
eBook - ePub
Microsoft Windows Server 2008 R2 Administrator's Reference
The Administrator's Essential Reference
- 712 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
Microsoft Windows Server 2008 R2 Administrator's Reference
The Administrator's Essential Reference
About this book
Microsoft Windows Server 2008 R2: The Administrators Essential Reference introduces the Windows Server 2008 R2, which is Microsofts flagship server operating systems latest release. The book explores its features; describes differences between the available editions; and discusses its deployment. After introducing Windows Server 2008 R2, the book explains its installation and configuration processes followed by its networking. It also examines different features, such as the active directory, internet information services 7.5, Hyper-V, and PowerShell V2. It discusses securing Windows Server 2008 R2 files and its print services, remote desktop services, high-availability and recovery features, and monitoring and troubleshooting; in addition, their delta changes are discussed in the final chapter. The book also explores the features that influence both Windows Server 2008 R2 and Windows 7. These features allow the server operating system to work with Windows 7. One feature is the BranchCache, which offers users who open files across a Wide Area Network a better end-user experience by caching copy in the branch office when a document or intranet Web site is opened for the first time. Another feature is DirectAccess, which is the new remote connectivity solution for Windows networks.
- Features information on how to plan, deploy, and administrate Windows Server 2008 R2 using best practice guidance
- Provides in-depth coverage of Hyper-V, DirectAccess, Remote Desktop Services, Active Directory, and BranchCache
- Includes Delta Changes to allow experienced administrators to quickly gain insight to changes between Windows Server 2008 and Windows Server 2008 R2
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
Chapter 1 Introduction to Windows Server 2008 R2
The latest release of Microsoft's flagship server operating system, Windows Server 2008 R2, builds upon the core functionality of Windows Server 2008 (R1) providing the most powerful, reliable, and feature-enhanced Microsoft server operating system to date. Windows Server 2008 R2 is arguably as important to the enterprise server as Windows 7 is to the desktop. Whether you are an experienced Windows Administrator or new to the Microsoft server operating system, this book will help you become more versed in managing a Windows Server 2008 R2 server environment.
This chapter will introduce you to Windows Server 2008 R2. It will explain some of the new features, such as PowerShell and BranchCache offered in the operating system. It will also explain the differences between the editions available and help you determine when to deploy each one. This chapter will conclude with the guidance for planning and designing your Windows Server 2008 R2 deployment.
What is new in Windows Server 2008 R2
The R2 release of Windows Server 2008 introduces some new and exciting features. These include not only enhancements to traditional technologies, such as Active Directory and Internet Information Server (IIS), but also newer technologies, such as Hyper-V and PowerShell. In this section, you will be introduced to a few of these new features.
Virtualization (Hyper-V)
If you are an experienced server administrator, you are probably well aware that virtualization is one of the hottest topics in the IT industry. With more green initiatives, increasing power costs, and the demand for administrators to manage more servers, virtualization has gone from an option to a requirement in many organizations. With the release of Windows Server 2008 (R1), it became clear that Microsoft intends to not only compete, but also become a leader in the virtualization market. With the first release of Windows Server 2008, Microsoft not only gave users a true hypervisor, but also chose to give it to them for free. Windows Server 2008 R2 builds upon Microsoft's virtualization strategy by bringing new features to Hyper-V such as Live Migration, enabling administrators to move virtual machines between two hosts with no downtime or service disruption. Windows Server 2008 R2 also introduces Cluster Shared Volumes (CSVs) for Hyper-V clusters. CSVs allow multiple Hyper-V hosts in a Failover Cluster configuration to simultaneously access the same disk volume. CSVs are at the core of the new Live Migration features in Windows Server 2008 R2 Hyper-V. Hyper-V will be covered in detail in Chapter 7.
BranchCache
BranchCache is a new feature designed to provide a better experience for branch office users. BranchCache in Windows Server 2008 R2 allows servers in branch offices to store a “cached” copy of files and Web sites in the local office for quicker access in that office. BranchCache can be deployed in one of the two modes: hosted BranchCache or distributed BranchCache. Using the hosted method, a cache server is located in the BranchOffice. When a client requests read access to a file from a server across a Wide Area Network (WAN), the file is initially copied across the WAN and opened on the Requesting Client. A copy is also saved in the cache on the hosted cache server in the branch office. The next time someone requests to open the file, it is pulled from the hosted cache server in the branch office instead of the original source across the WAN.
BranchCache can also be deployed in distributed mode. Distributed mode works similar to hosted mode in that it uses a cache in the local office. However, in distributed mode, a server is not needed in the branch office. All cached copies of files are stored on Windows 7 client computers in that office. When a Windows 7 client requests a file, it stores a copy in its local cache. The next time a computer needs to open the file, it pulls it from the cache on one of the peer Windows 7 clients on the local branch office network. BranchCache requires both Windows Server 2008 R2 file servers and Windows 7 clients.
Active Directory
Active Directory has become the cornerstone of Windows Server domains. It is the core of many network environments supporting not only users and computers, but also applications like Microsoft Exchange Server. Active Directory was first introduced in Windows 2000 Server and has evolved with more reliability and features with each server operating system release. Windows Server 2008 R2 delivers a series of new Active Directory features such as:
- Recycle Bin—The Recycle Bin allows administrators to restore deleted objects to Active Directory. This feature is welcome to any administrator who has accidentally deleted a user account on a Friday afternoon.
