
- 424 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
About this book
This book describes the various aspects of microbore column chromatography. It provides readers with an in-depth understanding of the supercritical fluid chromatography and microbore high-performance liquid chromatography.
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription.
No, books cannot be downloaded as external files, such as PDFs, for use outside of Perlego. However, you can download books within the Perlego app for offline reading on mobile or tablet. Learn more here.
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 1000+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn more here.
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more here.
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS or Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Yes, you can access Microbore Column Chromatography by F. J. Yang in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Technology & Engineering & Chemistry. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.
Information
1
Microbore Column Chromatography: A Unified Approach to Chromatography
FRANK J, YANG Vice President, Lee Scientific, Inc., Salt Lake City, Utah
Introduction
Microtaore column chromatography is a unified approach to chromatography, It can be depicted with the aid of the chromatography triangle shown in Figure 1. Microbore column chromatography offers high-resolution separation methodology within the scope of capillary gas chromatography (GC), supercritical fluid chromatography (SFC), and micro-high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). It covers the sample application domain of GC, SFC, and column liquid chromatography. Capillary GC, SFC, and micro-HPLC each has its own range of applications, instrumentation requirements, practical constraints, and technological uniqueness. However, the trend in the development of a unified microbore column chromatographic approach is apparent with the instrumentation development that allows the utilization of the same capillary column or columns of the same small capillary dimensions. Although developments in capillary GC, SFC, and micro-HPLC instrumentation and methodologies have taken place at different times, the separation techniques, column technology, and fundamental principles are parallel or identical in many aspects. In his book Dynamics in Chromatography, Giddings [1] argued that the divergence in thought mode between GC and LC is arbitrary, artificial, and counterproductive. As the column diameter becomes smaller, the practice of GC, SFC, and HPLC becomes more similar. Table 1 compares some functional aspects of capillary GC, capillary SFC, and micro-HPLC as practiced today. It points out many common features and the potential for the practice of a unified microbore column chromatography, that is, the use of the same injector, detector, column, and system components for applications in capillary GC, SFC, or micro-HPLC. Current column technology and detector advances will undoubtedly make microbore column chromatography a unified approach for the generation of total chromatographic information for an unknown sample.
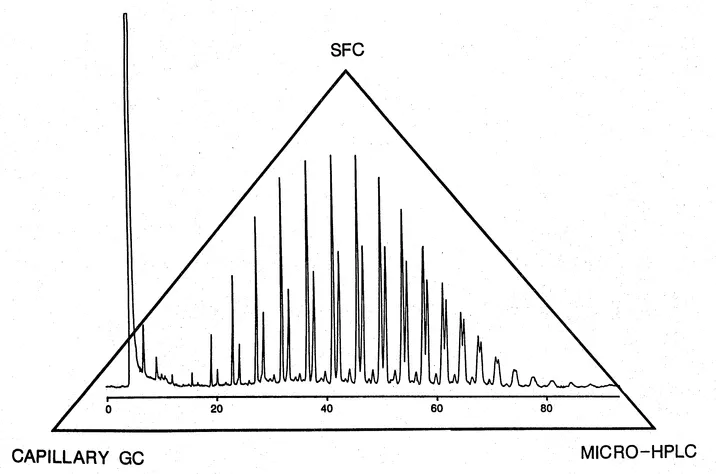
Fig. 1 Chromatography triangle of capillary GC, capillary SFC, and micro-HPLC. The figure depicted the high resolution capability of the microbore column chromatography. A unified approach to chromatography for the application sample domain of GC, SFC, and HPLC. Chromatogram of the separation of a polyglycol with an average molecular weight of 1800 (chromatogram courtesy of B. E. Richter, Lee Scientific).
