
eBook - ePub
Industrial Project Management
Concepts, Tools, and Techniques
- 320 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
Industrial Project Management
Concepts, Tools, and Techniques
About this book
Book of the Month Award---Industrial Engineering Magazine Whatever your business, getting the work done on time can make or break your organization. The faster the world moves, the more this becomes important. The expanding utility and relevance of project management has lead to its emergence as a separate body of knowledge embraced by various disc
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription.
No, books cannot be downloaded as external files, such as PDFs, for use outside of Perlego. However, you can download books within the Perlego app for offline reading on mobile or tablet. Learn more here.
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 1000+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn more here.
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more here.
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS or Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Yes, you can access Industrial Project Management by Adedeji Badiru,Abidemi Badiru,Adetokunboh Badiru in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Business & Project Management. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.
Information
1 Characteristics of Industrial Projects
IMPORTANCE OF INDUSTRIAL PROJECTS
Industry represents the pulse of economic development of any nation. The goods and services provided by industry directly influence the social, political, economic, and cultural structures of any population. Thus, successful industrial project management holds a key position in advancing local, regional, and national development. A community that cannot institute and sustain industrial vitality will eventually become politically delinquent and economically retarded. Project management is the process of managing, allocating, and timing resources to achieve a given goal in an efficient and expeditious manner. The intrinsic benefits of this definition are even more pronounced in fast-paced and globally influenced industrial projects.
TIME–COST–RESULT GOALS OF INDUSTRY
The objectives that constitute industrial project goals may be in terms of time, costs, or technical results. Projects can range from the very simple to the very complex. Owing to its expanding utility and relevance, project management has emerged as a separate body of knowledge that is embraced by various disciplines ranging from engineering and business to social services. Project management techniques are widely used in many endeavors, including construction management, banking, manufacturing, engineering management, marketing, health care delivery systems, transportation, research and development, defense, and public services. The application of project management is particularly of high value in industrial enterprises. In today’s fast-changing and highly competitive global market, every industrial enterprise is constantly striving to get ahead. Integrative project management offers one avenue to achieve that goal.
LASTING LEGACY OF PROJECT MANAGEMENT
Project management has had more direct impacts on human development than any other single discipline of study in the history of the world. From the time of ancient history and Mesopotamia’s early development to the modern times, acts of project management have brought to bear on human accomplishments. Early examples include the construction of Stonehenge in England, the erection of the Pyramids, and the development of the notable Wonders of the World. The ancient projects using gears and pulleys required extreme preparation, labor coordination, and cooperation. Although there was no formal discipline of project management in those ancient times, the processes of planning, organizing, scheduling, and control, no doubt, were used in accomplishing those feats. In spite of its long-standing benefits, it was only in the past few years that project management has emerged as a formal discipline; and it is now being globally recognized. The Project Management Institute has an envisioned goal that states, “Worldwide, organizations will embrace, value, and utilize project management and attribute their success to it.” This vision is already being broadly realized. This is evidenced by the rapid growth in project management professional memberships around the world. Interest in the discipline is growing rapidly around the world—in Europe, Asia, North America, South America, the Far East, the Caribbean, Africa, and so on. There is no single country that can claim not to be touched daily by the impact of project management processes.
ELEMENTS OF INDUSTRIAL OPERATIONS
Industrial development is one primary path to achieving national economic development. So, industry is very vital to the development of any nation. Historical accounts abound on how the industrial revolution had a profound effect on world development. A sustainable industrial development can positively impact the political, economic, cultural, and social balance in a community. In order to achieve and sustain industrial development, both the technical and managerial aspects of industrial projects must come into play. This book focuses on the integration of managerial approaches and analytical techniques to improve the planning, scheduling, and execution of industrial projects.
The primary goal of any industry is to plan operations ahead and allocate resources appropriately to improve industrial project efficiency, effectiveness, and productivity while reducing production waste (Lean) and improving product quality (Six Sigma). Using a formal project management approach makes it possible to achieve this goal. For projects to be effectively managed in an industrial system, managers and analysts must understand the industrial operating environment. Any high-tech industrial project is a complex undertaking that crosses diverse areas of endeavors. Both technical and organizational issues must be addressed in order to avoid system-wide project failures. This chapter covers the building blocks essential for the application of project management to industrial operations. The contents of this and the subsequent chapters will enable the project analyst to accomplish the following learning objectives:
• Understand the basic steps and components of project management.
• Learn best-practices approach to project planning, organizing, scheduling, and control.
• Use case examples as the basis for understanding “what went wrong” and how develop sustainable project solutions.
• Learn how to develop project scope and develop a project charter. • Using planning as the roadmap toward project success.
• Create cohesive project teams using the Triple C model of communication, cooperation, and coordination.
• Develop project work breakdown structure.
• Use a mix of qualitative and quantitative techniques to enhance project management.
• Develop compromise or tradeoff strategies for cost, schedule, and performance constraints.
Manufacturing is the process of creating a product by processing raw materials from an initial point through to the end product. It encompasses several functions that must be strategically planned, organized, scheduled, controlled, and terminated. A manufacturing cycle includes such functions as forecasting, inventory control, process planning, machine sequencing, quality control, decision analysis, production planning, cost analysis, process control, facility layout, work analysis, and a host of others. All of these are functions that fall within the process of planning, organizing, scheduling, and control cycles of project management. Industrial projects can be characterized by a combination of the following attributes:
• Large external stakeholders, customers, owners
• Internal stakeholders
• Short product life cycle (in high-tech industries)
• Variable investment sources
• Narrow margins for success.
