
- 226 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Milk Production Management
About this book
Milk Production Management, as the name implies, provides the information on different aspects related to Milk Production Management. The information in this book will be of practical utility for actual feeding of animals e.g. chapters on various rations, nutrient requirement tables, feeding of pregnant/lactating animals, feeding of calves, silage making, hydroponics technique, azolla production different feeds and fodders, fodder cultivation, computation of rations for dairy animals, feeding during scarcity periods etc. In this book different topics like common disease problems of dairy animals and their prevention and control, methods of selection, different breeding systems, semen collection and artificial insemination, different biotechniques used in animal husbandry, milking methods, embryo transfer technique, judging of cows and buffaloes, milk synthesis and milk secretion, record keeping at dairy farms, reproductive aspects of dairy animals etc. are also covered.
The book also covers different terms related to animal husbandry. This book is written in simple understandable language with description of those concepts which are useful for actual management of animals.
Note: T&F does not sell or distribute the Hardback in India, Pakistan, Nepal, Bhutan, Bangladesh and Sri Lanka.
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION TO ANIMAL HUSBANDRY
- Cattle
- Pigs
- Sheep
- Horses
- Poultry
- Sheep (northern Iraq)
- Goats (same region)
- Historical evidence shows that Veterinary Science was developed during Vedic Era in India and livestock used to play an important role in the society during 3000 B.C, as evidenced from Mohanjadaro and Harappa Civilization.
- The importance and role of livestock gradually increased and during 2000 B.C, Veterinary profession was a flourishing practice which can be traced from ‘Atharvaveda’ and ‘Rigveda’.
- Aryans who settled around riverine Northern India around 2400 – 1500 B.C were solely dependent on agriculture and livestock.
- Cattle were most prized possessions and were symbol of wealth and status.
- During the rule of Ashoka (300 B.C), hundreds of well equipped hospitals were established and veterinary profession gained much more importance.
- Vishnupuranam and Matysapuran described the criteria for selection of bulls for breeding purpose.
- Primitive man first used the members of family bovidae as a source of food. Domestication began when these animals were used as draft animals.
- Milking qualities were just sufficient for rearing of young ones.
- As civilization developed, feed became more abundant, methods of caring livestock improved. Under man’s selection they acquired qualities like rapid growth, better fat storage in body and increased milk production.
Modern Developments in Animal husbandry
- Selective breeding
- Advances in animal nutrition
- Vet medicine
- Artificial insemination
- Embryo transfer
Farm Specialists
- Breeders
- Milkers
- Feeders
- Health specialists Vets
The Cattle Family includes
- Cow
- Milking cow
- Heifer
- Milker
- Calf
- Ox
- Steer
- Bull
Cows' Life
- Gestation period is 9 months 9 days or 280 ± 5 days
- Newborn calf weighs 35-40 kg in crossbred cow & 20-25 kg in indigenous cow
- Dairy cows provide 90% of world’s milk production
- Farmers use machines to milk 100 cows for 1 hour
- Cattle and buffalo life span= 18-22 years
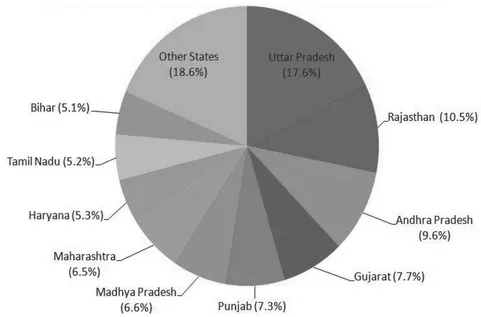
- Rank of India in total milk production: First
- Total milk production in 2017-18= 176.33 million tonnes.
- Cow milk production in India = 76 million tonnes
- Buffalo milk production in India=100.33 million tonnes
Uttar pradesh has highest buffalo population in India
- Rajasthan is the second largest milk producing state.
- Gujrat is third largest milk producer in India.
- Bihar and Jharkhand have largest cattle population in India.
- Total livestock population is 535.78 million in India and shown increase of 4.6% over livestock Census-2012.
- The Bovine population (Cattle, buffalo, Mithun and Yak) is 302.79 million in 2019 which shows an increase of 1.0% over the previous census.
- The total cattle population in India is 192.49 million in 2019 showing an increase of 0.8% over previous census.
- The female cattle (cow) population is 145.12 million, increased by 18.0% over the previous census (2012).
