
Total Quality Management (TQM)
Principles, Methods, and Applications
- 194 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Total Quality Management (TQM)
Principles, Methods, and Applications
About this book
Organisations are now focused on total customer satisfaction. However there is a lack of understanding the requirements and the customer needs. Total Quality Management (TQM) integrates all phases and ensures a defect free quality product. This textbook provides the understanding of all aspects of TQM and the implementation.
This textbook covers all aspects of TQM, discusses quality systems in detail, highlights the importance of the needs of the customer, and presents the concept of Total Productive Maintenance (TPM).
Written as a textbook for students of engineering and management, but also explains all quality systems which will be helpful to all organisations in choosing the correct quality system and helpful to managers in decision making while analyzing any process.
A solutions manual and power point presentations slides are available for qualified adoptions.
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
1
Concept of Quality
1.1 PRODUCTS AND SERVICES
- Customer expectations.
- Actual product/service received.
1.1.1 PRODUCT/SERVICE FEATURES
1.2 QUALITY OF PRODUCTS
- Functionality This refers to the main characteristics of a product and a service. It is defined as a set of alternatives that are related to the existence of a set of functions and their specified properties. All functions have specific properties that explain the quality of the product and its services. The functions are also those that justify the declared needs for the manufacture of qualitative products.
- Reliability Reliability is also the main feature of a quality product. Measurement of product reliability is done by finding the ‘mean time between failures’ (MTBF). It is an indicator of durability of products. For example, a car should not break down often, so the MTBF of a car can be specified as 1,000 running hours or 10,000 km.
- Usability Usability is also a hallmark of product quality. This shows the client’s ability to use the product. It is expected that the client can use any type of product without the help of experts. For example, a car may need a mechanic to repair it, but its owner can drive it if they are trained.
- Maintainability This refers to the ease of a product being able to be kept in its original state without creating a problem. The ability to keep a product for a while makes it expensive, but you may finally use a product for a long time. It may be defective during use and must be repaired to maintain its original quality at the lowest cost. It is measured as ‘Average Repair Time (MTTR).’
- Efficiency Efficiency is the relationship between production and input. It means what we do after consuming sources of inputs. Therefore, a quality product must be measurable by its effectiveness.
- Portability The quality of the product also has the particularity of portability. It is defined as a set of attributes that affect the ability of the software to transfer from one environment to another. It simply transfers different attributes from one place to another. The environment can be hardware, software or an organisation.
1.3 SERVICE QUALITY
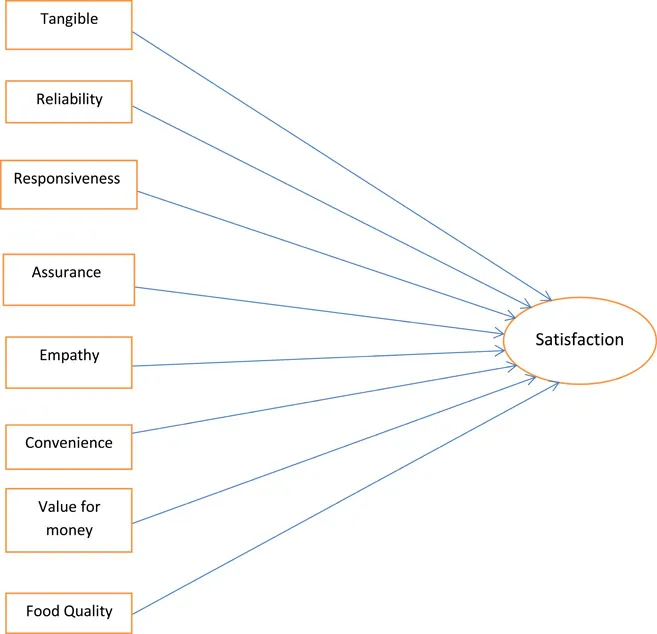
- Quality of customer service Customer service is important in any organisation. The current challenge for the sector is to meet the needs of customers. In a service sector, satisfying customers and knowing their implicit requirements is more difficult. For example, Flipkart, Amazon and Snapdeal are online services that always meet the needs of their customers.
- Quality of service design The design of quality services consists, first of all, of formulating a plan to satisfy a specific need or problem. The services are usually made to order, so it is important that the service is designed according to the specific requirements of the client. For example, the software developed for an organisation requires the complete specific program for the unique design requirements.
- Quality of service delivery The quality of delivery is important in all sectors, but services are key criteria to success. There are so many organisations that work in delivery, such as Ekart Logistics, etc. So it is better for business growth.
1.4 DEFINITION OF QUALITY
- Quality is defined as degree of excellence.
- A quality process or product is fit for its purpose. Evolution of this definition took place in quality circles. It is applicable to any process, product, or service. It thus makes this definition useful, but it is a bit difficult to measure quality according to this definition.
- In manufacturing, a measure of excellence or a state of being free from defects and deficiencies is called ‘quality.’
- Garvin (1984) divides the definition of quality into five categories, including product-based, user-based, and value-based. Further, he gave eight attributes to define quality: Performance, features, reliability, conformance, durability, serviceability, aesthetics and perceived quality, etc.
- According to Crosby (1979) ‘Quality is conformance to requirements/specifications.’ This is an ideal definition for quality control teams that need to validate processes, systems, services, and product quality. Depending on the requirements, they can easily validate compliance and identify nonconformities. The problematic part of this definition is that it can offer a biased and subjective view of quality. In many cases, the requirements are little more than the ideas of the business stakeholders. Often there is no objective validation that these ideas give a quality result.
- Deming stated that the definition of quality is ‘meeting or exceeding customer expectations.’
- According to Juran (1979) ‘Quality is a measure of fitness for use.’
- In the mathematical method, quality is defined as the ratio of performance to expectation.
- Case1. If, P > E it means quality is best
- Case2. If, P = E it means quality is good
- Case3. If, P < E it means quality is worst
- QUALITY also stands for
- Q = Quest for excellence
- U = Understanding customers’ needs
- A = Action to achieve customer appreciation
- L = Leadership
- I = Involving all people
- T = Team spirit for common goal
- Y = Yardstick to measure progress
- Quality is cost. Traditionally, the quality of the product was considered in terms of the cost of the materials. A gold watch is of better quality than a plastic watch. High-quality sheets have a number of threads of 180 or more. High-quality moisturiser for hands has a high shea butter content.
- Quality is price.It is the price that customers might be willing to pay for a product or a service. Quality is a crucial part of many business models. Different definitions of quality have been put forth by economists. According to some economists, quality is synonymous with the expensiveness of the product. In other words, the bigger the price of the product, the higher would be its quality.
- The manufacturing industry was the first to seriously consider quality. Concerns regarding the quality of pr...
Table of contents
- Cover
- Half Title
- Series Page
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Dedication
- Contents
- Preface
- Acknowledgements
- Author Biographies
- Chapter 1 Concept of Quality
- Chapter 2 Total Quality Management (TQM)
- Chapter 3 Quality Management Practices
- Chapter 4 Customer Involvement
- Chapter 5 Employer Involvement and Supplier Participation
- Chapter 6 Cost of Quality
- Chapter 7 Organising for Quality
- Chapter 8 Human Aspect in Quality Management
- Chapter 9 Total Productive Maintenance (TPM)
- Chapter 10 Quality Management Systems
- Index