Microbore column chromatography is growing rapidly. Its development and advances in instrumentation, column technology, and applications are vast. Detailed discussions of various aspects of microbore column chromatography are given by many contributing authors in the subsequent chapters. A brief introduction of state of-the-art capillary GC, SFC, and micro-HPLC is given in the following sections.
| Capillary GC | SFC | Micro-HPLC | |
| Column types | Open-tubular, packed capillary | Open-tubular, packed capillary, 1 mm i.d. LC packed column | Open-tubular, packed capillary, 1 mm i.d. LC packed column |
| Key system components | Column oven | High pressure pump Column oven | High pressure pump Column oven |
| Mobile phase | High pressure gases | Supercritical fluids | Liquid solvents |
| Sample injection | Split/splitless (syringe) | Spilt (valve) | Split (valve) |
| Cold on-column (syringe) | Direct (valve) | Direct (valve) | |
| Temperature-programmable (syringe) | Time-controlled sampling (valve) | Time-controlled sampling (valve) | |
| Split (valve) | |||
| Time-controlled sampling (valve) | |||
| Detectors | FID, TSD, FPD, PID, ECD, MED, MS, FTIR | FID, TSD, FPD, ECD, UV, fluorescence, MS, FTIR | TSD, FPD, UV, fluorescence, MS, FTIR |
| Samples | Volatiles | Volatiles and nonvolatiles | Volatiles and nonvolatiles |
| Thermally stable | Thermally stable and labile | Thermally stable and labile | |
| Low molecular weights | Low and high molecular weight | Low and high molecular weight | |
| Nonionic | Nonionic | Ionic and Nonionic |
Capillary GC
Capillary GC utilizes both open-tubular and packed capillary columns. As an example of its versatility, fused silica columns packed with conventional GC packing material are being used in high-efficiency separation of congeners in fruit brandies [2]. There is great potential for the use of short capillary columns packed with small particles (⩽10 μm) for high-speed analysis and resolution of complex samples. A capillary-packed column has several advantages over the conventional 2-mm-inner diameter (i.d.) GC-paeked column, not only in column efficiency and speed of analysis but also in enhancement in trace detection. Because of the reduced solute peak dilution in a capillary diameter-packed column, the minimum detectable concentration of the solute zones is greatly enhanced when a concentration-dependent detector such as TCD or ECD is employed.
Open-tubular capillary GC, proposed in 1957 by Golay [3], is enormously important in the practice of modern gas chromatography. Its rapid growth is evidenced by the exponential increase in the number of journal publications and routine laboratory applications in recent years. Advances in open-tubular capillary GC technology, practice, and application have been reviewed in many recent books [4—7]. Open-tubular capillary GC methodology has replaced many routine packed column practices, particularly, for new methodologies developed for the analysis of complex samples.
Open-tubular capillary GC has been developed to its full potential following- the invention of fused silica open-tubular columns [8], the development of reliable capillary GC sampling techniques, commercialization of capillary gas chromatographs, and an intense education and training process. The major reasons for the interest and application of open-tubular capillary GC are:
- Unsurpassed resolving power for the rapid separation of complex samples. A one million theoretical plate can be obtained in an analysis time of 30 minutes using a 20 m open-tubular column with a diameter of 25 μm. The column can resolve, with unit resolution, as many as 550 solute components in an analysis time of 30 minutes.
- Excellent reproducibility in peak area and peak retention. ...
Table of contents
- Cover
- Half Title
- Series Page
- Title
- Copyright
- Preface
- Contents
- Contributors
- 1 Microbore Column Chromatography: A Unified Approach to Chromatography
- 2 Packing Materials and Packing Techniques for Micro-HPLC Columns
- 3 Gradients in Microbore LC: Techniques and Applications
- 4 Advances in Optical Detectors for Micro-HPLC
- 5 Principles and Applications of Photodiode Array Fluorescence Detection in Microcolumn LC
- 6 Practice and Application of Microcolumn LC with Inductively Coupled Plasma Atomic Emission Spectrometric Detection
- 7 Practice and Applications of On-Line Multidimensional Chromatography Using Micro-HPLC and Capillary GC
- 8 Capillary Supercritical Fluid Chromatography: Practical Aspects
- 9 Detection Systems for Capillary Supercritical Fluid Chromatography
- 10 Principles and Applications of Supercritical Fluid Chromatography with Mass Spectromic Detection
- 11 Practice and Applications of Supercritical Fluid Chromatography in the Analysis of Industrial Samples
- Index