- The exotic /crossbred and indigenous/ non-descript cattle population in India is 50.42 million and 142.11 million respectively.
- The indigenous/ non-descript female cattle population has increased by 10% in 2019 as compared to previous census.
- The population of the total exotic/crossbred cattle has increased by 26.9% in 2019 as compared to previous census.
- Buffalo population in India =109.85 millions showing an increase of about 1.0% over previous census (2012).
- The total milch animal (in milk and dry) in cows and buffaloes is 125.34 million, an increase of 6.0% over the previous census.
- The total sheep population in India is 74.26 million in 2019, increased by 14.1% over previous census.
- The goat population in the country in 2019 is 148.88 million showing an increase of 10.1% over the previous census.
- The total pig population in India is 9.06 million in 2019, declined by12.03% over the 2012 census.
- The total Mithun population in India is 3.9 lakhs in 2019, increased by 30% over previous census.
- The Yak population in India is Fifty eight thousand in 2019, decreased by 24.67% over previous census.
- The total horses and ponies in India are 3.4 lakhs in 2019, decreased by 45.6% than the previous census.
- The total population of Mules in the India is Eighty four thousand in 2019, decreased by 57.1% than previous census.
- The population of Donkeys in India is 1.2 lakhs in 2019, decreased by 61.23% than previous census.
- The Total Camel population in India is 2.5 kakhs in 2019, decreased by 37.1% than previous census.
- The total poultry in India is 851.81 Million in 2019, increased by 16.8% than previous census.
- The total Backyard poultry in India is 317.07 Million in 2019, increased by 45.8% than previous census.
- The total commercial poultry in India is 534.74 Million in 2019, increased by 4.5% than previous census.
Common Animal Husbandry Terms
- Buller or Nymphomaniac: A cow apparently always in heat.
- Back crossing: Mating of crossbred back to one of the pure parents used to produce it.
- Balanced ration: Ration that contains all the nutrients in right proportions and quantities as per requirement of particular animal is called balanced ration.
- Bull Calf: A male calf under one year of age.
- Bull: It is un -castrated sexually matured male of the species.
- Bullock: Castrated male Ox.
- Calf starter: Concentrate feed offered to the young calves after 2 weeks of age.
- Calf: A young animal of bovine species under one year of age.
- Casting: It is throwing down the animal slowly and safely and securing the limbs for various purposes like surgical operations, castration, hoof trimming, shearing etc.
- Castration: It is the removal of testicles or dysfunctioning of testicles in male.
- Challenge feeding: The practice of feeding higher levels of concentrate to challenge the cow to reach her maximum milk production.
- Concentrates: Feeds that contain less than 18% crude fibre and more than 60% TDN are called concentrates such as grains, oilcakes, grain by products etc.
- Cow: It is a female of bovine species that has calved at least once.
- Cross breeding: A system of breeding between two established breeds.
- Cryptorchid: A male animal in which one or both the testicles fail to descend into the scrotal sac.
- Culling: Removal of undesirable or unproductive animals from herd.
- Deticking: Removal of the external parasites like ticks, lice, mites present on the body surface of animal.
- Deworming: Removal of the internal gastro intestinal parasites from the body.
- Disbudding: Removal of the horn buds of the calf by mechanical or chemical methods to arrest growth of horns.
- Dry period: The time interval between date of drying off the cow to the date of next calving.
- Energy feeds: Feeds containing less than 20% crude protein are called energy feeds.
- Lactation period: The number of days a cow secretes milk following each parturition.
- Free martin: When twin calves of different sexes are born, the bull calf is normal whereas the heifer calf is sterile. The sterile heifer calf is called freemartin.
- Gestation period: The period of pregnancy in animals.
- Grading up: Systems of breeding in which pure bulls are used for improvement in non descript females for several generations.
- Heifer calf: A female calf under one year of age.
- Heifer: A female individual above 1 year of age that has not yet calved.
- Inbreeding: A system of breeding between very closely related animals.
- Inheritance: Transmission of genes from parents to the offspring in next generation.
- Intercalving period: No. of days between two successive calvings.
- Lactation Curve: The graphical representation of the rate of milk secretion during lactation is called Lactation Curve.
- Lactation length: The time interval between the date of calving to the date of drying the animal expressed in days.
- Maintenance ration: A ration given daily to the animal to maintain in resting non production condition with good health.
- Open animal: Female animals that have not been bred.
- Parturition: Act of delivery in animals.
