Things
- Section II - Middleware for IoT
- Section III - The Cloud of Things
- References
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription
No, books cannot be downloaded as external files, such as PDFs, for use outside of Perlego. However, you can download books within the Perlego app for offline reading on mobile or tablet. Learn how to download books offline
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 990+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn about our mission
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more about Read Aloud
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS and Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Yes, you can access The Internet of Things in the Cloud by Honbo Zhou in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Computer Science & Computer Networking. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.