
- 240 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
Measuring Circuits
About this book
This series of circuits provides designers with a quick source for measuring circuits. Why waste time paging through huge encyclopedias when you can choose the topic you need and select any of the specialized circuits sorted by application?This book in the series has 250-300 practical, ready-to-use circuit designs, with schematics and brief explanations of circuit operation. The original source for each circuit is listed in an appendix, making it easy to obtain additional information.
- Ready-to-use circuits
- Grouped by application for easy look-up
- Circuit source listings
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
1
Battery Monitoring Circuits
Battery Status Indicator
Low-Battery Indicator I
Low-Battery Indicator II
Battery-Level Indicator
Battery-Threshold Indicator
Voltage-Detector Relay for Battery Charger
Battery-Charge/Discharge Indicator
Precision Battery-Voltage Monitor for HTS
Low-Voltage Monitor
Undervoltage Indicator for Battery-Operated Equipment
Battery-Condition Indicator
Equipment-On Reminder
Battery-Voltage Monitor
Battery Monitor
Lithium Battery State-of-Charge Indicator
Step-Up Switching Regulator for 6-V Battery
Dynamic, Constant-Current Load for Fuel Cell/Battery Testing
Car Battery-Condition Checker
Car-Battery Monitor
Car Battery-Condition Checker
Car-Battery Monitor
The sources of the following circuits are contained in the Sources section, which begins on page 217. The figure number in the box of each circuit correlates to the source entry in the Sources section.
BATTERY STATUS INDICATOR
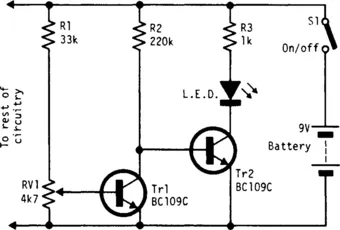
Fig. 1-1 ELECTRONIC ENGINEERING
This indicator continually monitors the battery voltage during use and consumes only about 250 μA (until the end point is reached). Near the end point, Tr1 turns off, allowing Tr2 to illuminate the LED to increase current drain, which further leads to a distinct turn-off point.
LOW-BATTERY INDICATOR I
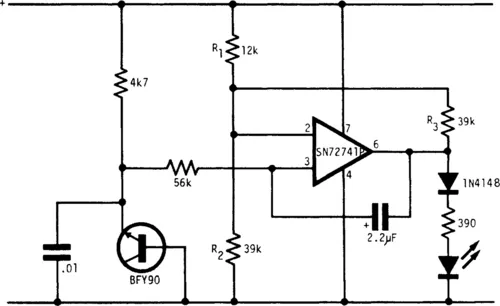
Fig. 1-2 ELECTRONIC ENGINEERING
Under good battery conditions, the LED is off. As the battery voltage falls, the LED begins to flash until, in the low-battery condition, the LED lights continuously. Designed for a 9-V battery, with the values shown the LED flashes from 7.5 to 6.5 V.
LOW-BATTERY INDICATOR II
The indicator flashes an LED when the battery voltage drops below a certain threshold. The 2N4274 emitter-base junction serves as a zener, which establishes about 6 V on the L161’s positive input. As the battery drops, the L161 output goes high. This turns on the Darlington, which discharges C1 through the LED. The interval between flashes is roughly two seconds and gives a low-battery warning with only 10-μA average power drain.
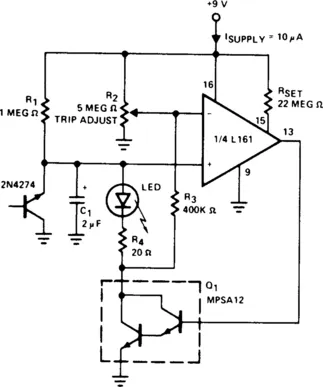
Fig. 1-3 SILICONIX
BATTERY-LEVEL INDICATOR
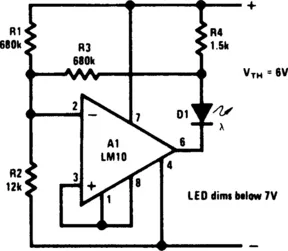
Fig. 1-4 NATIONAL SEMICONDUCTOR
BATTERY-THRESHOLD INDICATOR
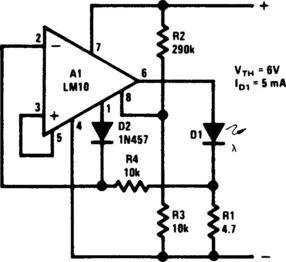
Fig. 1-5 NATIONAL SEMICONDUCTOR
VOLTAGE-DETECTOR RELAY FOR BATTERY CHARGER
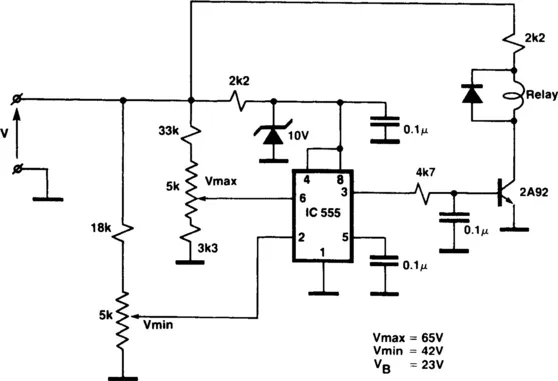
Fig. 1-6 ELECTRONIC ENGINEERING
While the battery is being charged, its voltage is measured at V. If the measured voltage is lower than the minimum, the relay will be energized, which will connect the charger circuit. When...
Table of contents
- Cover image
- Title page
- Table of Contents
- Other Books in this Series
- Copyright
- Introduction
- Chapter 1: Battery Monitoring Circuits
- Chapter 2: Comparator Circuits
- Chapter 3: Bridge Circuits
- Chapter 4: Capacitance Measuring Circuits
- Chapter 5: Counter Circuits
- Chapter 6: Current-Measuring Circuits
- Chapter 7: Dip-Meter Circuits
- Chapter 8: Display Circuits
- Chapter 9: Field-Strength Meter Circuits
- Chapter 10: Frequency-Measuring Circuits
- Chapter 11: Indicator Circuits
- Chapter 12: Light-Measuring Circuits
- Chapter 13: Measuring and Test Circuits
- Chapter 14: Oscilloscope Circuits
- Chapter 15: Power-Measuring Circuits
- Chapter 16: Probe Circuits
- Chapter 17: Resistance and Continuity-Measuring Circuits
- Chapter 18: Signal-Injector Circuits
- Chapter 19: Tachometer Circuits
- Chapter 20: Temperature Measuring Circuits
- Chapter 21: Voltage-Indicator/Monitor Circuits
- Sources
- Index
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription
No, books cannot be downloaded as external files, such as PDFs, for use outside of Perlego. However, you can download books within the Perlego app for offline reading on mobile or tablet. Learn how to download books offline
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 990+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn about our mission
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more about Read Aloud
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS and Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Yes, you can access Measuring Circuits by Rudolf F. Graf in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Design & Industrial Design. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.