- Pasture: Fodder crops grown on the land for grazing animals.
- Pedigree Bull: The bull whose ancestral record is known.
- Persistency: Ability of the animal to sustain good daily milk for a longer period i.e, the slope of descending phase of lactation curve is known as Persistency.
- Phenotype: The visible character of an individual animal.
- Production ration: A portion of the ration given daily in excess of maintenance requirement for purpose of growth, production and work.
- Protein supplements: Feeds that contain 20% or more protein are called protein supplements.
- Ration: The total amount of feed offered to an animal is during a 24 hour period of time is called ration.
- Roughage: Feeds that contain more than 18% crude fiber and less than 60% TDN are called roughage such as hay, silage, fodder etc.
- Scrub Bull: It is non-descript type of stray village cattle.
- Selection: The process of including certain animals in a population for becoming parents of next generation.
- Breed: Animal having a common origin and characteristics that distinguish them from other groups within the same species.
- Service period: The period between parturition to successful conception expressed in days.
- Silage making: It is a method of conservation of green fodder in which Controlled fermentation of green fodder in a specially prepared silo is carried out.
- Stud Bull: Bull that is used for breeding purposes.
- Test cross: Mating of a crossbred back to its recessive parent.
- Dry cow: A cow that is not producing milk.
- Variation: It is a tool to measure differences of character or trait between animals.
- Weaning: Separation of the calf from the cow and feeding them artificially.
- Animal husbandry: It is defined as the branch of science and art of management of common farm practices like scientific feeding, breeding, health care of common domestic animals aiming for maximum returns
- Puberty: The period of life at which the reproductive organs first became functional. This is characterised by estrus and ovulation in the female and semen production in the male.
- Agalactia: Failure to secrete milk following parturition.
- Anorexia: Lack of appetite.
- Artificial insemination: The injection of mechanically procured semen into the reproductive tract of the female without coition and with the aid of mechanical or surgical instuments.
- Colostrum: The first milk produced by the female immediately after giving birth to young.
- Conception: The action of conceiving or beco...
Table of contents
- Cover
- Half Title
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Contents
- Preface
- 1. Introduction to Animal Husbandry
- 2. Distinguishing Characteristics of Indian and Exotic Breeds of Dairy Animals and their Performance
- 3. External Body Parts of Cows and Buffaloes
- 4. Feed Nutrients Required by Animal Body
- 5. Feeding Standards
- 6. General Dairy Farm Practices- Identification, Dehorning, Castration, Exercising, Grooming, Weighing
- 7. Systems of Housing Dairy Animals and Maintenance of Hygiene and Sanitation at Dairy Farm Premises
- 8. Care of Animals at Calving and Feeding and Management of Calves
- 9. Management of Lactating and Dry Cows and Buffaloes
- 10. Identification Common Feeds and Fodder or Classification of Feedstuffs
- 11. Preparation of Rations for Adult Animals
- 12. Measures of Feed Energy
- 13. Systems of Breeding of Dairy Animals
- 14. Dairy Farm Records and their Maintenance
- 15. Common Disease Problems of Dairy Animals, their Prevention and Control
- 16. Digestive System of Cattle/Buffaloes
- 17. Male Reproductive System
- 18. Female Reproductive System
- 19. Estrous Cycle in Cows / Buffaloes
- 20. Artificial Insemination and Its Advantages
- 21. Nutrients and Fertility in Animals
- 22. Ovulation, Fertilization, Gestation, Pregnancy Diagnosis and Parturition
- 23. Methods of Selection of Dairy Animals
- 24. Structure and Function of Mammary System
- 25. Milk Secretion and Milk Let Down
- 26. Methods of Milking, Procedure of Milking and Practices for Quality Milk Production
- 27. Factors Affecting Milk Composition of Animals
- 28. Cleaning and Sanitation of Milking Equipments
- 29. Embryo Transfer and their Role in Animal Improvement
- 30. Introduction to Biotechniques in Dairy Animal Production
- 31. Demonstration of Semen Collection, Processing
- 33. Handling and Restraining of Dairy Animals
- 33. Judging of Cows and Buffaloes
- 34. Preparation of Animal for Show
- 35. Silage Making
- 36. Nutritional Management and Milk Composition
- 37. Improved Varieties of Fodders for Animals
- 38. Hydroponics Technique for Fodder Production
- 39. Azolla Production and Its use in Animal Feeding
- 40. Feeding Care of Animals During Scarcity Period
- Questions
- References