
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
Contract management with CATS CM® version 4
About this book
This book describes version 4 of CATS CM®. This methodology for contract management
can be used in both private and public sector organizations, and is valid for both demand
and supply side.
Contract management is the realization of intended contract objectives by proactively
monitoring the fulfillment of all contractually established responsibilities, obligations,
procedures, agreements, conditions and rates, resolving all ambiguities, contradictions and
white spaces, managing all contract-related risks, and implementing all desired changes to
the contract, during the execution phase.
CATS CM® offers a methodical and scalable approach to contract management. It
provides a description of the principles, roles, and main issues for the contract manager
and the best way of working. In addition to a description of the methodology, CATS CM®
version 4 also offers specific tools for implementing contract management, for policy as
well as for processes.
Increasingly, organizations recognize the importance of being in control of their business
ecosystem. CATS CM® assists organizations to increase control of their joint responsibility
both from a procurement and delivery point of view. A large number of organizations have
chosen CATS CM® as the standard for their contract management processes.
This new version of CATS CM® has been developed with these various practices in mind.
CATS CM® version 4 is based on the principle that the management of a contract in execution has strong similarities on both sides of the contract, i.e. demand and supply; both can best be described as working in conjunction with each other.
This book is intended for all who are responsible for, or deal with the execution of
contracts: contract managers, business managers, delivery managers, project managers,
service managers, facility managers, buyers, procurement managers, compliance managers,
risk managers, account managers, sales managers and HR managers, along with their
directors and board members on both sides of the contract.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
Topic
EducationSubtopic
Architecture General
■ INTRODUCTION
Companies are entering into a rapidly increasing number of contracts, driven in part by specializations and niche players in the market, as well as acceleration caused by technological developments. For quite some time now, the make-or-buy decision clients have to make is not being made based on an individual need that must be fulfilled. Ever more frequently, companies are choosing to make a strategic choice to ‘buy’. Sometimes, this is even necessary because organizations no longer have in-house expertise in a broad range of areas.
It is not just the number of contracts that is increasing, but the form of collaboration is changing as well. Consequently, this increasingly results in the ecosystem described in the introduction to this book. That means that the relationship between client and supplier must be structured in a different way. As a result, this changed relationship requires contracts that are more flexible and more focused on value creation and the adjustment of contracts that do not yet offer that flexibility. Furthermore, contracts are increasingly contributing to the full implementation of processes. The effects of a possible discrepancy in the contract agreements increase and the response time to deal with them gets shorter. This is why contract management must become more proactive. Proactive contract management means: focused on activities linked to the execution and modification of a contract while concentrating on anticipating specific situations where possible or necessary.
Entrepreneurship is inextricably linked to having contracts. Contracting parties are increasingly aware that entering into contracts with due care is not sufficient to control the realization of the desired results, and it offers insufficient direction to the above-mentioned collaboration dynamics. This makes effective and efficient contract management crucial. The first chapter of this book explains what effective and efficient contract management entails and how CATS CM helps to achieve this. CATS stands for Contract Administration and Tracking Scenarios.
Our vision on proactive contract management is based on the idea of having effective and efficient contract management. Chapter 2 lists the most important definitions and explanations. Chapter 3 is a description of the determining factors for successful contract management and its implementation at a strategic, tactical and operational level. Last but not least, Chapter 4 describes the CATS contract life cycle, the role of contract management during those stages, and it delves deeper into the other processes that sustain this contract life cycle at an operational level.

As soon as an organization enters into contracts, each one of those specific contracts requires specific actions. This is a form of contract management. So, it is not a question of whether or not organizations need to use contract management but how they can execute the already existing contract management more effectively and efficiently. Applying CATS CM results in effective and efficient contract management through optimizing realizing of the contract objectives, minimizing possible contract risks, achieving costs savings and avoiding unnecessary costs. This chapter explains the correlation between organizational goals and contract objectives, and the elements of effective and efficient contract management.
■ 1.1 ORGANIZATIONAL GOALS AND CONTRACTS
Every organization has a mission and vision that determine its organizational goals. To realize those goals, the organization establishes a strategy that also takes laws and other regulations into account. Based on this strategy, the organization describes its goals for the short, medium and long term. When the organization enters into a contract with another party to realize its own organizational goals, these goals will also determine the contract objectives. The contract will describe how the objectives, for which the contract has been set up, are to be translated into performance. This performance can involve the delivery of both products and services. Figure 1.1 diagrams the relationship between organizational goals, contract objectives, and contract performance.
Every client uses suppliers, and therefore contracts, to carry out its activities to a lesser or greater extent, in order to realize its goals. Suppliers make choices when it comes to the products and services they offer and the markets in which they want to operate. Since the 1990s, the percentage of ‘contributions from suppliers’ relative to overall operations has been increasing significantly. Studies indicating that more than 70 percent of the total costs incurred by organizations can be attributed to the purchase or procurement of goods and services only confirm this. One of the main indicators that procurement has become even more important is the fact that Management Boards of both large and small organizations are choosing to appoint a Chief Procurement Officer (CPO), so that a solid embedding in the financial column is becoming the norm rather than the exception.