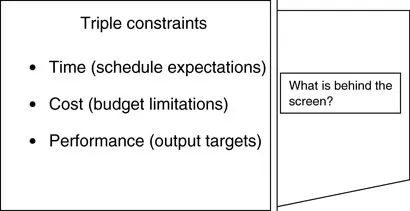
As with all projects, industrial projects are subject to three basic constraints of time, cost, and performance as illustrated in Figure 1.1. Any other constraint in the project environment will somehow fall under one of these three constraints. Several factors lurk behind the screen of the triple constraints. Issues such as workforce capability, operating tools, and process structure impinge on the project’s ability to be delivered on time, within budget, and in line with performance expectations.
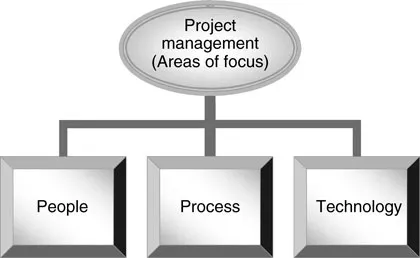
Industrial operations are predicated on strategic operations, which utilize high-tech tools, knowledge workers, and complex processes. Consequently, project management in an industrial operation implies the management of people, process, and technology, as shown in Figure 1.2, to satisfy the triple constraints.
While the proliferation of technology in industry has led to a loss of jobs, it has also led to the creation of new types of jobs, and so the coupling of technology and manufacturing has spawned a need for retraining of workers and realignment of functions. Even though high technology is sometimes blamed for stifling creativity and restricting traditional personal workmanship, it has also been credited with fostering industrial innovation.
This requires new management approaches. Effectively managing industrial technology requires project management skills on the part of management, employees, and clients in order to ensure the successful design, development, production, transfer, introduction, and implementation of various forms of technology to generate products and or services. Innovative applications of new and existing management techniques are needed to address the rapidly changing nature of industrial operations. Project management approaches are at the forefront of such applications.
DEPENDENCY ON HUMAN CAPITAL
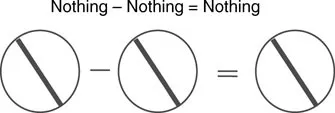
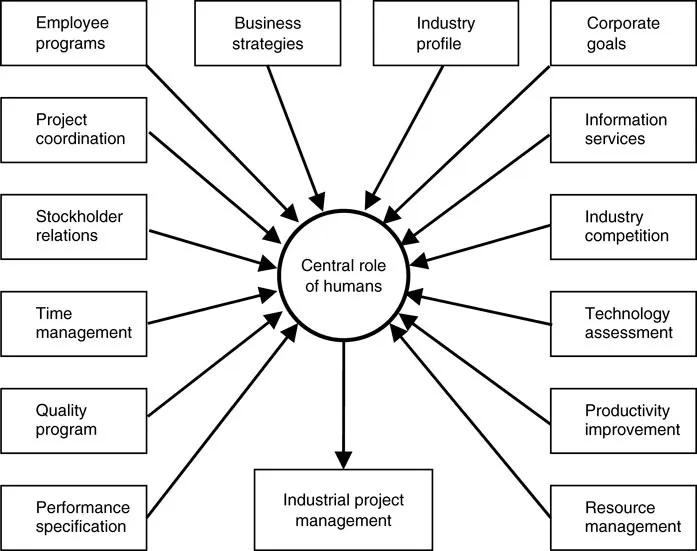
In spite of the increasing proliferation of automation in industry, human capital still holds a major role in accomplishing industrial output. Investment in human resource assets should be a primary focus of any organization’s project efforts. The success of the Toyota production system is not due to any magical properties of the approach, but rather due to the consistency, persistence, and dedication of the humans who apply the Toyota approach to all their industrial projects. This cannot be achieved without giving something (e.g., operator training, technology tools, and doable process) to obtain desired outputs. Recalling the cliché of “nothing from nothing is nothing,” as illustrated graphically in the following figure, industrial organizations should invest in their human capital in order to maximize project output. Figure 1.3 shows the central role of people in the various aspects of an industrial system.
GLOBAL INDUSTRIAL COMPETITION
Many North American manufacturers cannot compete globally on the basis of labor cost, where improvement efforts are often directed. The competitive advantage for many manufacturers will come from app...
Table of contents
- Cover
- Half Title
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Dedication
- Table of Contents
- Preface
- Acknowledgments
- Authors
- Chapter 1 Characteristics of Industrial Projects
- Chapter 2 Principles of Project Management
- Chapter 3 Time and Schedule Management
- Chapter 4 Project Duration Diagnostics
- Chapter 5 Schedule Compression Techniques
- Chapter 6 Resource Analysis and Management
- Chapter 7 Techniques for Project Forecasting
- Chapter 8 Six Sigma and Lean Project Management
- Chapter 9 Project Risk Analysis
- Chapter 10 Project Economic Analysis
- Chapter 11 Industrial Project Management Case Studies
- Appendix A Project Terms and Definitions
- Appendix B Project Acronyms
- Index