
Kotlin at a glance
Use of Lambdas and higher-order functions to write more concise, clean, reusable, and simple code
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Kotlin at a glance
Use of Lambdas and higher-order functions to write more concise, clean, reusable, and simple code
About this book
Basic guide to develop an App in Android by using Kotlin Key Features
- Comprehensive coverage of all the concepts of Kotlin
- Simple language, crystal clear approach, user friendly book
- Concepts are duly supported by several examples and self-explanatory analogies.
Description
"Kotlin at a Glance" is a book that gives an in-depth knowledge about Kotlin. This book mainly focused on Kotlin programming language and its comparison to Java. By reading this book, the readers can make themselves familiar with the language's most important features and aspects.With a complete overview of OOPs, null safety, generics, and many other interesting features, this book is a perfect choice for fresher and experienced Java developers who want to learn more about this alternative JVM language.For reading this book, there's no need for any prior Kotlin knowledge, as the basics are explained in the book. Moreover, the required functional programming concepts are also described.The readers of this book will also learn to develop an app in android using Kotlin. Moreover, this book is for everyone who is on their way of becoming a developer. What will you learn
- Introduction to OOP, Java, Kotlin
- Kotlin Architecture, Token, Input, Operator, Array, Function
- Looping / Control Flow / Iteration
- Null Safety, Kotlin Lambda Functions and Exception Handling
- Constructor, Inheritance, Abstract Keyword, Polymorphism
- Collection, Coroutines, Generics
- Regex, Interoperability with Java, Android
- Who this book is for
This book will prove to be a "must-have" for beginners as well as experienced professionals as it is a stepping stone for learning the technology. Table of Contents
1. OOP in Brief
2. An Introduction to Java
3. An Introduction to Kotlin
4. Kotlin Architecture
5. Kotlin Token
6. Kotlin Input
7. Kotlin Operator
8. String Operations
9. Conditional Statements
10. Jumping Statement
11. Looping / Control Flow / Iteration
12. Kotlin Array
13. Null Safety
14. Kotlin Function
15. Function Scope
16. Kotlin Lambda Functions and Exception Handling
17. Kotlin OOPs
18. Constructor
19. Inheritance
20. Abstract Keyword
21. Polymorphism
22. Collection
23. Coroutines
24. Generics
25. Regex
26. Interoperability with Java
27. Kotlin for Android
28. Extras
29. Interoperability with JavaScript
30. Glossary
31. Important Question About the Author
Swati Saxena is expert in Java programming and coding as she is MCA, OCJP ( Oracle Certified Java Professional ) and ADST, having in-depth knowledge of subject and very vast experience in developing and training. Her knowledge and teaching is always praised by her mentor as well as students. She has written "C programming and coding Question Bank with solution', "Java-A Complete Practical Solution" for BPB Publications. The alumnus of her, are well placed in many reputed organisations all over India.
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
CHAPTER 1
OOP in Brief
Advantage of OOPs Over Procedure-oriented Programming Language
- OOPs makes development and maintenance easier, where as, in procedure-oriented programming language, it is not easy to manage the code if it grows as the project size grows.
- OOPs provides data hiding, whereas, in procedure-oriented programming language, a global data can be accessed from anywhere.
- OOPs provides the ability to simulate real-world events much more effectively.
- We can provide the solution of real world problem if we are using object-oriented programming languages.
- State
- Behavior
- Identity
- Responsibility
Features of OOP
- Abstraction
- Encapsulation
- Inheritance
- Polymorphism
Abstraction
- It makes the application secure by making data private and avoiding the user-level error that may corrupt the data
- It avoids code duplication
| Social Survey | Health Care | Employment |
Name | Name | Name |
Age | Age | Age |
Marital status | Address | Address |
Religion | Blood group | Qualification |
Income group | Weight | Department |
Address | Previous record | Job responsibility |
……. | …….. | …….. |
Encapsulation
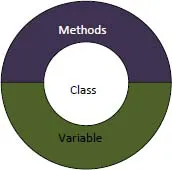
- Encapsulation is useful in hiding the data of a class from an illegal direct access
- Encapsulation helps us in binding the data and the member functions of a class
- Encapsulation also helps us to make a flexible code which is easy to change and maintain
Inheritance
Table of contents
- Cover
- Kotlin at a Glance
- Copyright
- Dedication
- Preface
- Table of Contents
- Chapter 1: OOP in Brief
- Chapter 2: An Introduction to Java
- Chapter 3 An Introduction to Kotlin
- Chapter 4: Kotlin Architecture
- Chapter 5: Kotlin Token
- Chapter 6: Kotlin Input
- Chapter 7: Kotlin Operator
- Chapter 8: String Operations
- Chapter 9:Conditional Statements
- Chapter 10: Jumping Statement
- Chapter 11: Looping / Control Flow / Iteration
- Chapter 12: Kotlin Array
- Chapter 13: Null Safety
- Chapter 14: Kotlin Function
- Chapter 15: Function Scope
- Chapter 16: Kotlin Lambda Functions and Exception Handling
- Chapter 17: Kotlin OOPs
- Chapter 18: Constructor
- Chapter 19: Inheritance
- Chapter 20: Abstract Keyword
- Chapter 21: Polymorphism
- Chapter 22: Collection
- Chapter 23: Coroutines
- Chapter 24: Generics
- Chapter 25: Regex
- Chapter 26: Interoperability with Java
- Chapter 27: Kotlin for Android
- Chapter 28: Extras
- Chapter 29: Interoperability with JavaScript
- Glossary
- Important Question