
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Enterprise AI For Dummies
About this book
Master the application of artificial intelligence in your enterprise with the book series trusted by millions
In Enterprise AI For Dummies, author Zachary Jarvinen simplifies and explains to readers the complicated world of artificial intelligence for business. Using practical examples, concrete applications, and straightforward prose, the author breaks down the fundamental and advanced topics that form the core of business AI.
Written for executives, managers, employees, consultants, and students with an interest in the business applications of artificial intelligence, Enterprise AI For Dummies demystifies the sometimes confusing topic of artificial intelligence. No longer will you lag behind your colleagues and friends when discussing the benefits of AI and business.
The book includes discussions of AI applications, including:
- Streamlining business operations
- Improving decision making
- Increasing automation
- Maximizing revenue
The For Dummies series makes topics understandable, and as such, this book is written in an easily understood style that's perfect for anyone who seeks an introduction to a usually unforgiving topic.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
Exploring Practical AI and How It Works
Demystifying Artificial Intelligence



“We propose that a 2-month, 10-man study of artificial intelligence be carried out during the summer of 1956 at Dartmouth College in Hanover, New Hampshire. The study is to proceed on the basis of the conjecture that every aspect of learning or any other feature of intelligence can in principle be so precisely described that a machine can be made to simulate it.”
- What the fuss is all about, what AI can do for you, and what it can’t.
- Why now and not 20 years ago, and why AI is suddenly all the rage and wherever you look you see news about everything from self-driving cars to AI-powered showerheads.
- How it works, and how all the moving parts fit together to solve interesting and challenging problems.
Understanding the Demand for AI
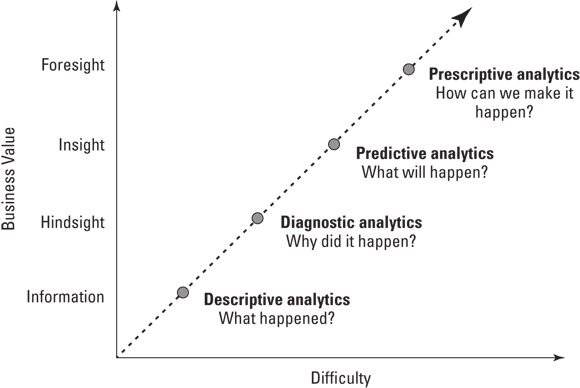
Converting big data into actionable information
- Descriptive analytics = information

- Diagnostic analytics = hindsight
- Predictive analytics = insight
- Prescriptive analytics = foresight
Descriptive analytics
Diagnostic analytics
Predictive analytics
Prescriptive analytics
AI-powered analytics
Relieving g...
Table of contents
- Cover
- Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Part 1: Exploring Practical AI and How It Works
- Part 2: Exploring Vertical Market Applications
- Part 3: Exploring Horizontal Market Applications
- Part 4: The Part of Tens
- Index
- About the Author
- Advertisement Page
- Connect with Dummies
- End User License Agreement
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app