eBook - ePub
Medical Biochemistry
Antonio Blanco, Gustavo Blanco
This is a test
Share book
- 826 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
Medical Biochemistry
Antonio Blanco, Gustavo Blanco
Book details
Book preview
Table of contents
Citations
About This Book
Medical Biochemistry is supported by over forty years of teaching experience, providing coverage of basic biochemical concepts, including the structure and physical and chemical properties of hydrocarbons, lipids, proteins, and nucleotides in a straightforward and easy to comprehend language. The book develops these concepts into the more complex aspects of biochemistry using a systems approach, dedicating chapters to the integral study of biological phenomena, including particular aspects of metabolism in some organs and tissues, and the biochemical bases of endocrinology, immunity, vitamins, hemostasis, and apoptosis.
- Integrates basic biochemistry principles with molecular biology and molecular physiology
- Provides translational relevance to basic biochemical concepts though medical and physiological examples
- Utilizes a systems approach to understanding biological phenomena
Frequently asked questions
How do I cancel my subscription?
Can/how do I download books?
At the moment all of our mobile-responsive ePub books are available to download via the app. Most of our PDFs are also available to download and we're working on making the final remaining ones downloadable now. Learn more here.
What is the difference between the pricing plans?
Both plans give you full access to the library and all of Perlego’s features. The only differences are the price and subscription period: With the annual plan you’ll save around 30% compared to 12 months on the monthly plan.
What is Perlego?
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 1000+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn more here.
Do you support text-to-speech?
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more here.
Is Medical Biochemistry an online PDF/ePUB?
Yes, you can access Medical Biochemistry by Antonio Blanco, Gustavo Blanco in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Biological Sciences & Biochemistry. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.
Information
Chapter 1
Chemical Composition of Living Beings
Abstract
Biogenic elements are essential components of living organisms. They include: (1) primary elements (O, C, H, N, Ca, and P), which comprise ∼98% of the total body mass of an adult human and participate in the composition of essential body molecules; (2) secondary elements (Na, K, Cl, S, Mg), which exist as salts and inorganic ions and Fe, which is part of important molecules, as hemoglobin; and (3) trace elements or oligoelements (I, Cu, Zn, Mo, Se, and Co), which are present in very scarce amounts, but are key to body function. The biogenic elements combine to form biological compounds. These include inorganic and organic substances. Among the inorganic compounds is water, the solvent present in body fluids and tissues. It comprises 65% of the total body weight of an adult individual. Other inorganic compounds are nonsoluble, such as calcium phosphate, which is an essential component of bone. The organic biological compounds include proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids. Others, such as vitamins, hormones, and pigments have carbon as a key component and perform essential roles.
Keywords
biogenic elements
biological compounds
Biogenic elements
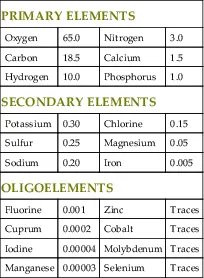
Life emerged on Earth many millions of years after the planet was first formed. Only a small number of elements within the inorganic matter of the Earth’s crust and atmosphere were selected as the building blocks of all living organisms. These basic elements of life are called biogenic elements. Mammals, animals of great complexity, are composed of merely 20 elements, 4 of which (oxygen, carbon, hydrogen, and nitrogen) are the most abundant, comprising approximately 96% of the total body mass (Table 1.1).
Table 1.1
Elements of the Human Body and Their Relative Abundance
| PRIMARY ELEMENTS | |||
| Oxygen | 65.0 | Nitrogen | 3.0 |
| Carbon | 18.5 | Calcium | 1.5 |
| Hydrogen | 10.0 | Phosphorus | 1.0 |
| SECONDARY ELEMENTS | |||
| Potassium | 0.30 | Chlorine | 0.15 |
| Sulfur | 0.25 | Magnesium | 0.05 |
| Sodium | 0.20 | Iron | 0.005 |
| OLIGOELEMENTS | |||
| Fluorine | 0.001 | Zinc | Traces |
| Cuprum | 0.0002 | Cobalt | Traces |
| Iodine | 0.00004 | Molybdenum | Traces |
| Manganese | 0.00003 | Selenium | Traces |
Values are expressed as a percent of total body mass.
All elements of the human body, with the exception of iodine (which has an atomic number of 53), are placed within the first 4 periods of the periodic table and possess atomic numbers lower than 34. Among the four most abundant ones, oxygen has the highest atomic number (8). While oxygen is relatively common on Earth, the other fundamental elements of living organisms are less abundant, suggesting that they have properties, which gave them a selective advantage in becoming the basic units of life. For example, carbon, and not silicon, has been the element around which life developed despite the fact that silicon is widespread and constitutes approximately 21% of the total Earth’s weight.
Carbon belongs to the same group in the periodic table and shares many of the properties of silicon. However, carbon can form more stable chemical bonds, long branched chains, double and triple bonds, covalent bonds with different atoms, and adopts a variety of different spatial conformations. This gives carbon the unique potential to generate a variety of chemical combinations that are essential for the makeup of the molecules of living organisms.
The selection of the other elements that accompany carbon as components of the living matter depends on the size of these atoms and their ability to share electrons in covalent bonds. The smaller atomic size of these elements favors their capacity to establish more stable bonds and stronger molecular interactions.
Taking into consideration their relative amounts, biogenic elements can be classified into three main categories:
1. ...