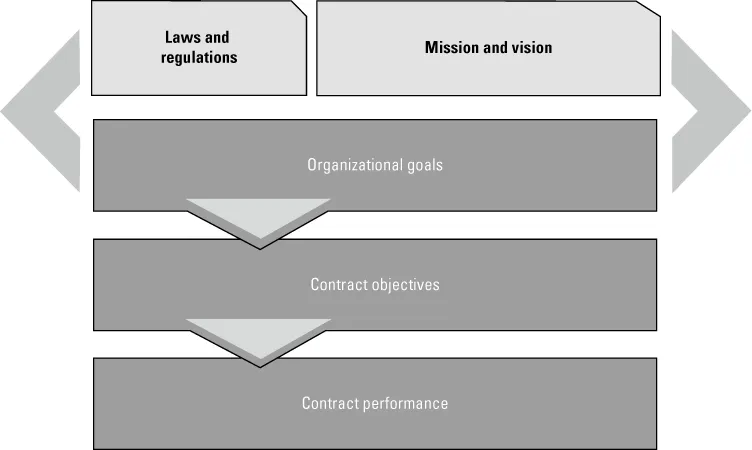
Figure 1.1 The relationship between organizational goals, contract objectives and contract performance
■ 1.2 EFFECTIVENESS OF CONTRACT MANAGEMENT WITH CATS CM
As described above, contract objectives are derived from the organizational goals. Such a relationship can still be a perfect match at the time the contract is finalized, but this balance may shift over time. The organizational goals may change and, partly influenced by the rapidly changing environment, the way contracts are executed is also in constant flux. Relationships between contractual parties can change, the required technical solution may already have been outstripped by the market, and contracted volumes may no longer meet the need.
Effective contract management ensures that the contract realizes the intention, for the correct compensation, with acceptable risks, and with the efforts planned by the organization. Whenever an organization’s needs change, effective contract management ensures that these changed needs lead to changes in the contract. The effects of good contract management contribute to achieving the contract objectives, the best possible relationship between contractual performance and contract value, as well as to savings and avoiding costs incurred by the organization in executing the contracts. The more contracts, and the more complex they are, the bigger the advantages of contract management.
1.2.1. Improved realization of contract objectives
The contract objectives describe what the organization wants to realize with the contract, and this applies to both purchaser and seller. Contract management following the CATS CM methodology is primarily focused on contract objectives and so it contributes substantially to achieving them. Sometimes, this contribution can be directly demonstrated in monetary terms, but there may also be a qualitative contribution.
A unique category of contract objectives are those related to compliance, meaning that the organization complies with laws and regulations. This is something every organization has to deal with. Even though there are many different areas in which laws and regulations are applied, there are some elements that apply to a broad range of laws and regulations to which good contract management contributes:
■ Adequate documentation is very important.
■ An organization is held responsible for structuring and implementing a quality system that guarantees compliance with laws and regulations.
■ The compliance control measures carried out by the organization must be defined and their execution and conclusions must be visibly documented.
■ Non-compliance has severe consequences (financial, reputation, continuity).
Considering these elements in advance, while the contract is being drafted, ensures that there is adequate focus on the completeness of the documentation, the control measures that must be implemented, and the assessment of these measures as soon as the contract comes into effect. This is even more applicable when some of the documentation or control measures have been outsourced as part of the contract.
Due to the abovementioned reasons, compliance officers and internal audit department staff are increasingly promoting contract management implementation.
1.2.2. Relationship between performance and contract value
The contract value is the sum of the client’s budgeted expenditure based on the contract with the supplier. The contract value reflects the compensation for the deliverables. The supplier benefits from a higher compensation while a lower compensation is a financial advantage for the client. This might lead to the assumption that a supplier focuses exclusively on achieving the highest possible contract value and the client the lowest. However, things are not that simple. For suppliers who invoice their budgeted sales to the penny and achieve exactly the expected return, contract management does not seem to have gained them anything on paper. However, without proactive contract management, they might not have achieved the expected return. For the supplier, contract management can have a substantial impact in terms of client satisfaction, more efficient use of internal resources, or the opportunity to try new innovations.
A client who pays the agreed amount to the supplier while, at the same time receiving a modified service that still meets the changing u...
Table of contents
- Cover
- Title
- Copyright
- Contents
- Introduction
- Part I: A Vision on Proactive Contract Management
- Part II: The CATS CM Methodology
- Part III: Applying the CATS CM Methodology
- Part IV: Implementing, Measuring And Improving Contract Management
- Afterword
- About the authors
- Appendix A: Possible content of a contract file
- Appendix B: List of Terms CATS CM version 4
- Index
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription
No, books cannot be downloaded as external files, such as PDFs, for use outside of Perlego. However, you can download books within the Perlego app for offline reading on mobile or tablet. Learn how to download books offline
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 990+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn about our mission
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more about Read Aloud
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS and Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Yes, you can access Contract management with CATS CM® version 4 by Gert-Jan Vlasveld,Linda Tonkes in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Education & Architecture General. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.