- Active Directory Administrative Center—Active Directory Administrative Center provides a new way for Windows administrators to perform common tasks within their Active Directory domains. It is a GUI built on top of PowerShell, giving administrators an intuitive and easy-to-use tool to complete daily tasks such as reset passwords, create new user accounts, and manage groups and organizational units.
- Active Directory PowerShell cmdlets—PowerShell, with the Active Directory cmdlets, provides a rich command line interface to script and automate common Active Directory tasks. Windows Server 2008 R2 contains over 75 cmdlets to perform actions, such as creating new users, resetting passwords, and managing group membership.
- Active Directory Best Practices Analyzer (BPA)—The Active Directory BPA is a tool to help ensure that your Active Directory deployment is healthy and properly configured. The Active Directory BPA scans your Active Directory deployment and looks for configuration issues or common problems. The Active Directory BPA will then provide a report and recommended remediation steps for the discovered issues. New administrators will find this tool especially helpful to locate misconfigurations or early warning signs within their Active Directory domains.
Internet Information Server 7.5
Windows Server 2008 R1 introduced a fresh, redesigned version of IIS. Windows Server 2008 R2 further enhanced IIS by adding new features like a BPA, a new version of FTP services, and enhanced auditing.
PowerShell
PowerShell is now preinstalled with Microsoft operating systems. PowerShell is a powerful administrative scripting shell written specifically for IT Professionals in charge of managing Windows systems. Windows Server 2008 R2 comes with PowerShell 2.0 as well as a host of cmdlets that can be used to manage various roles and features of the operating system including IIS, Active Directory, and Remote Desktop Services. PowerShell 2.0 now has the added advantage of the ability to send commands remotely instead of having to be logged on to the server to execute cmdlets and scripts.
DirectAccess
DirectAccess is a new remote connectivity feature included as part of the Windows Server 2008 R2 and Windows 7 better together story. DirectAccess allows Windows 7 clients to connect to a Windows Server 2008 R2 network via a secure ipsec connection without the need for traditional VPN (virtual private network) access. This new technology not only allows Windows 7 clients to connect back to the corporate network, but also allows systems on the corporate network to initiate a connection back to the Windows 7 client. This provides a new mechanism for remote management of computers that are rarely physically connected to the company's local area network (LAN). Figure 1.1 depicts a remote client accessing corporate applications via DirectAccess.
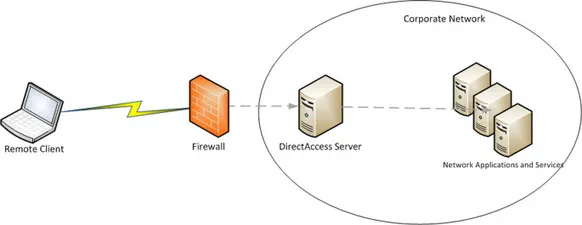
Figure 1.1 Windows Server 2008 R2 DirectAccess.
File Classification Infrastructure
As part of Windows Server 2008 R2's file and security services, Microsoft has added the File Classification Infrastructure (FCI). FCI is a new service that allows administrators to automatically create classification metadata for files based upon the type or the location of the file stored. Retention policies can be created based upon this classification to ensure that actions, such as deletion, are taken on documents that are older than the defined retention period. The FCI provides many new benefits to organizations that have regulatory requirements for managing electronic documents and records. FCI will be covered in more detail in Chapter 10.
Remote Desktop Services
Windows Terminal Services has been renamed to Windows Remote Desktop Services with the release of Windows Server 2008 R2. Remote Desktop Services provides the same functionality as the traditional terminal services did with some new enhancements to provide greater security and a better end-user experience. We will explore Remote Desktop Services in detail in Chapter 8.
Windows Server 2008 R2 editions
Windows Server 2008 R2 is available in six editions. It is important to understand the difference between these editions so that you can determine the edition that best meets your organization's needs. Table 1.1 outlines the key differences between Window...
Table of contents
- Cover
- Title Page
- Copyright
- Dedication
- Table of Contents
- About the Author
- Acknowledgments
- Chapter 1: Introduction to Windows Server 2008 R2
- Chapter 2: Installing and Configuring Windows Server 2008 R2
- Chapter 3: Windows Server 2008 R2 Networking
- Chapter 4: Feature Focus
- Chapter 5: Windows Server 2008 R2 File and Print Services
- Chapter 6: Internet Information Services 7.5 Feature Focus
- Chapter 7: Hyper-V Feature Focus
- Chapter 8: Windows Server 2008 R2 Remote Desktop Services
- Chapter 9: Windows Server 2008 R2 High-Availability and Recovery Features
- Chapter 10: Securing Windows Server 2008 R2
- Chapter 11: Power Shell V2 Feature Focus
- Chapter 12: Windows Server 2008 R2 Monitoring and Troubleshooting
- Chapter 13: Windows Server 2008 R2 and Windows 7
- Chapter 14: Windows Server 2008 R2 Delta Changes
- Index
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription
No, books cannot be downloaded as external files, such as PDFs, for use outside of Perlego. However, you can download books within the Perlego app for offline reading on mobile or tablet. Learn how to download books offline
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 990+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn about our mission
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more about Read Aloud
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS and Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Yes, you can access Microsoft Windows Server 2008 R2 Administrator's Reference by Dustin Hannifin in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Computer Science & Cyber Security. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.